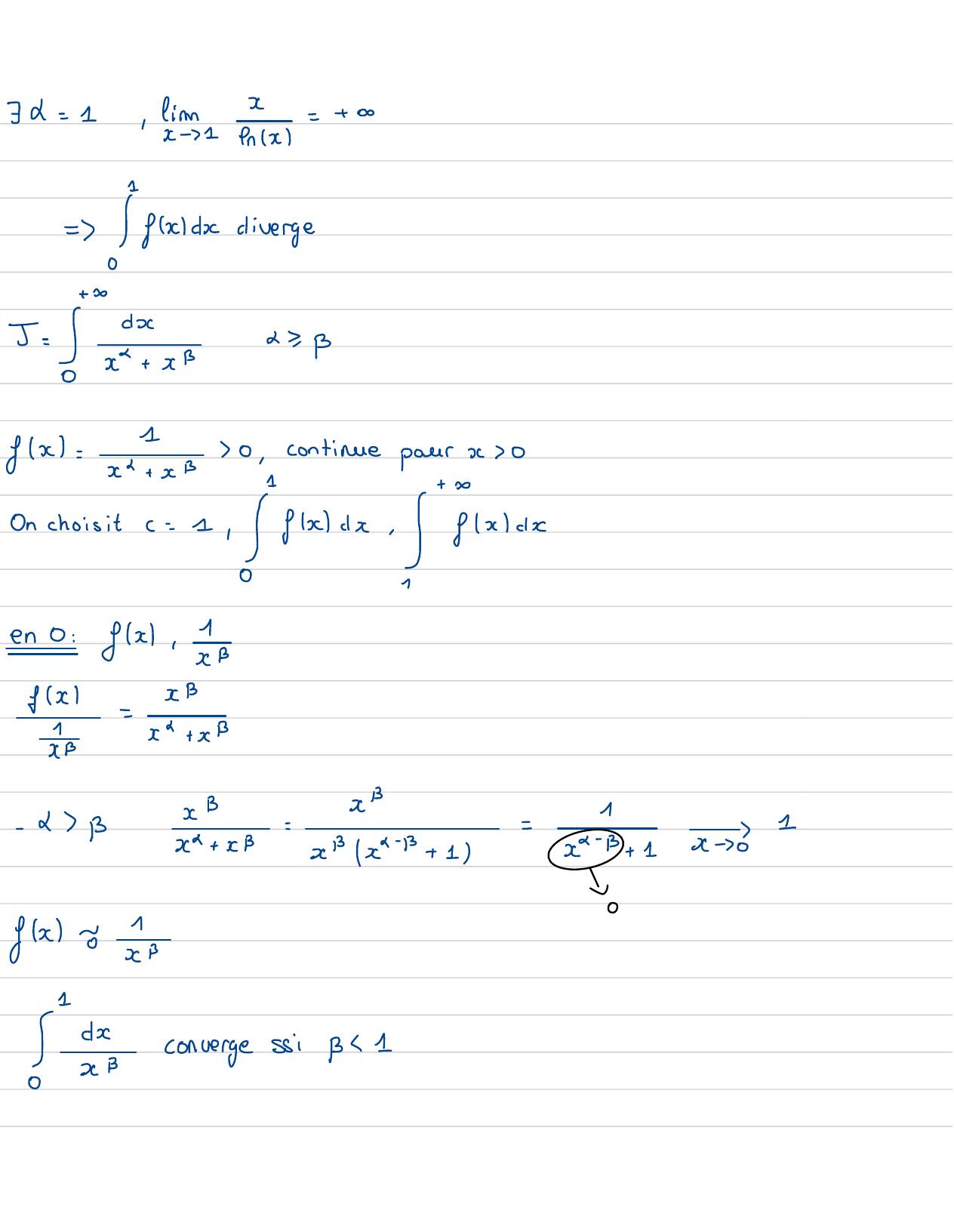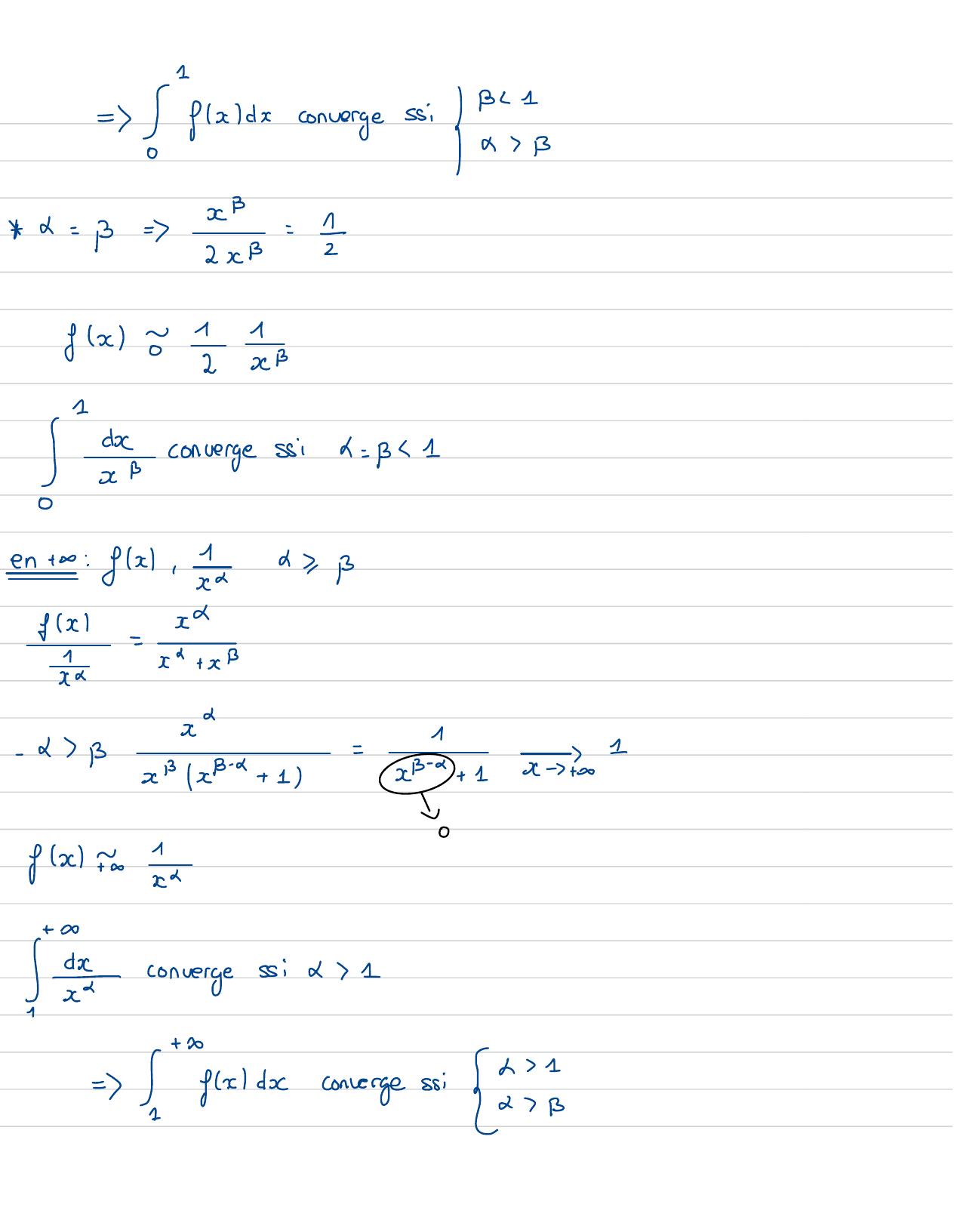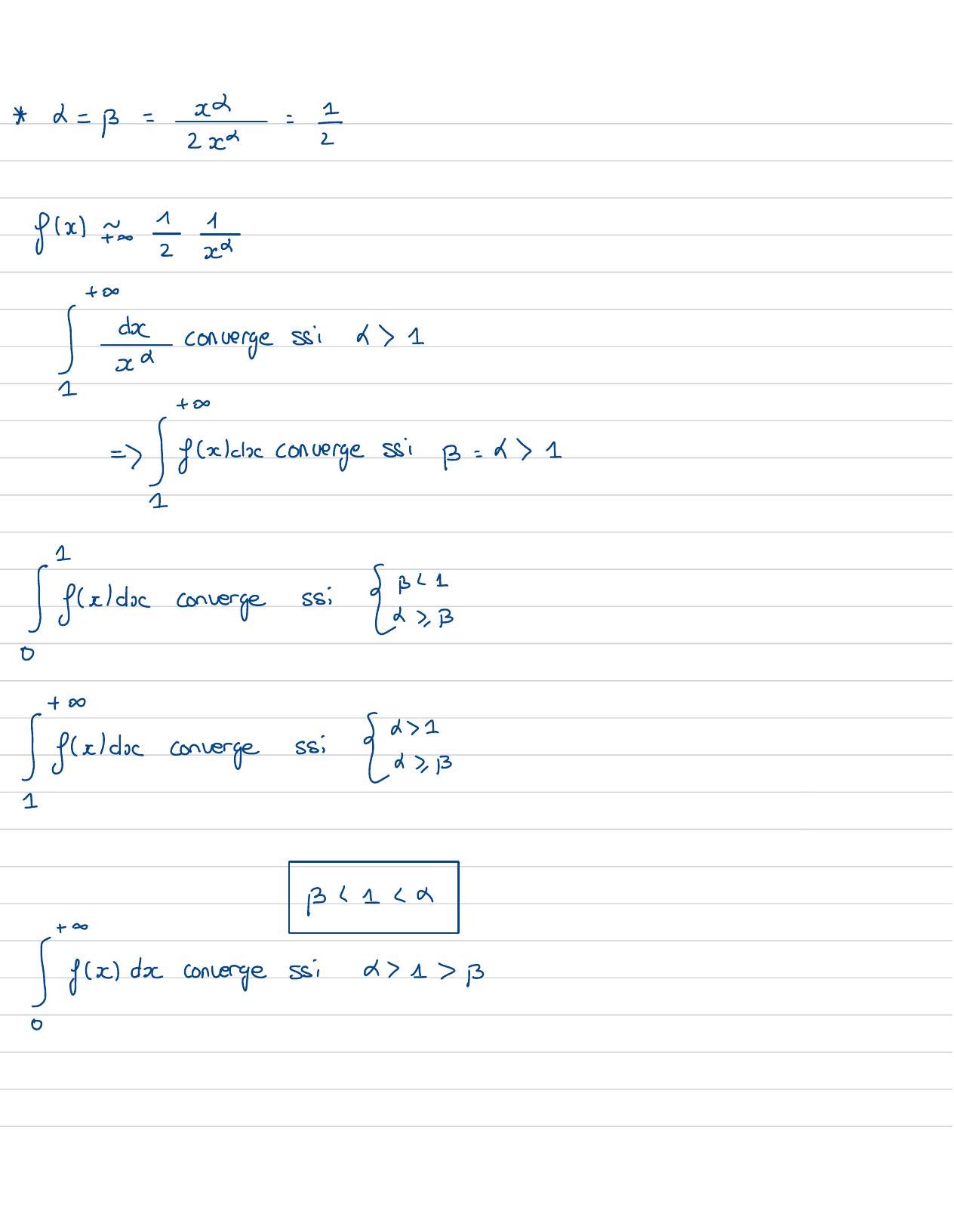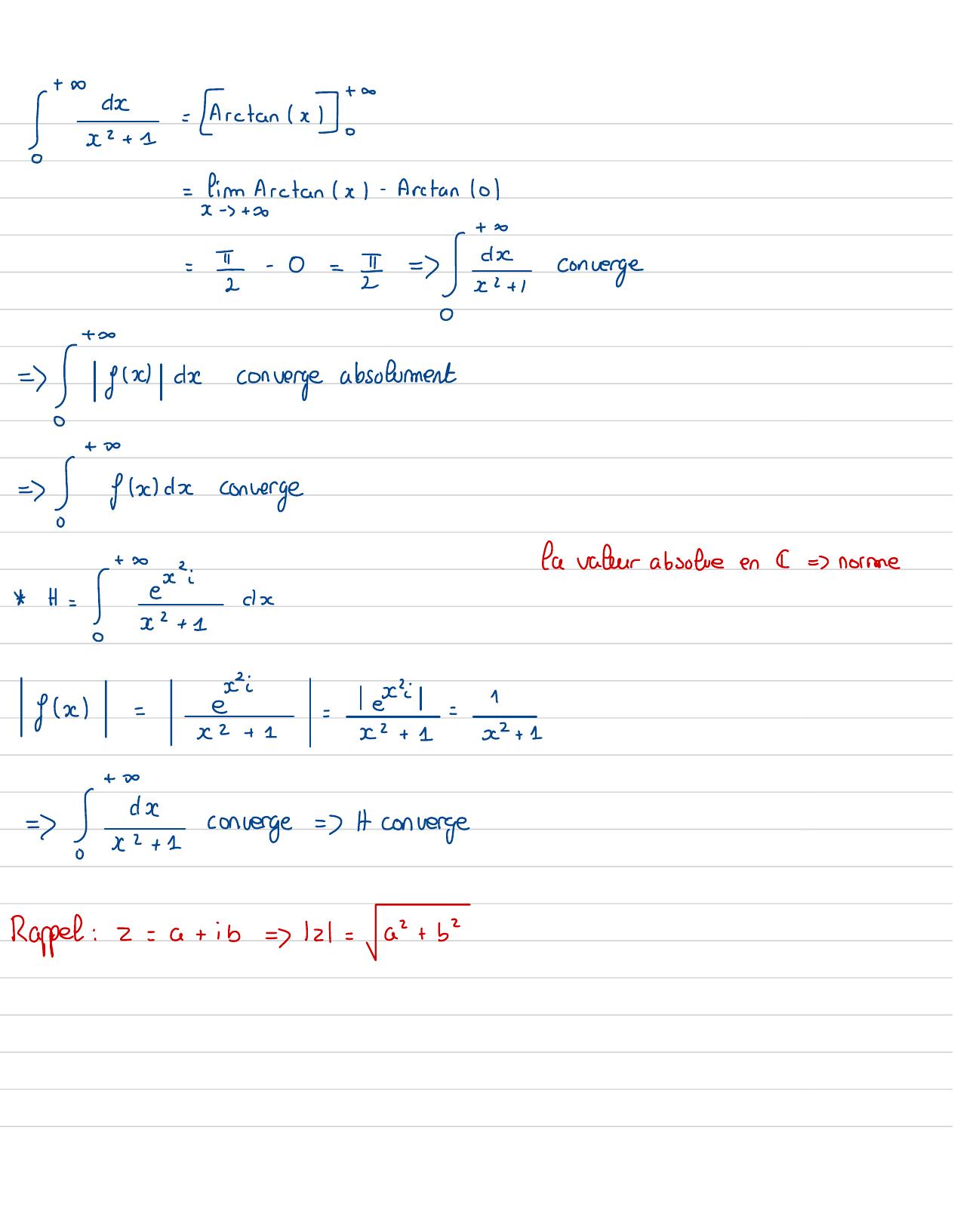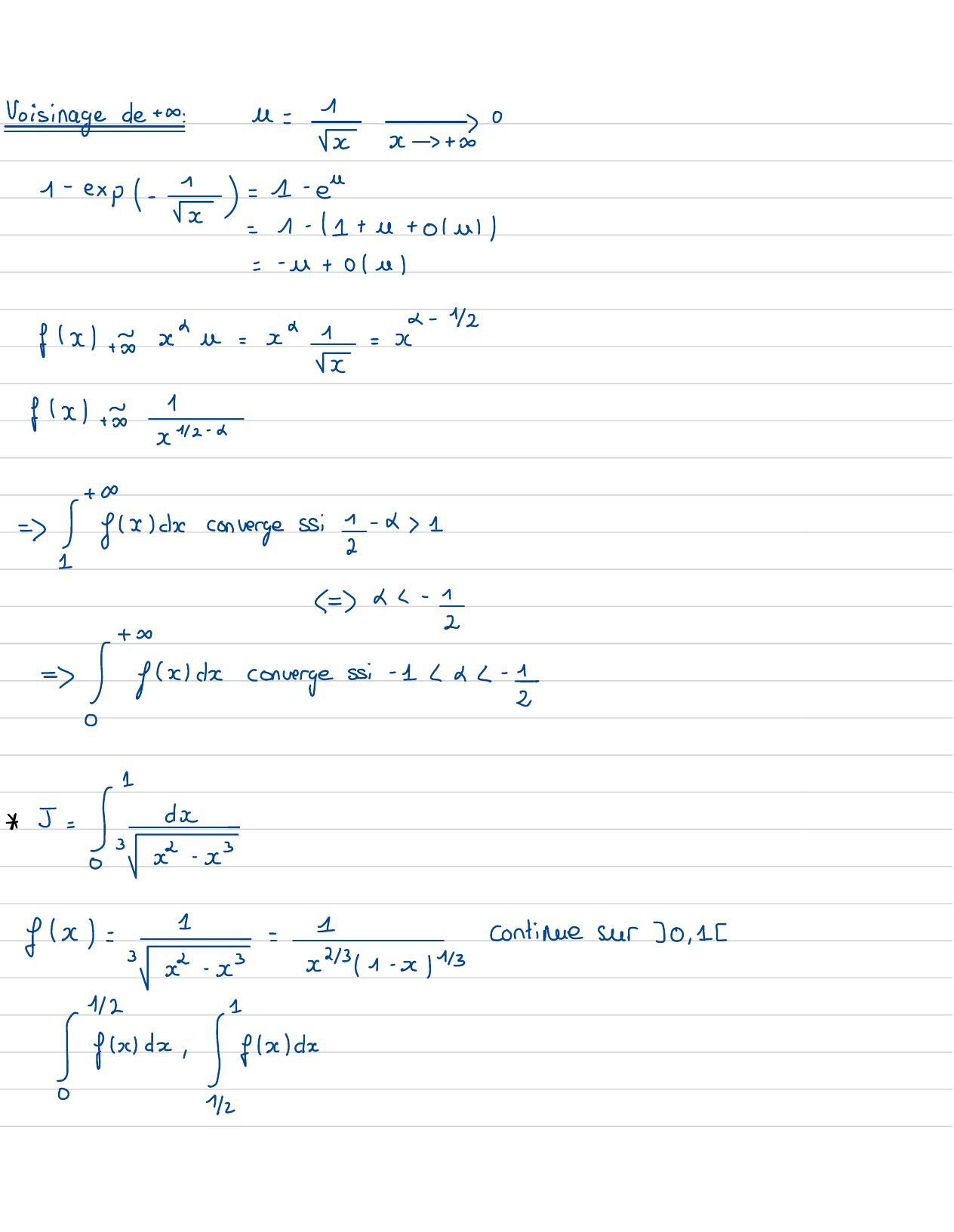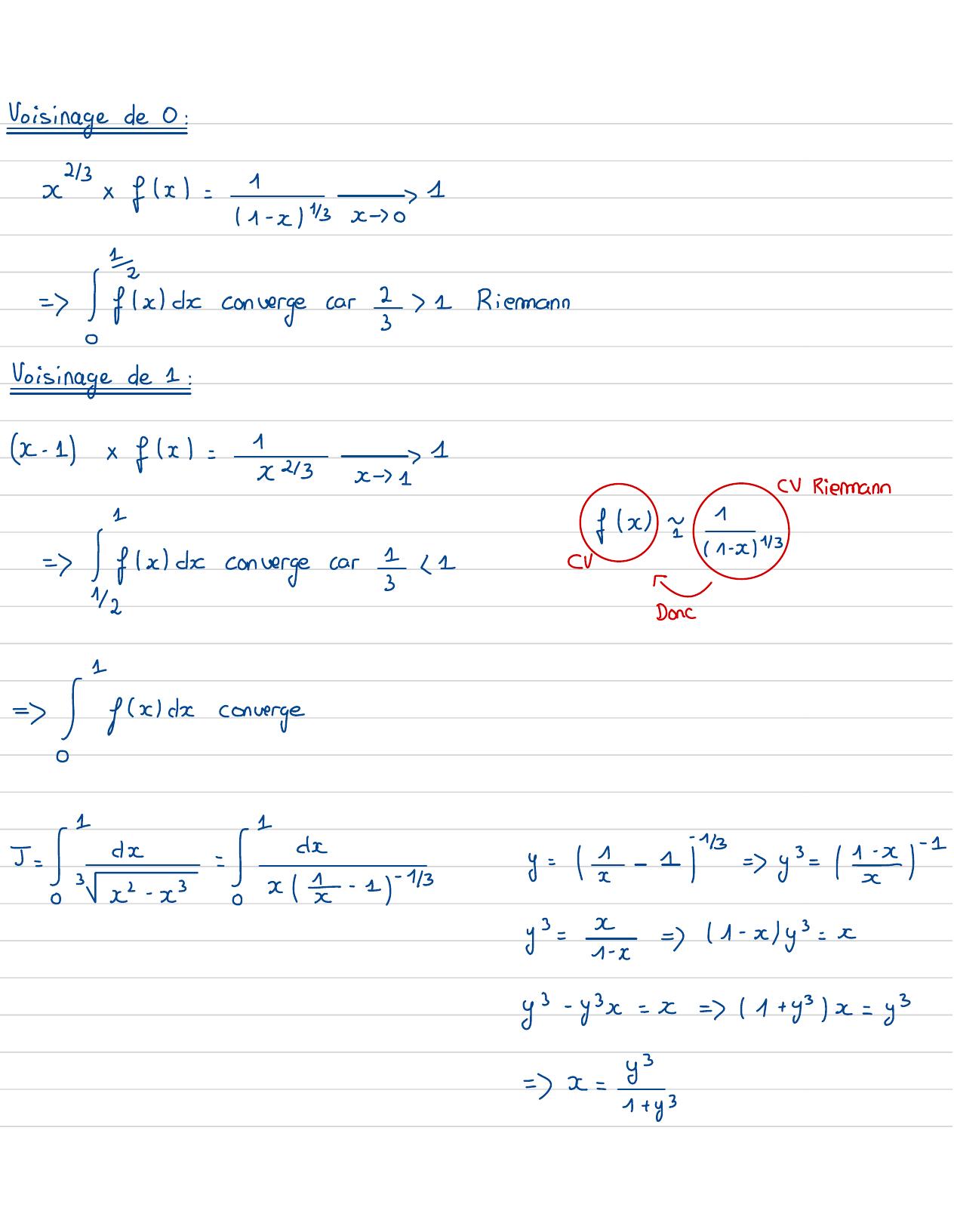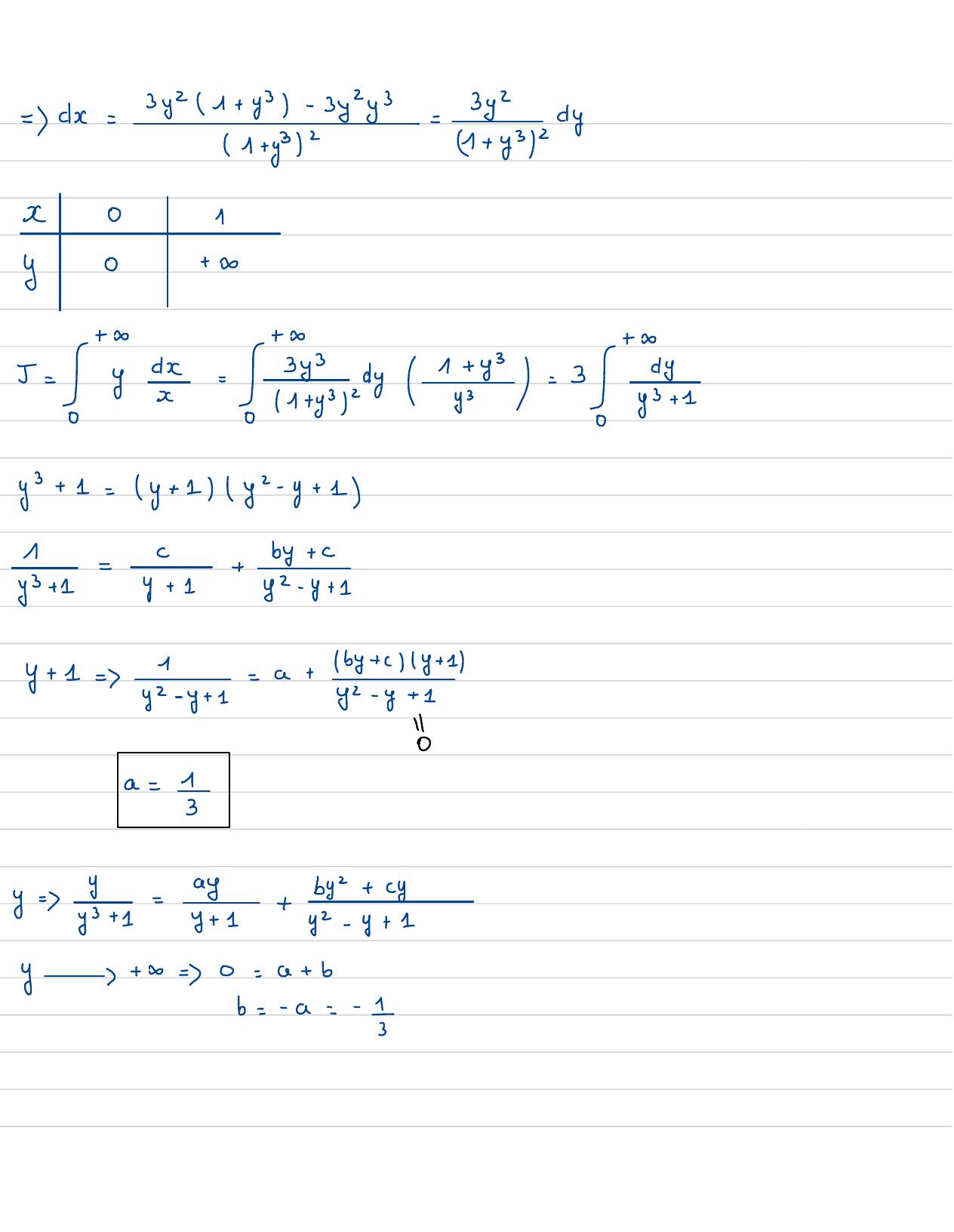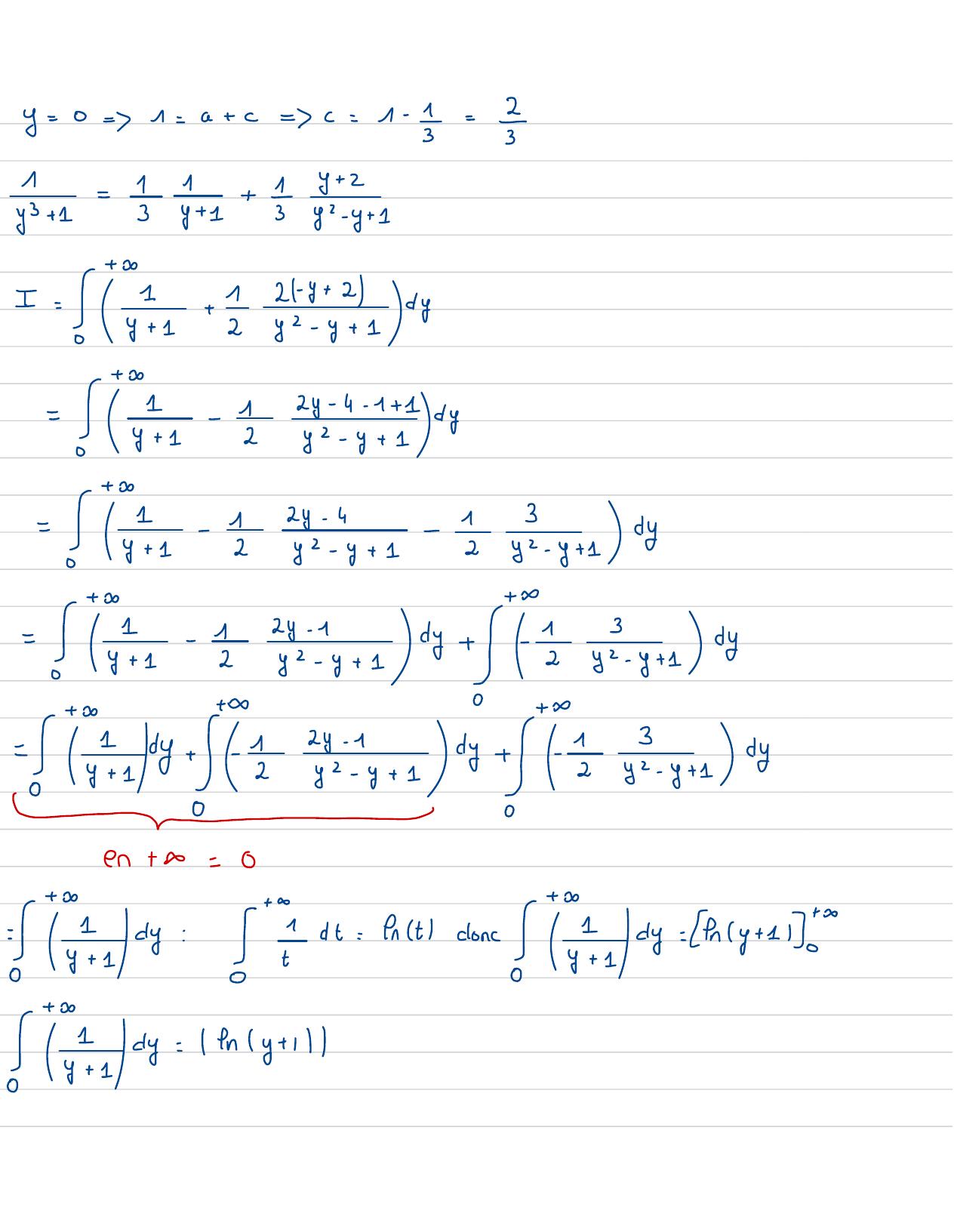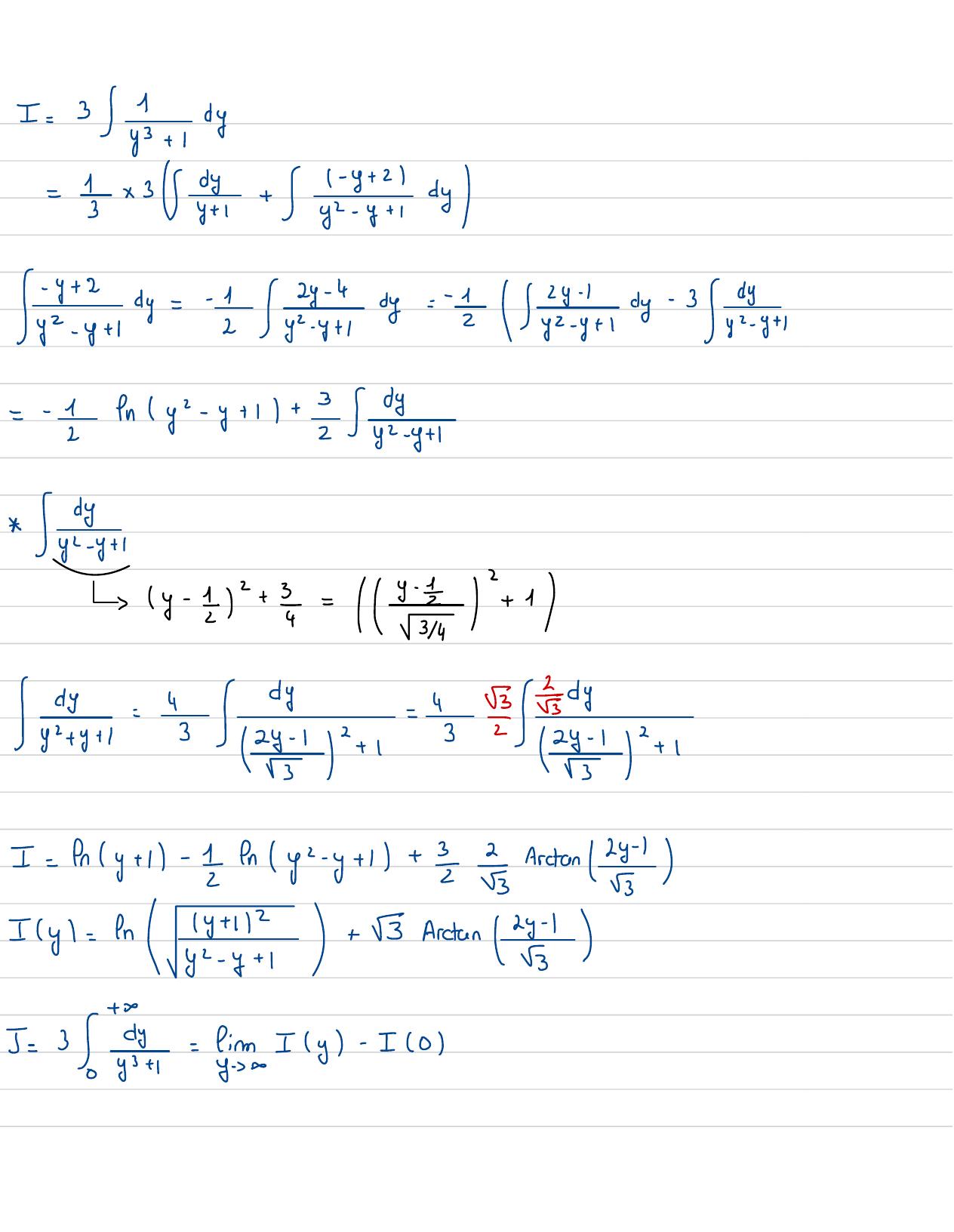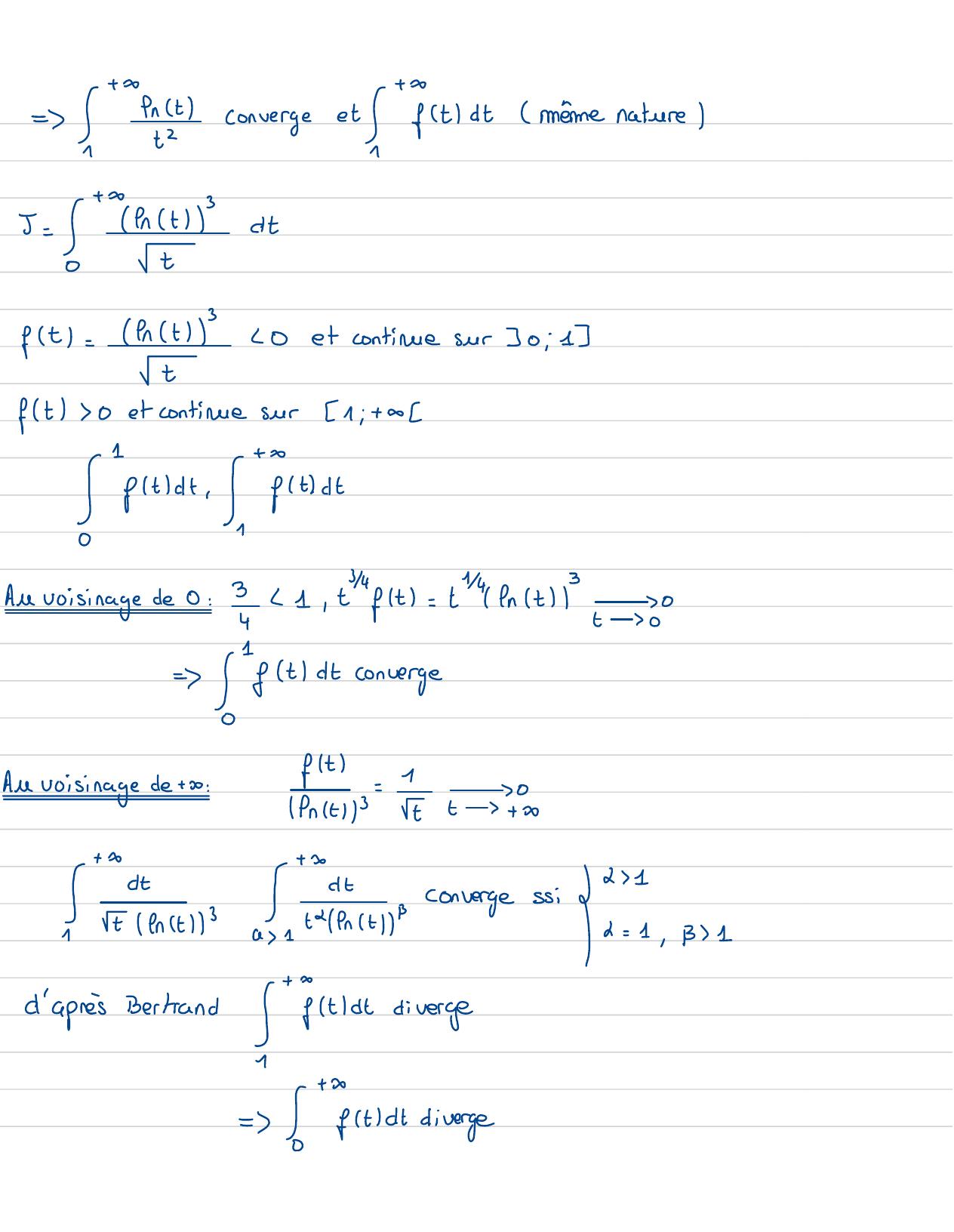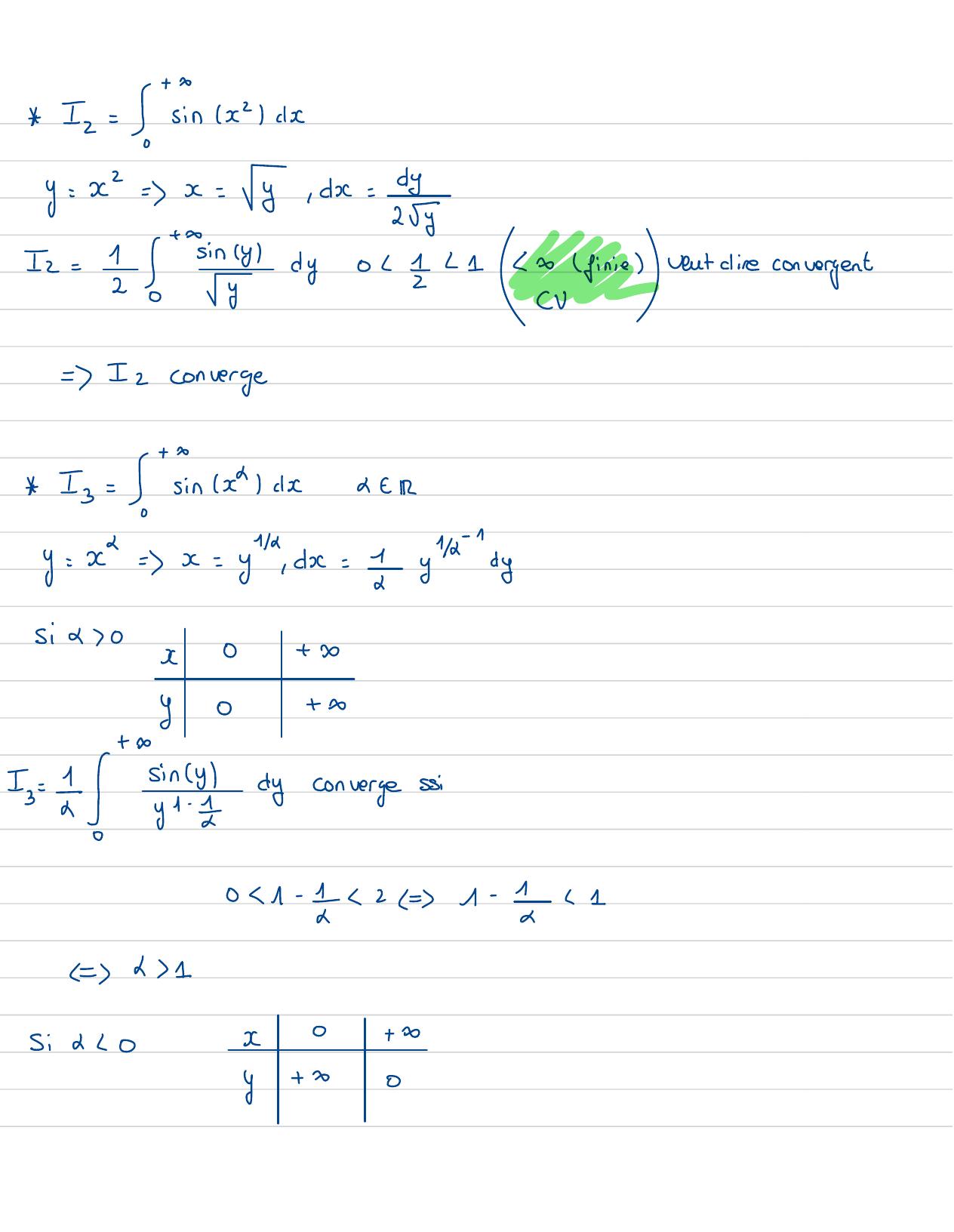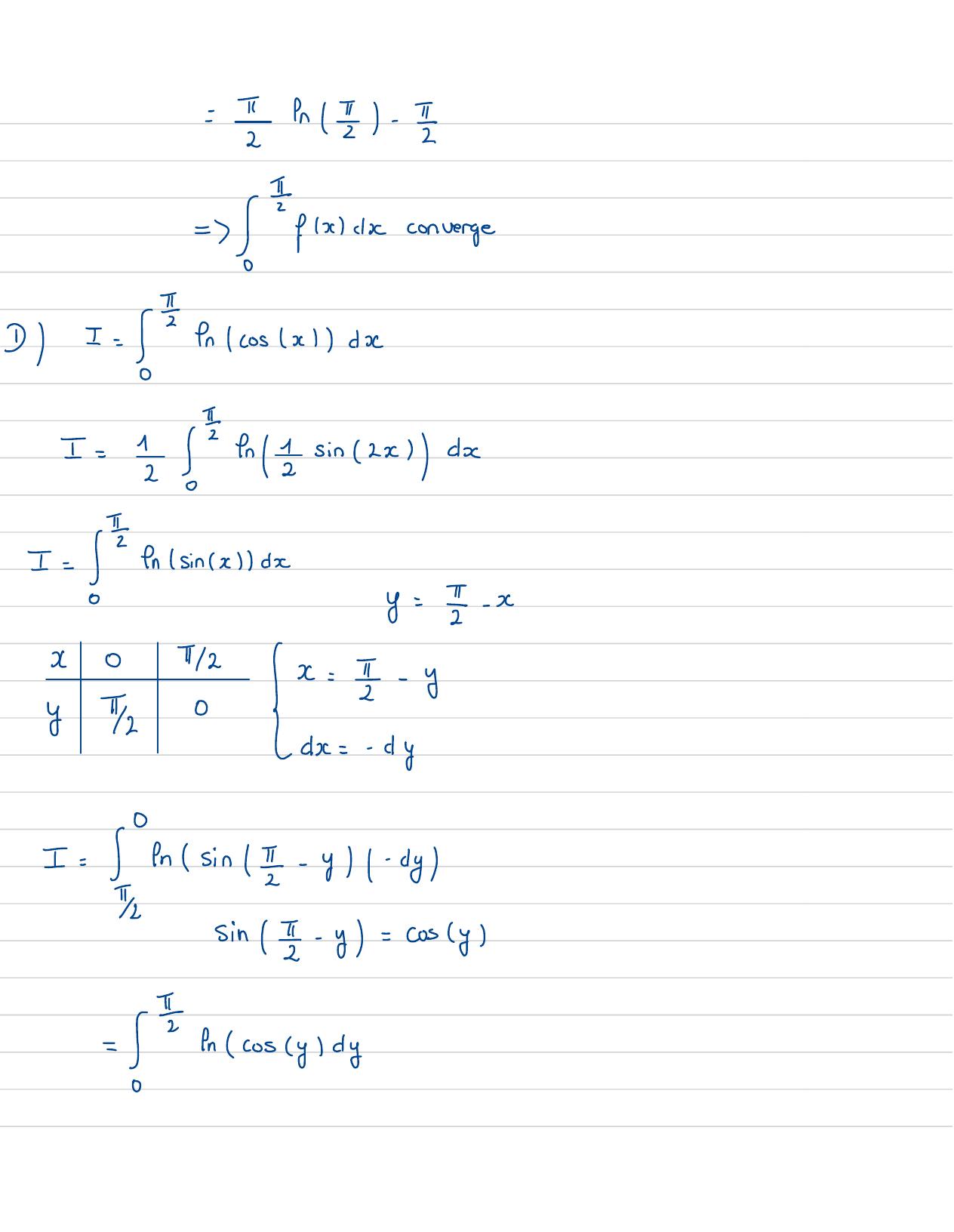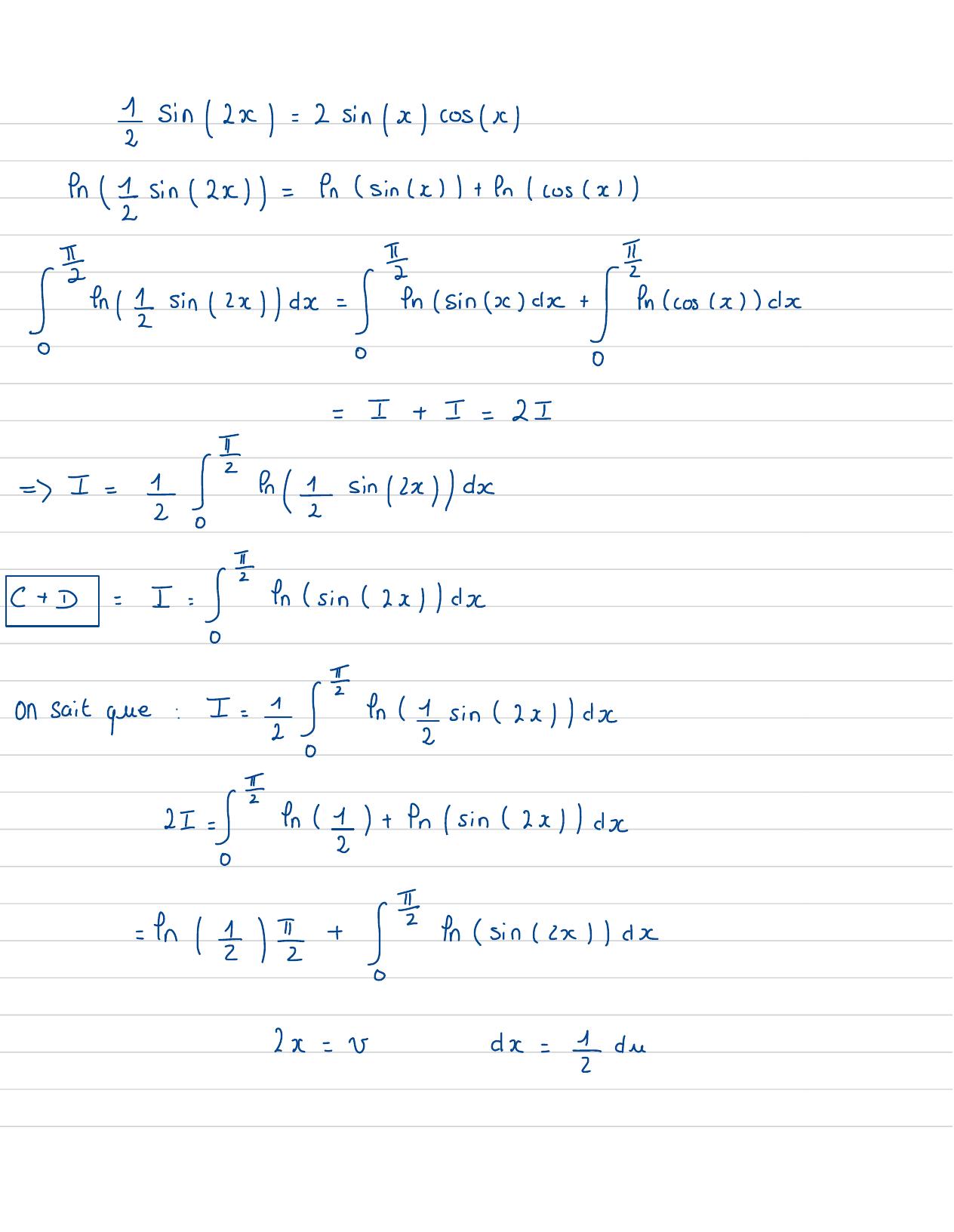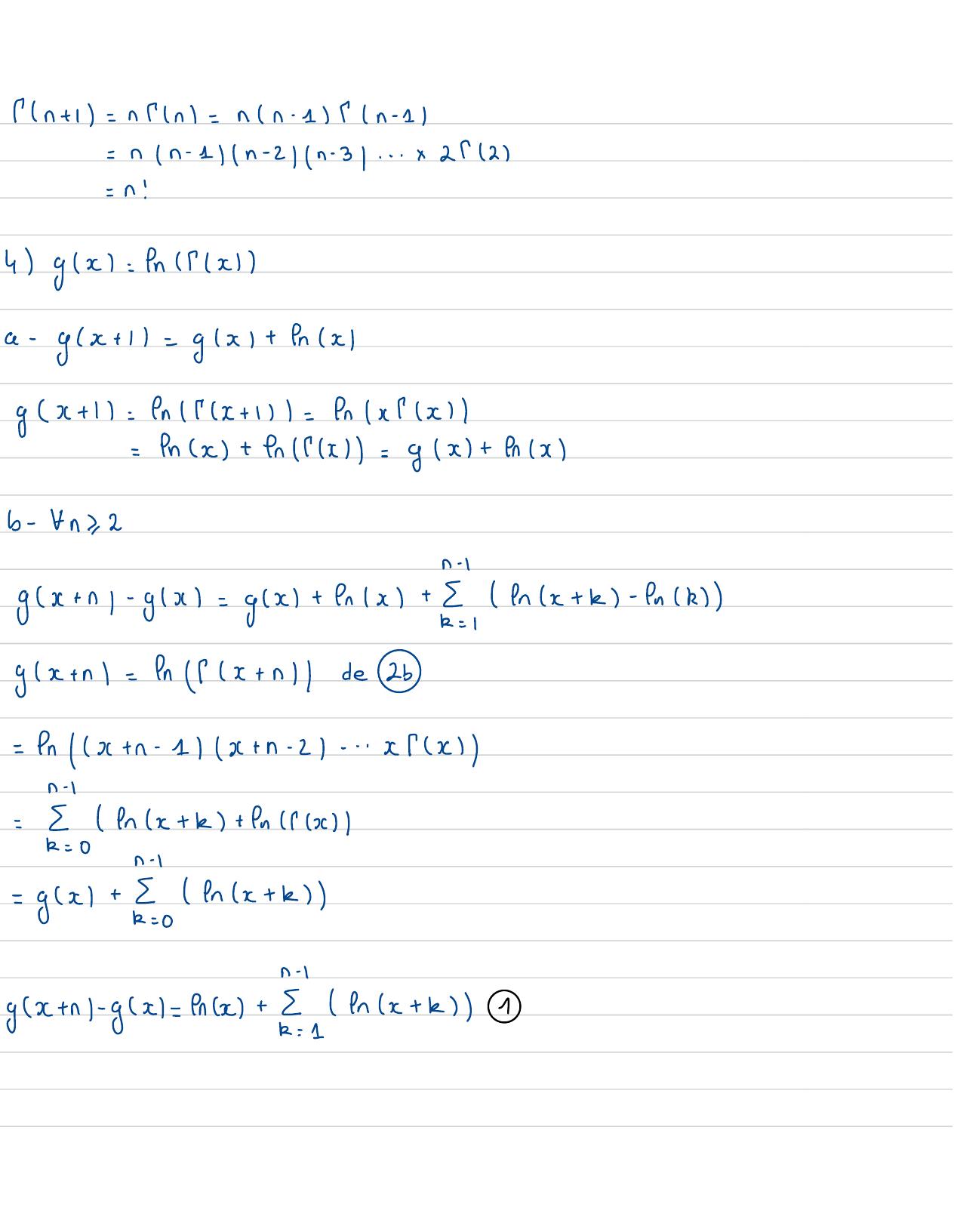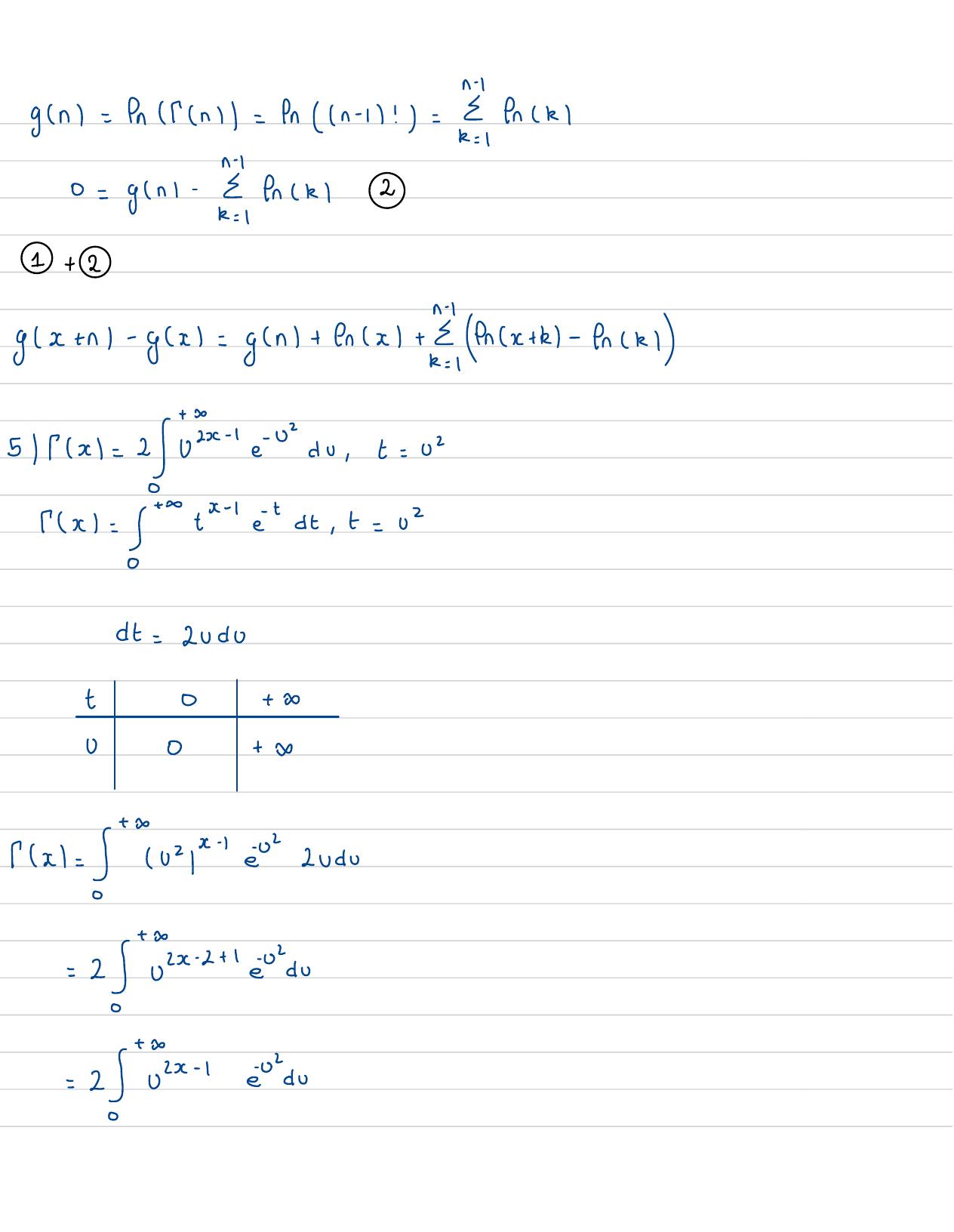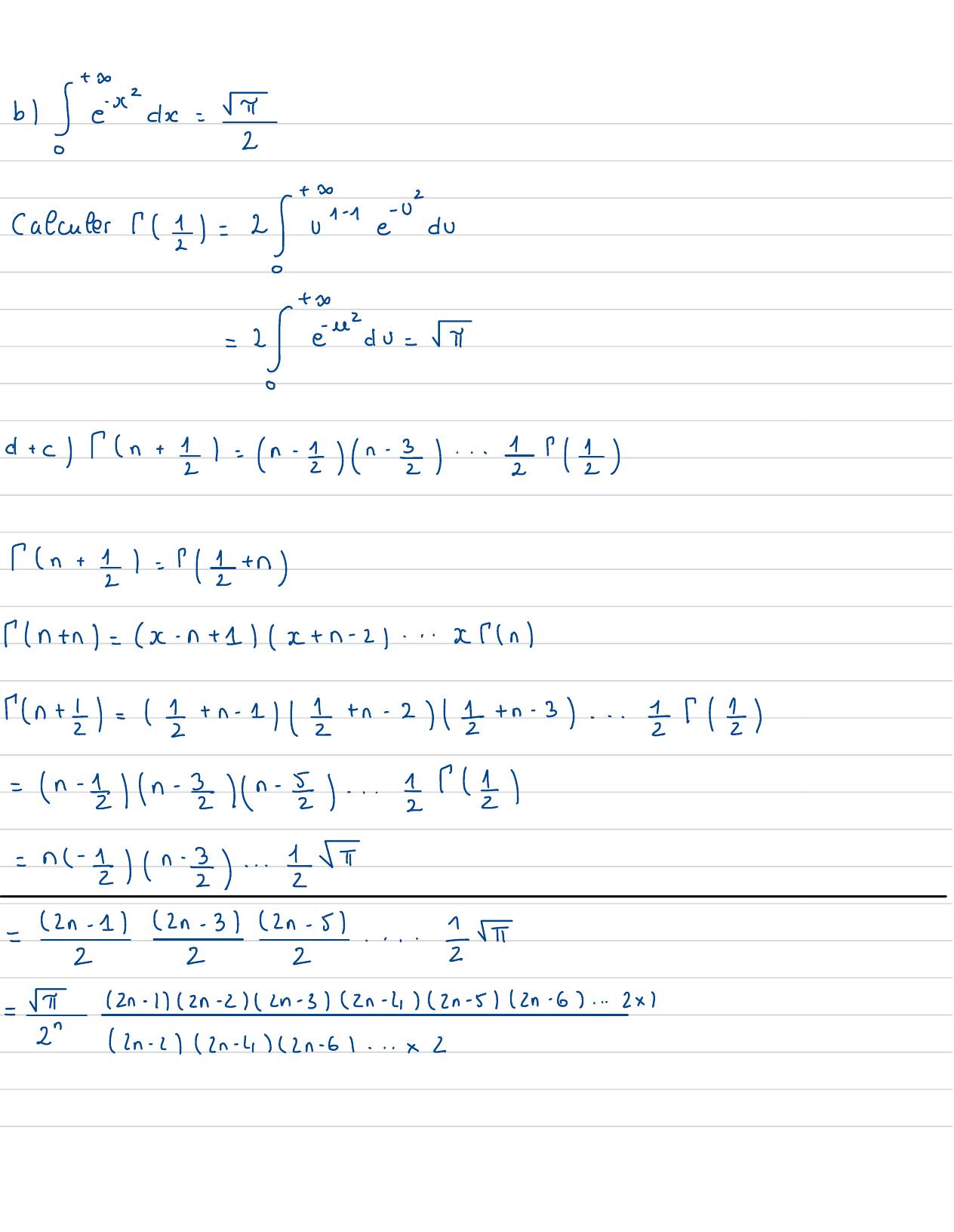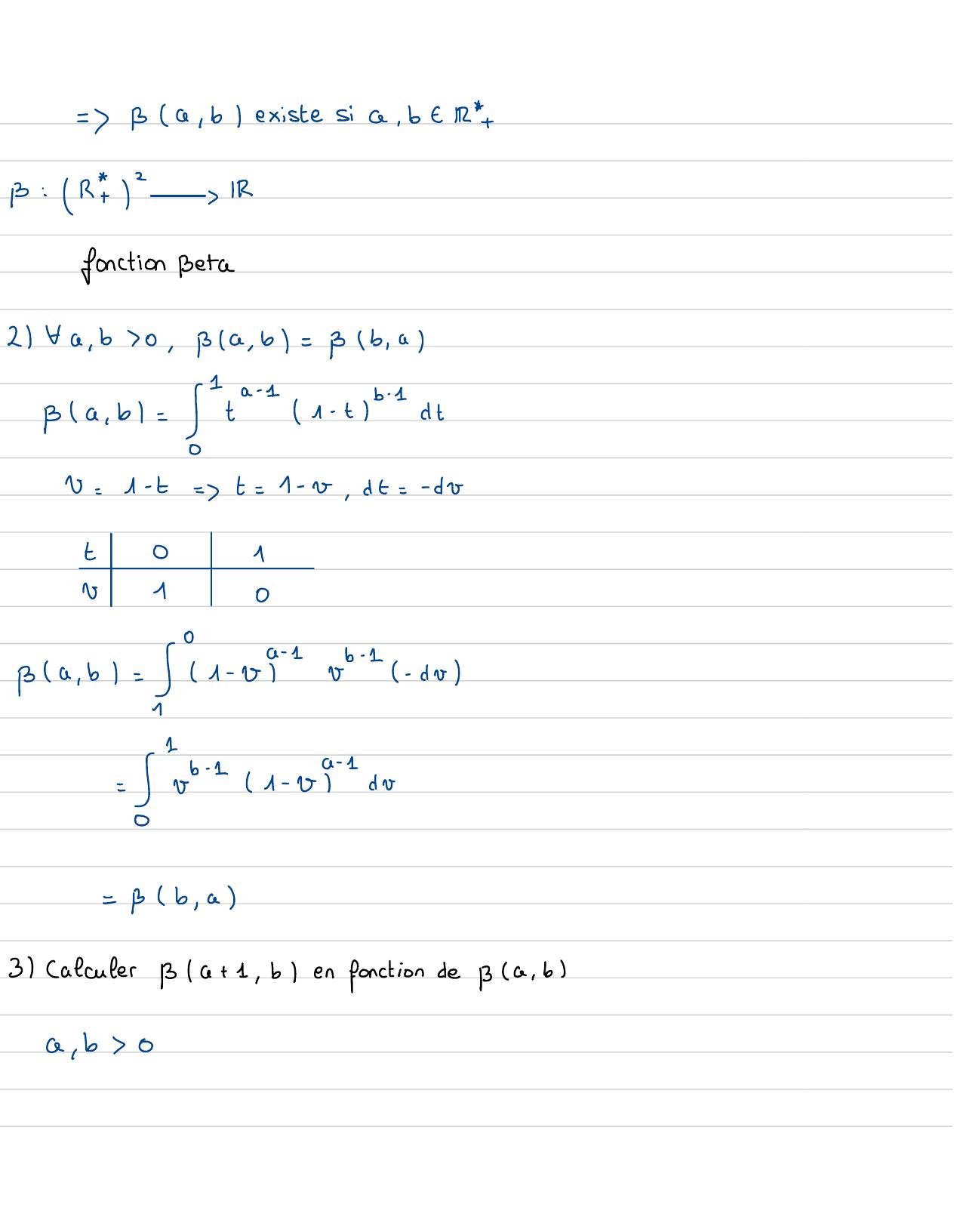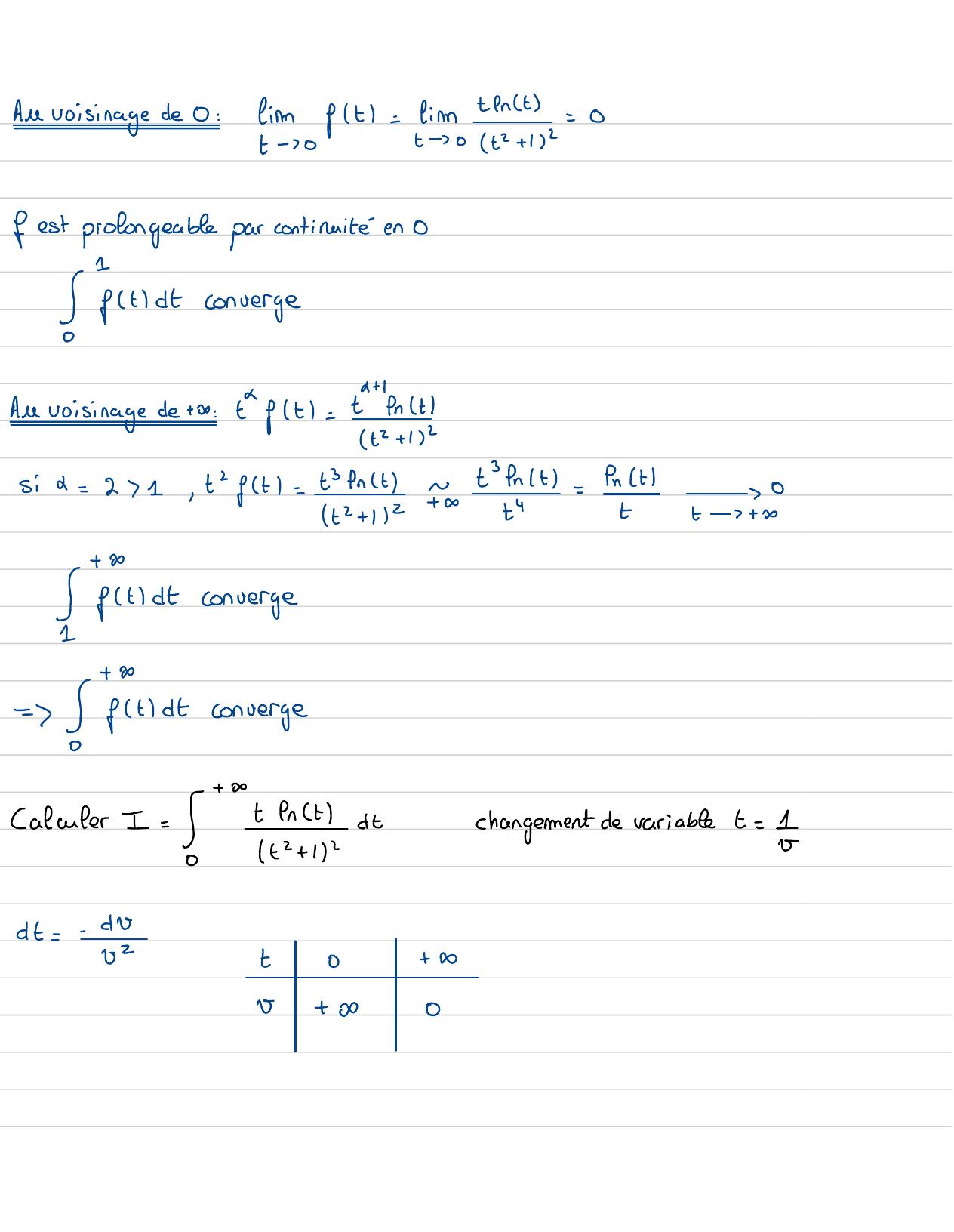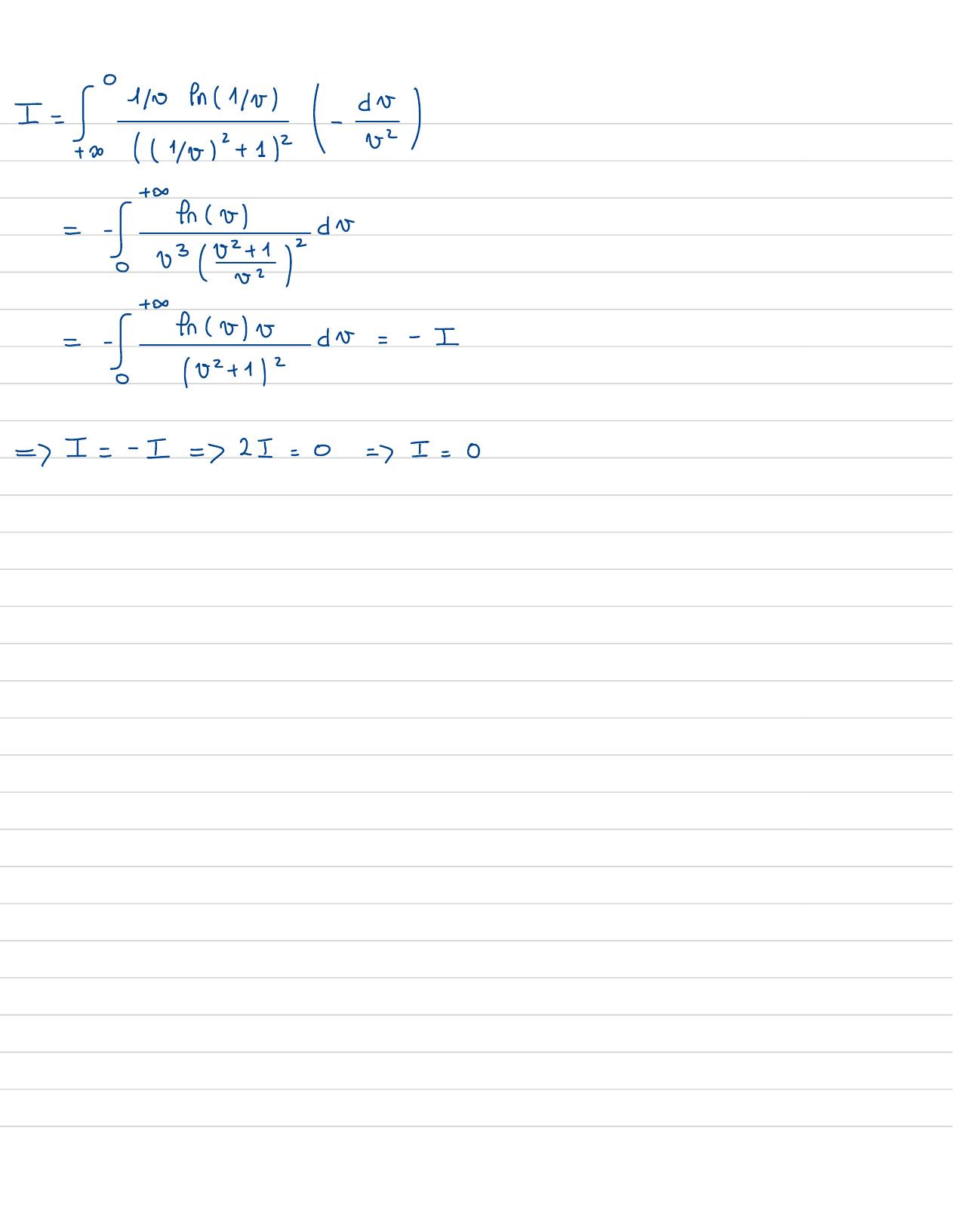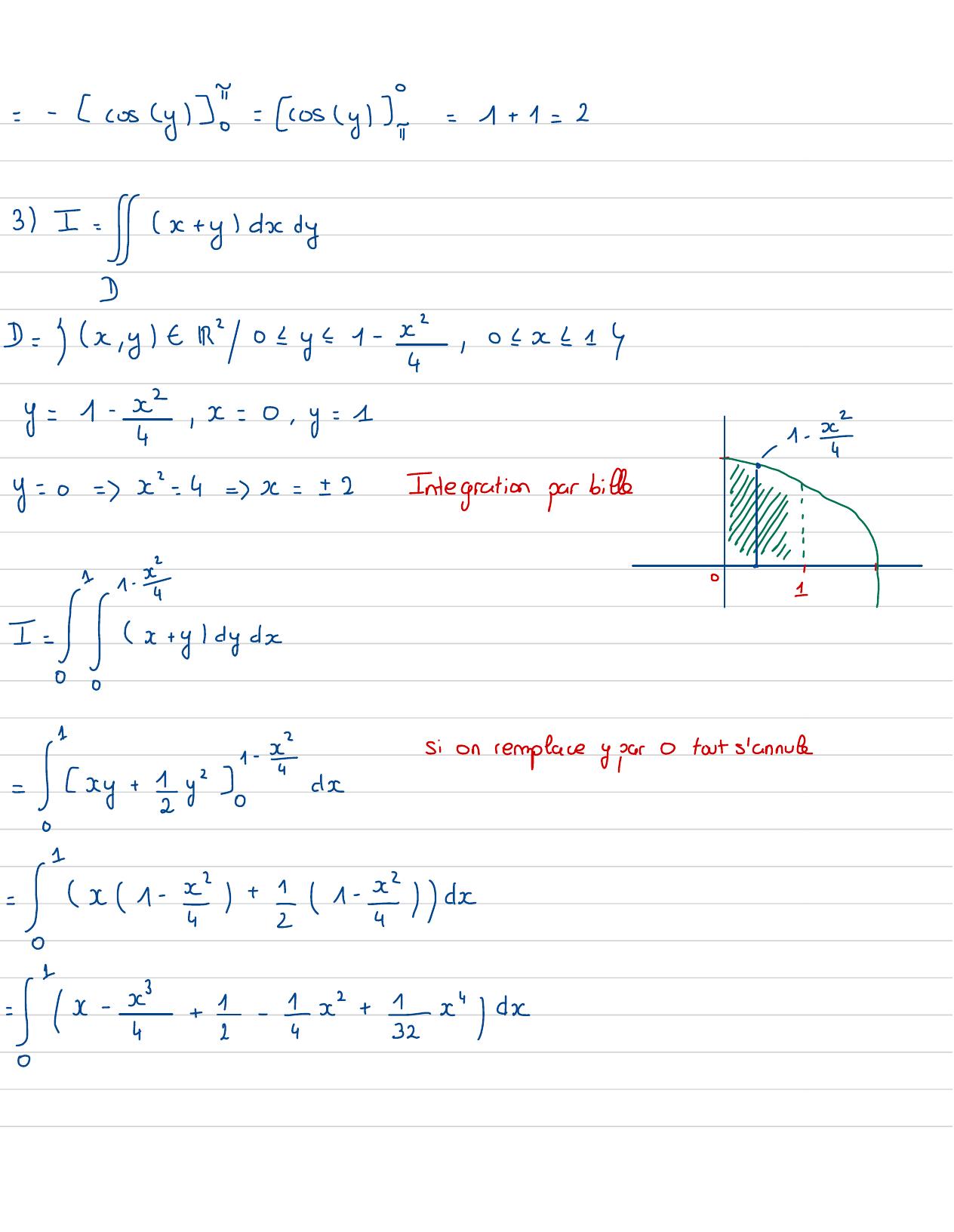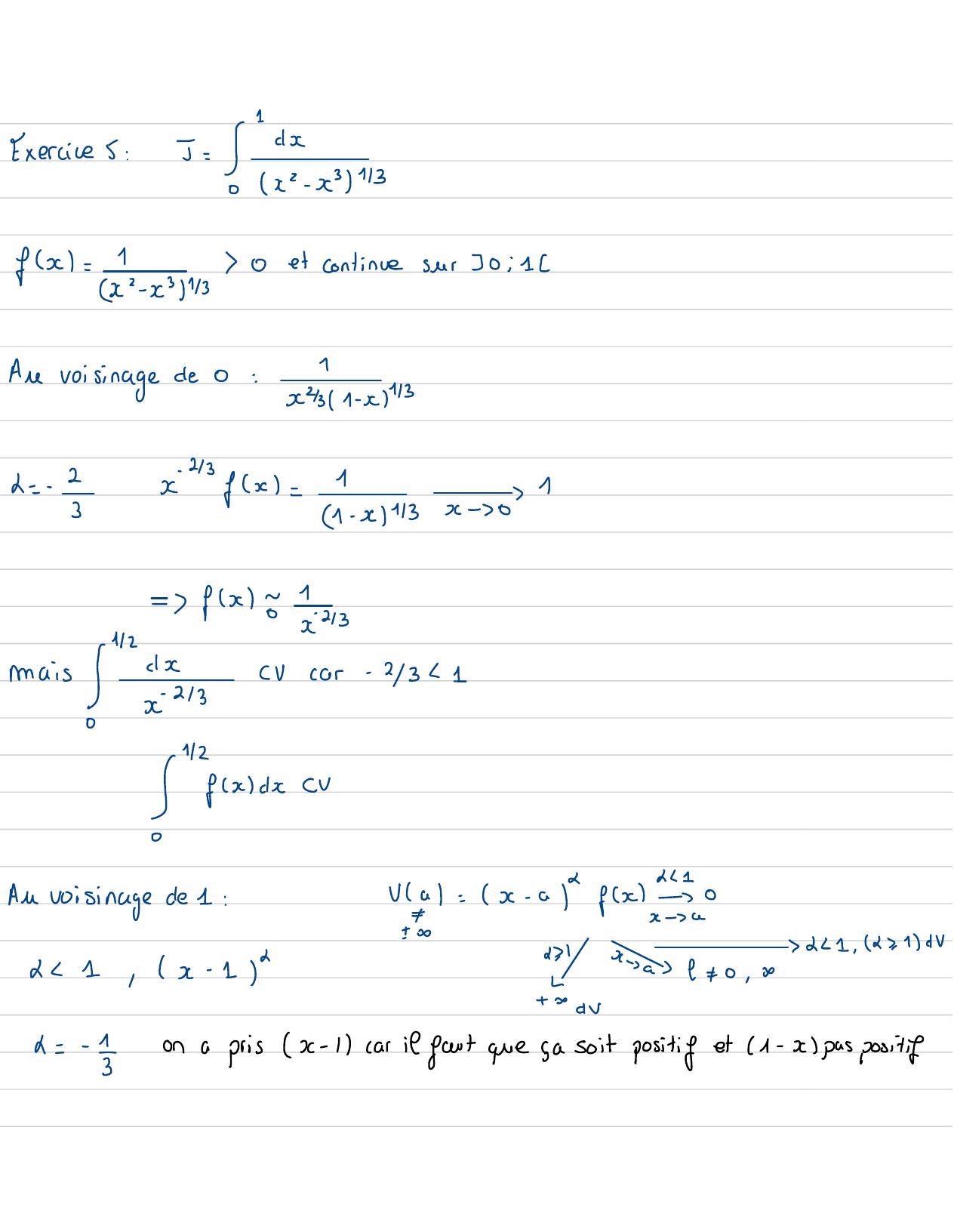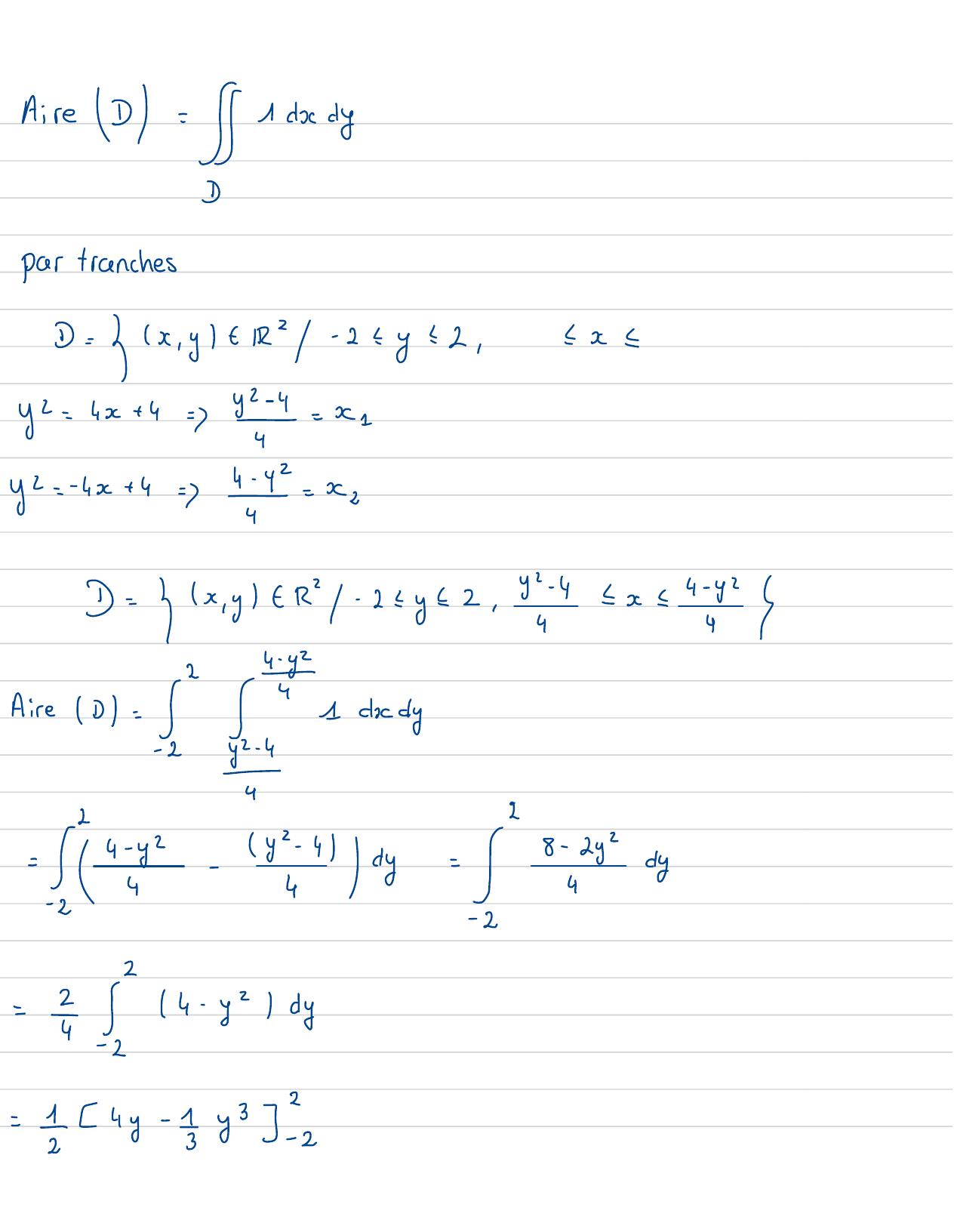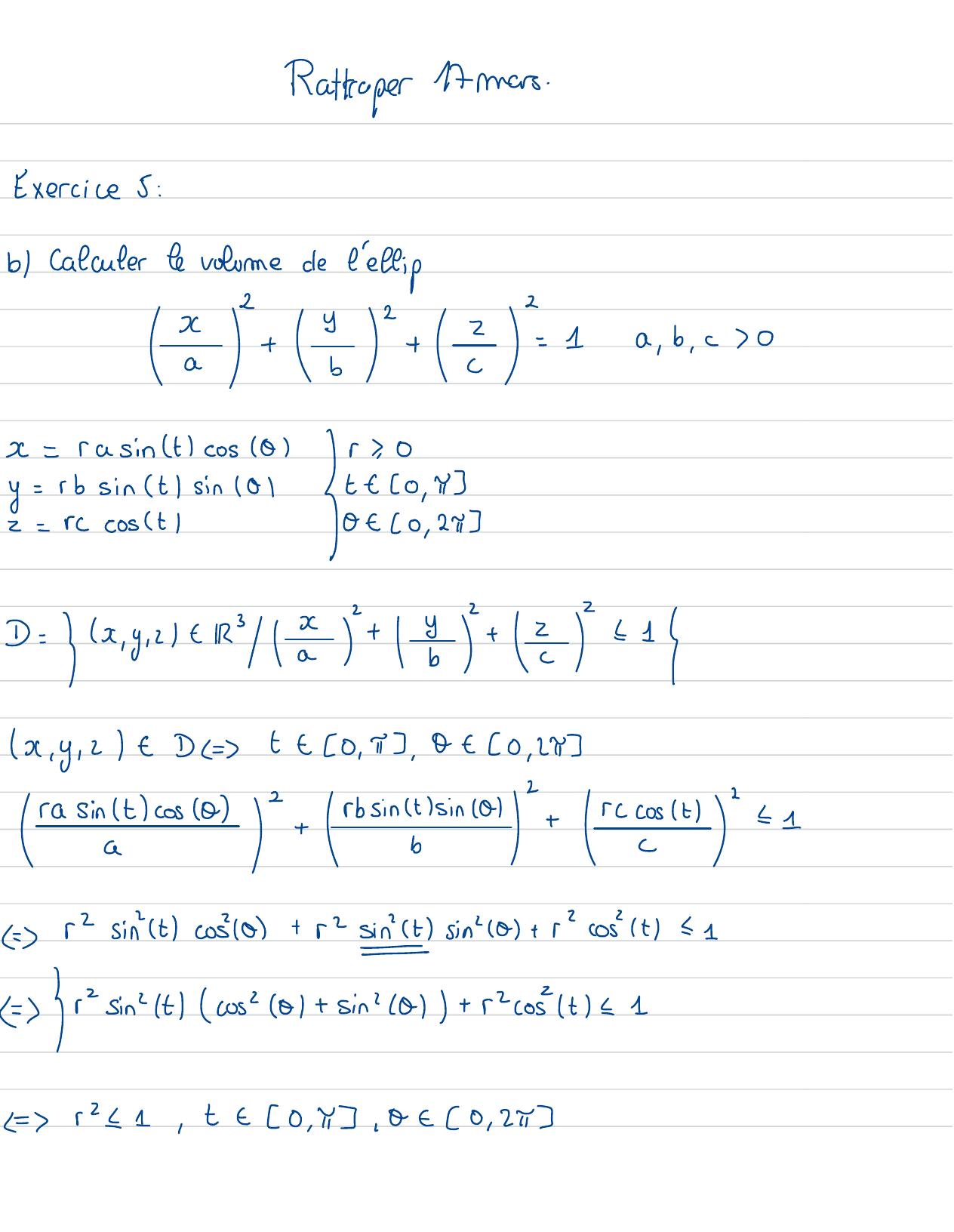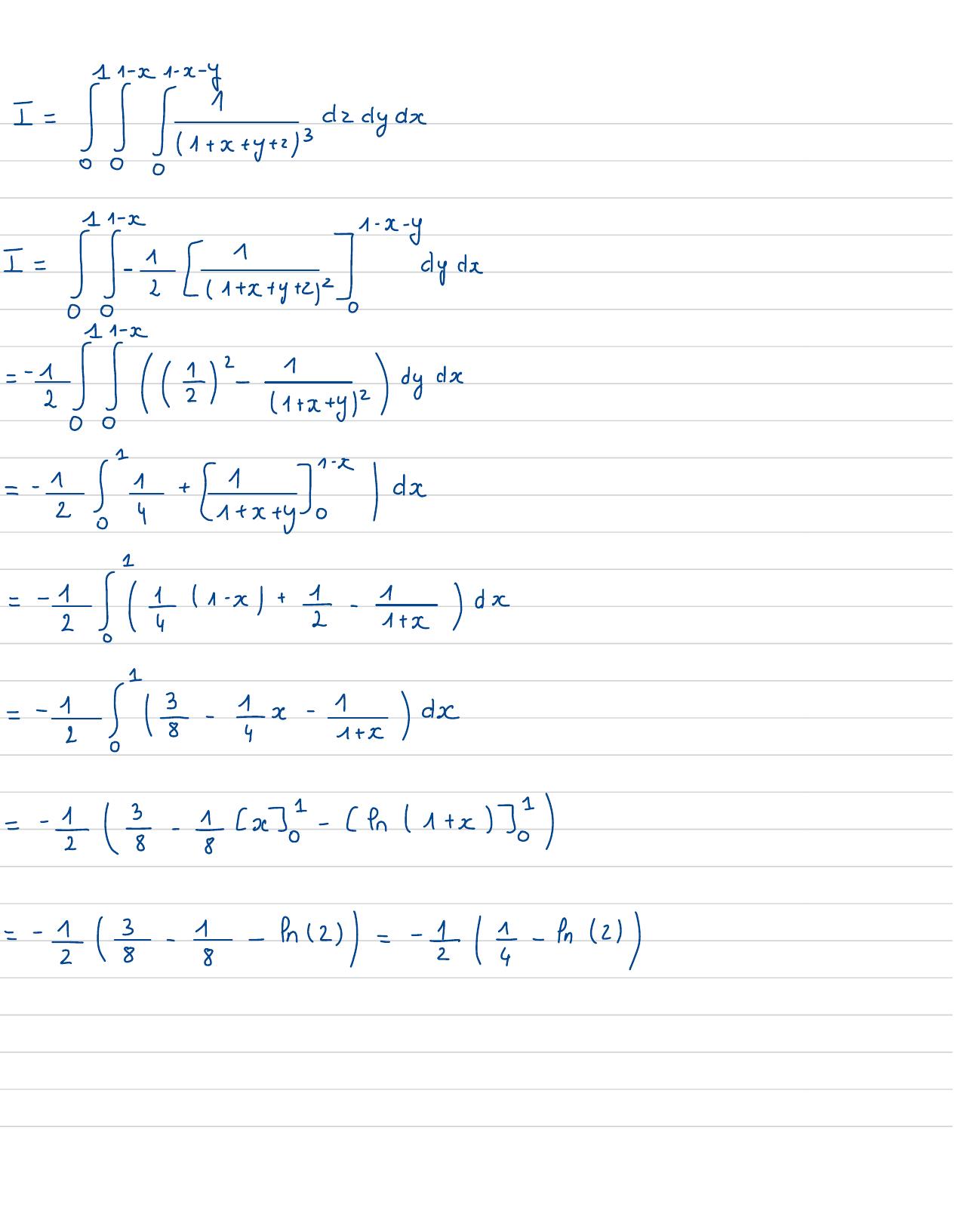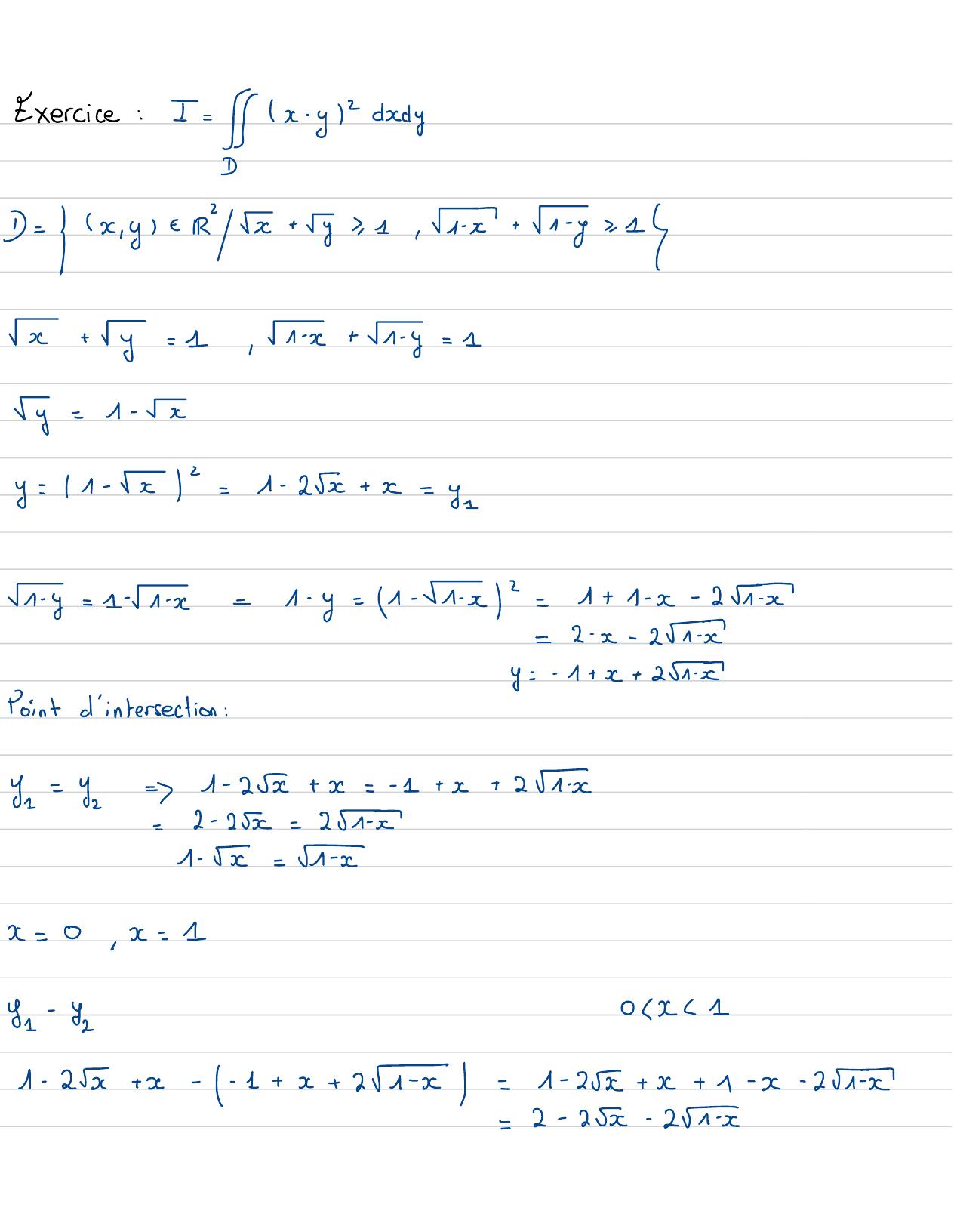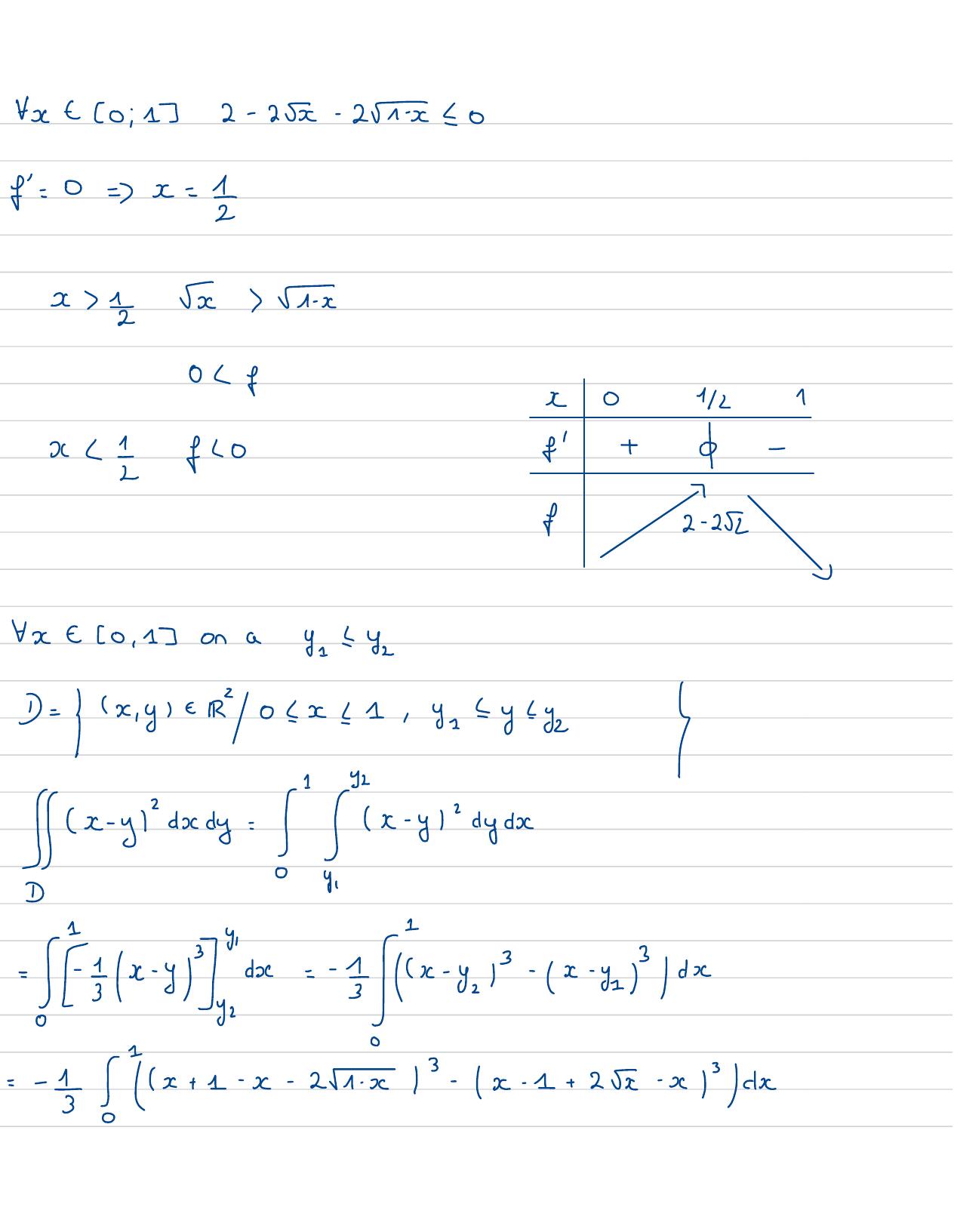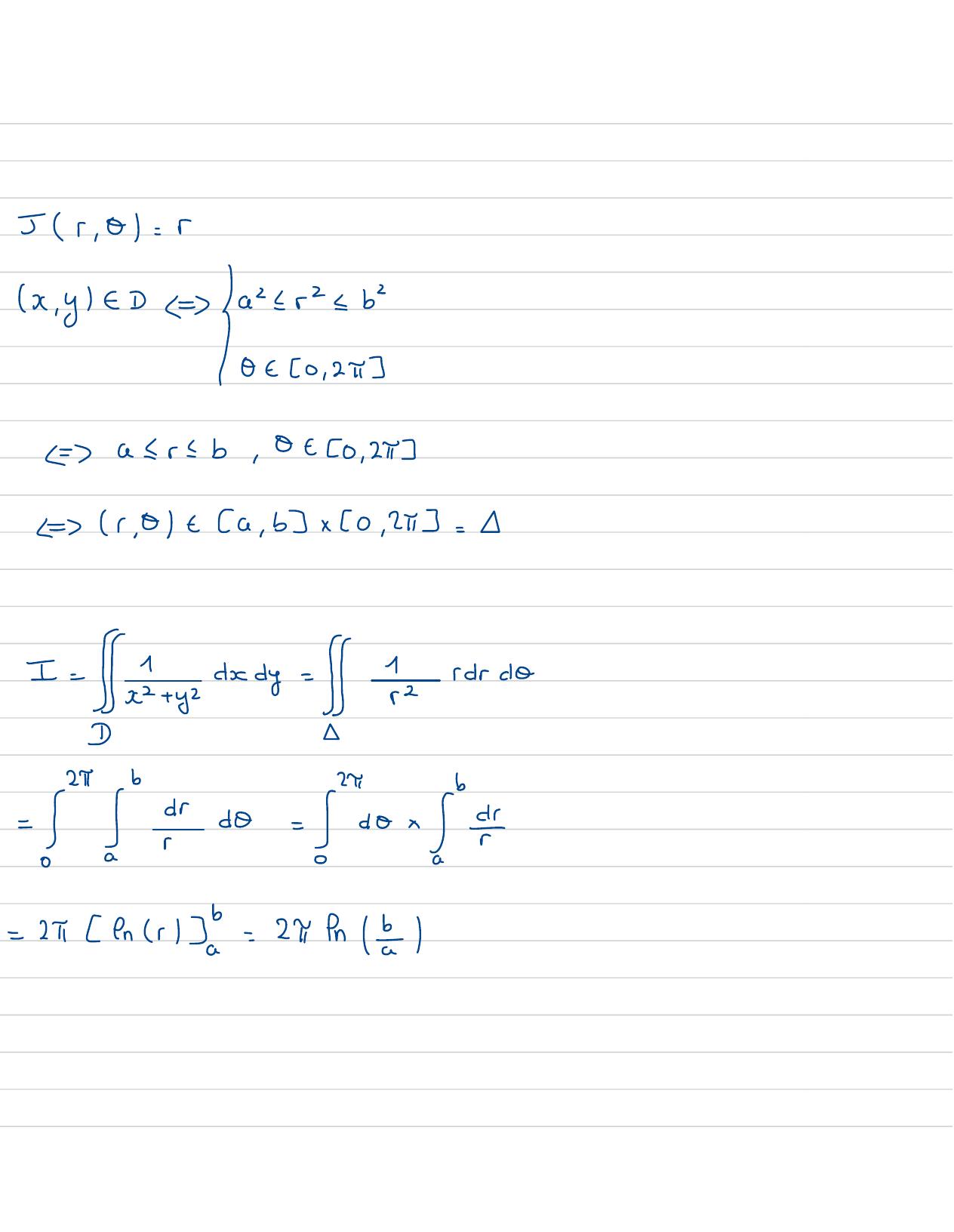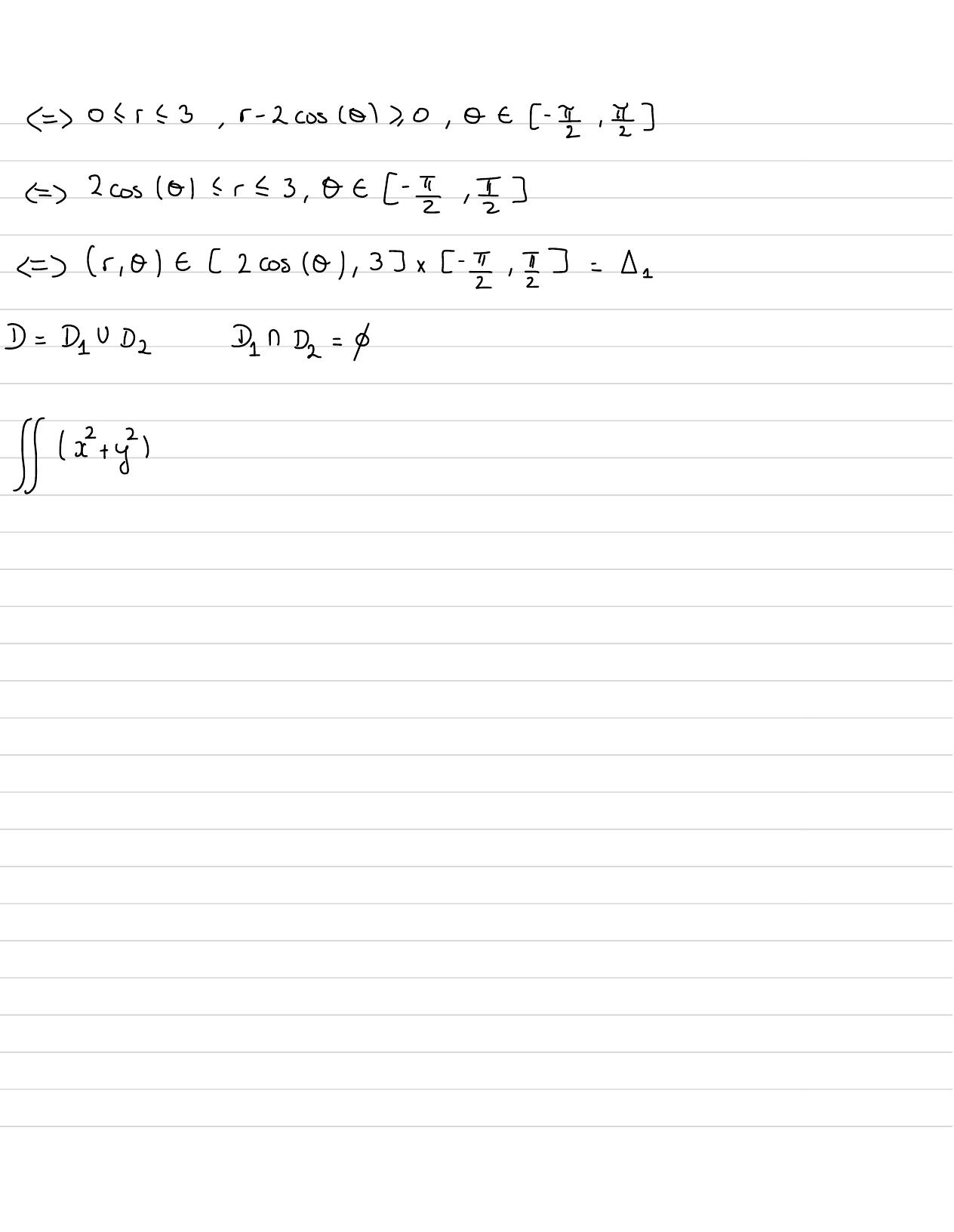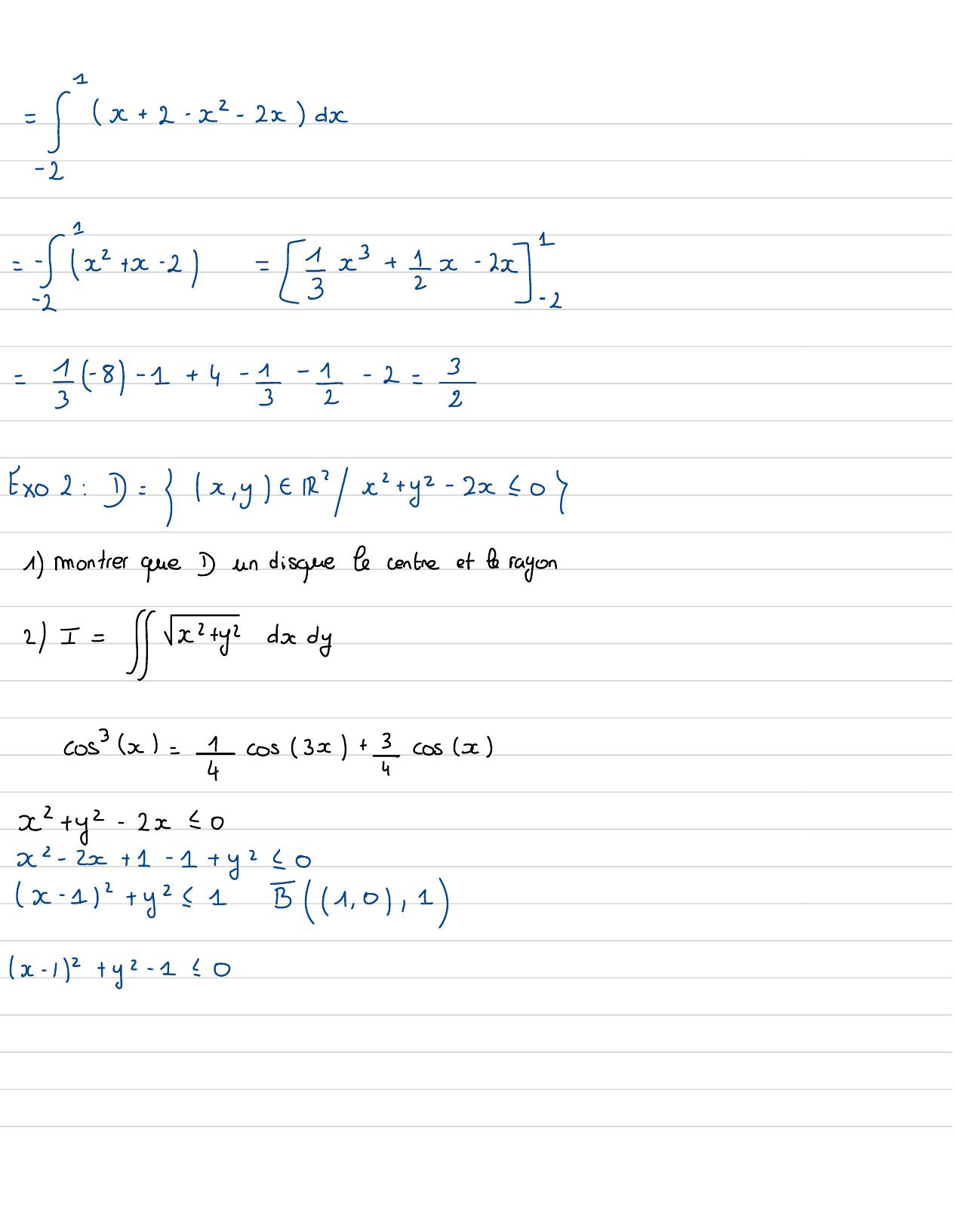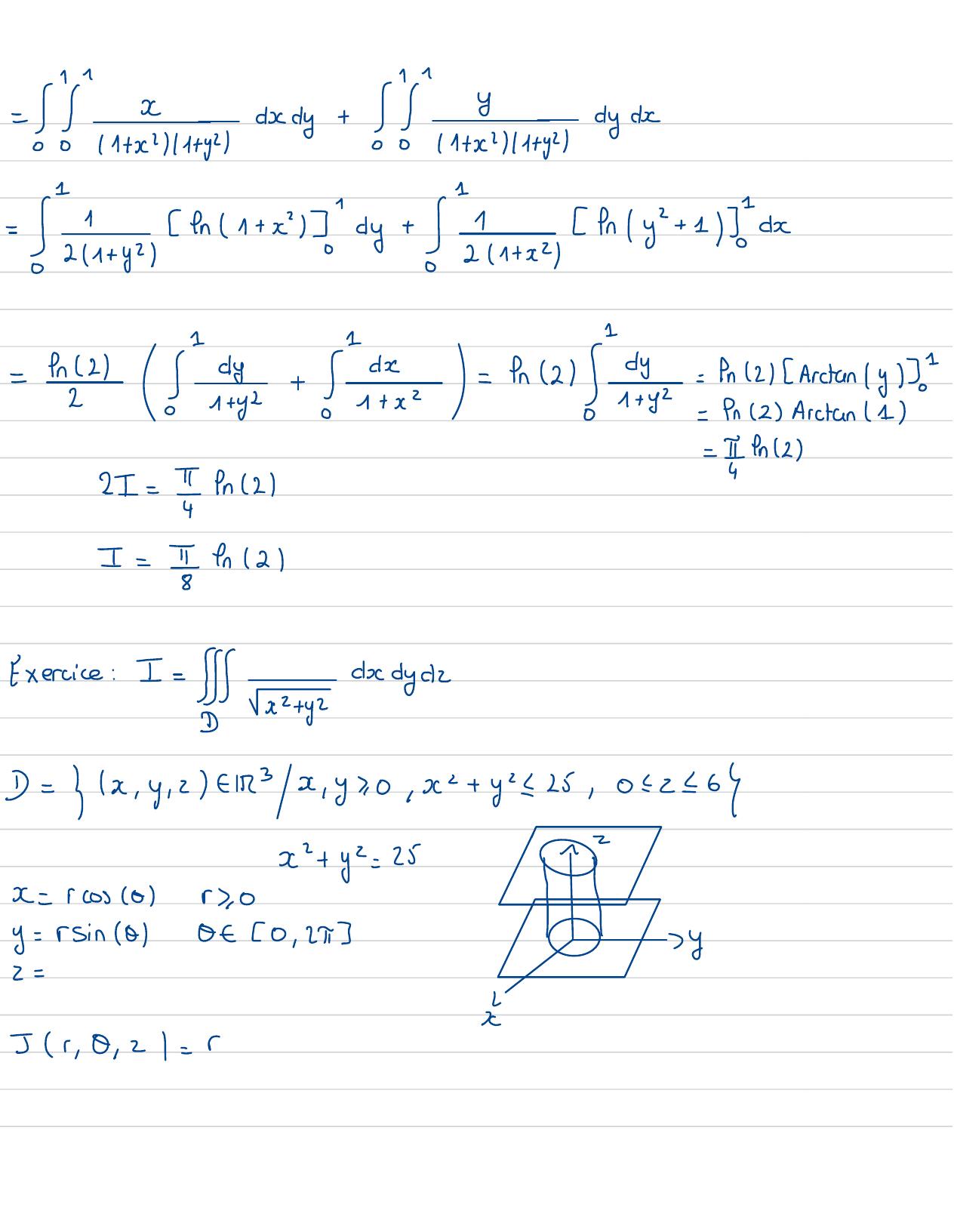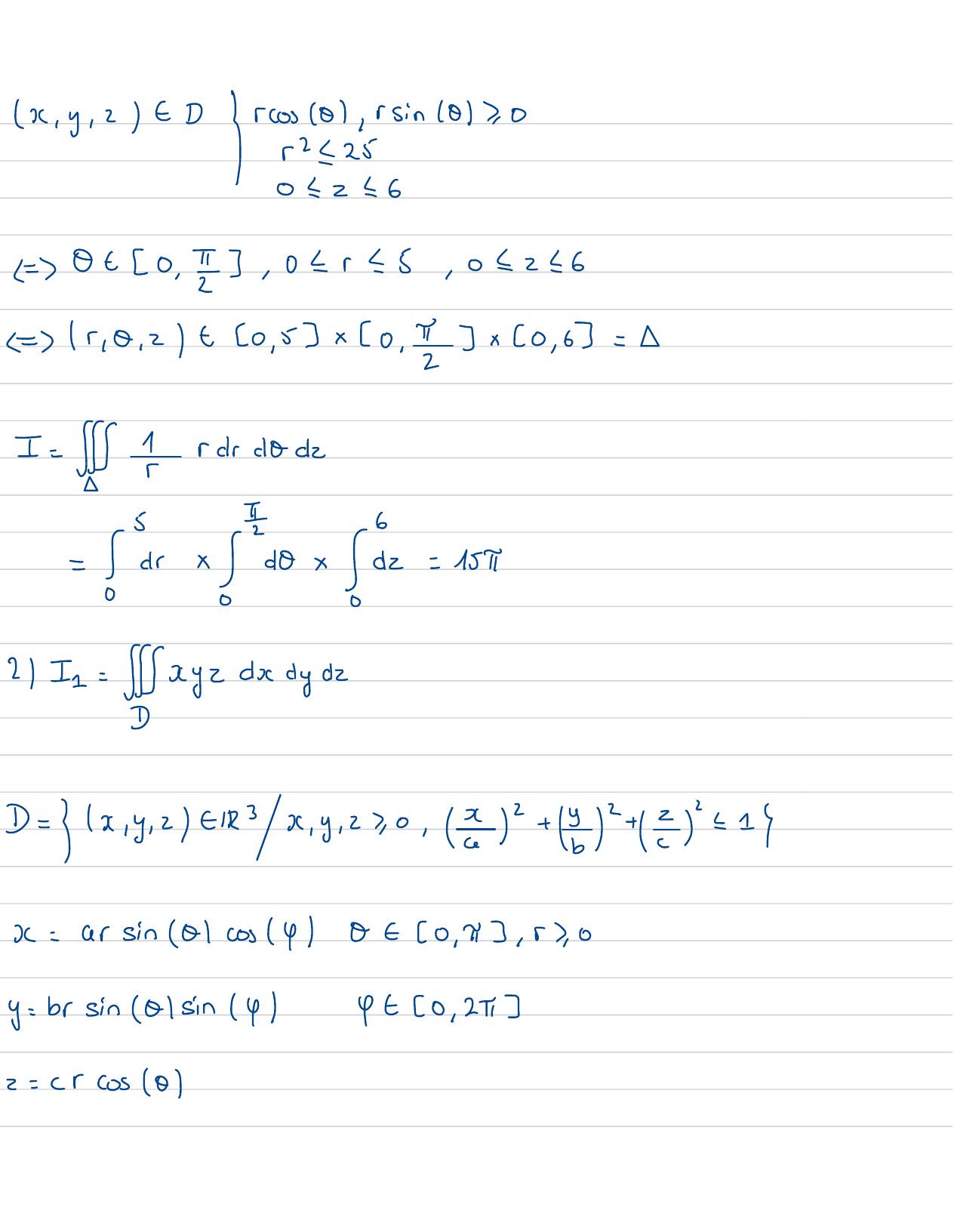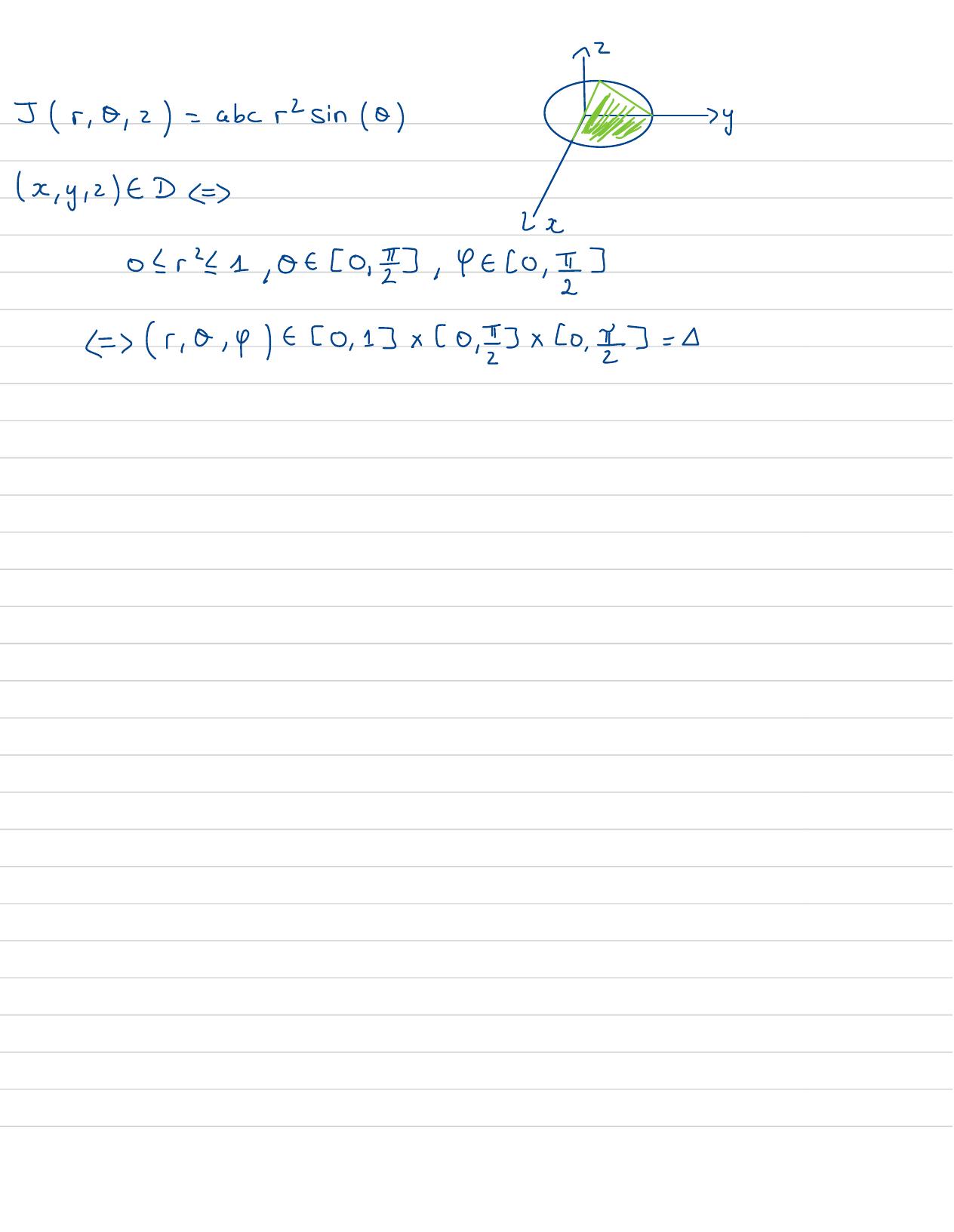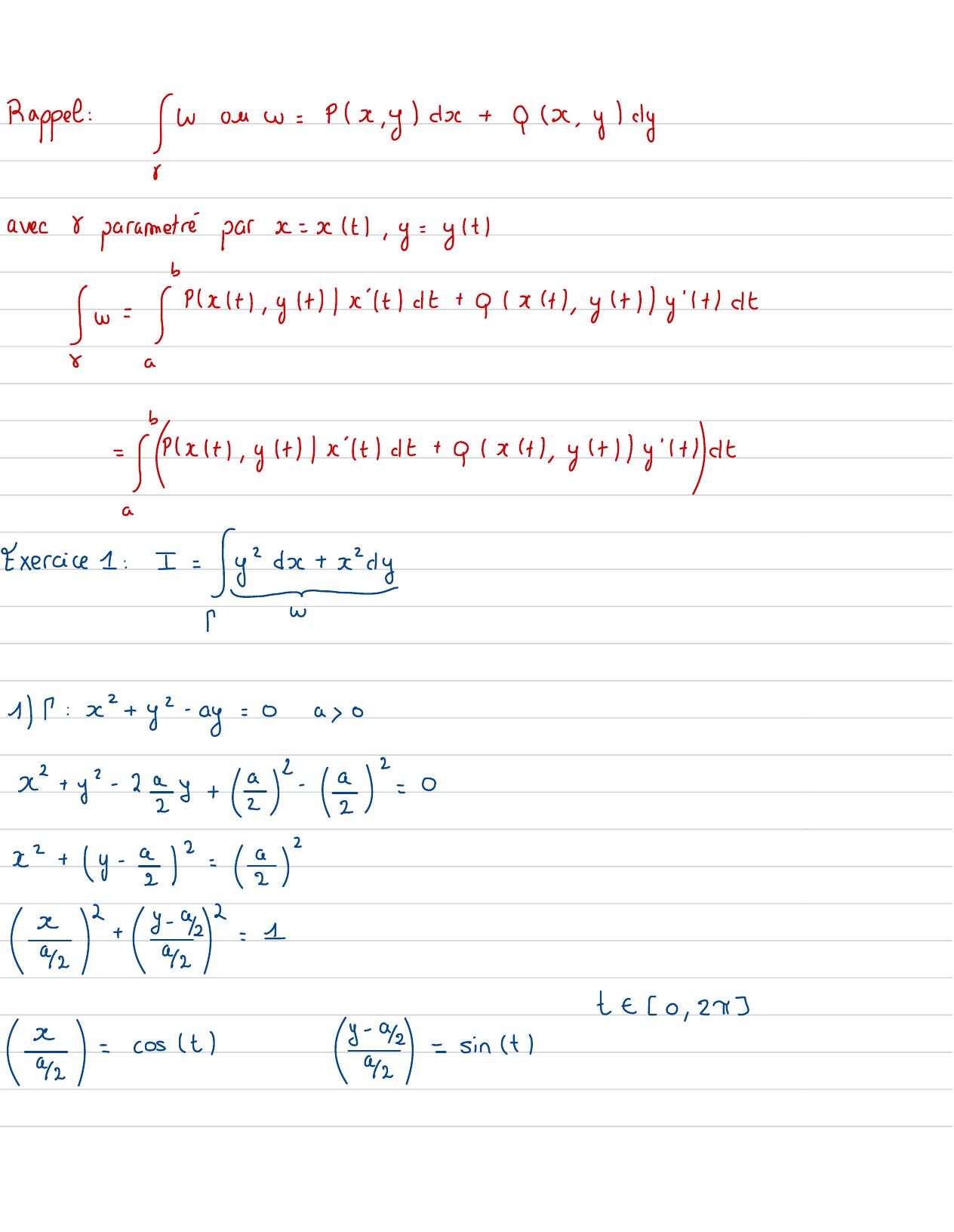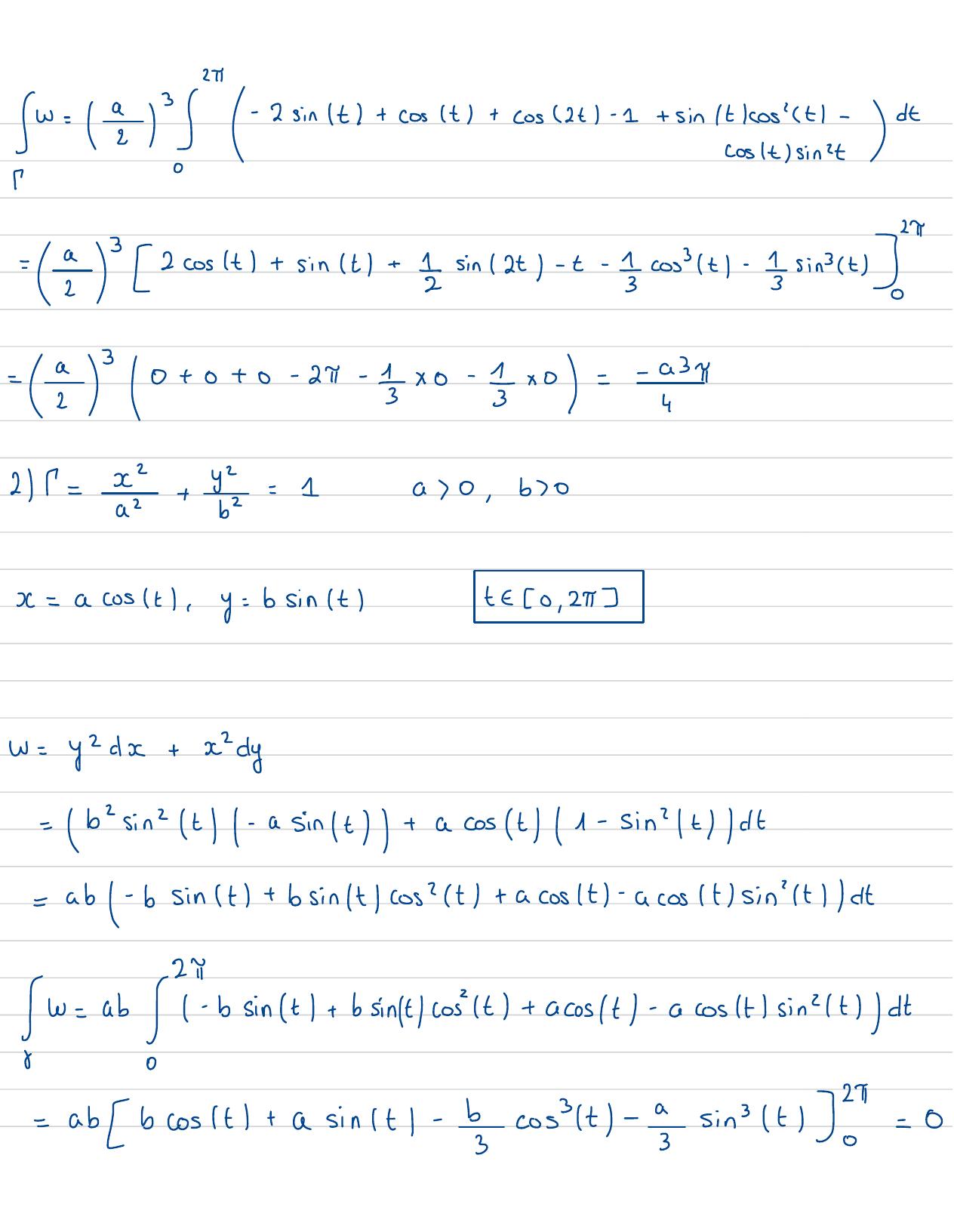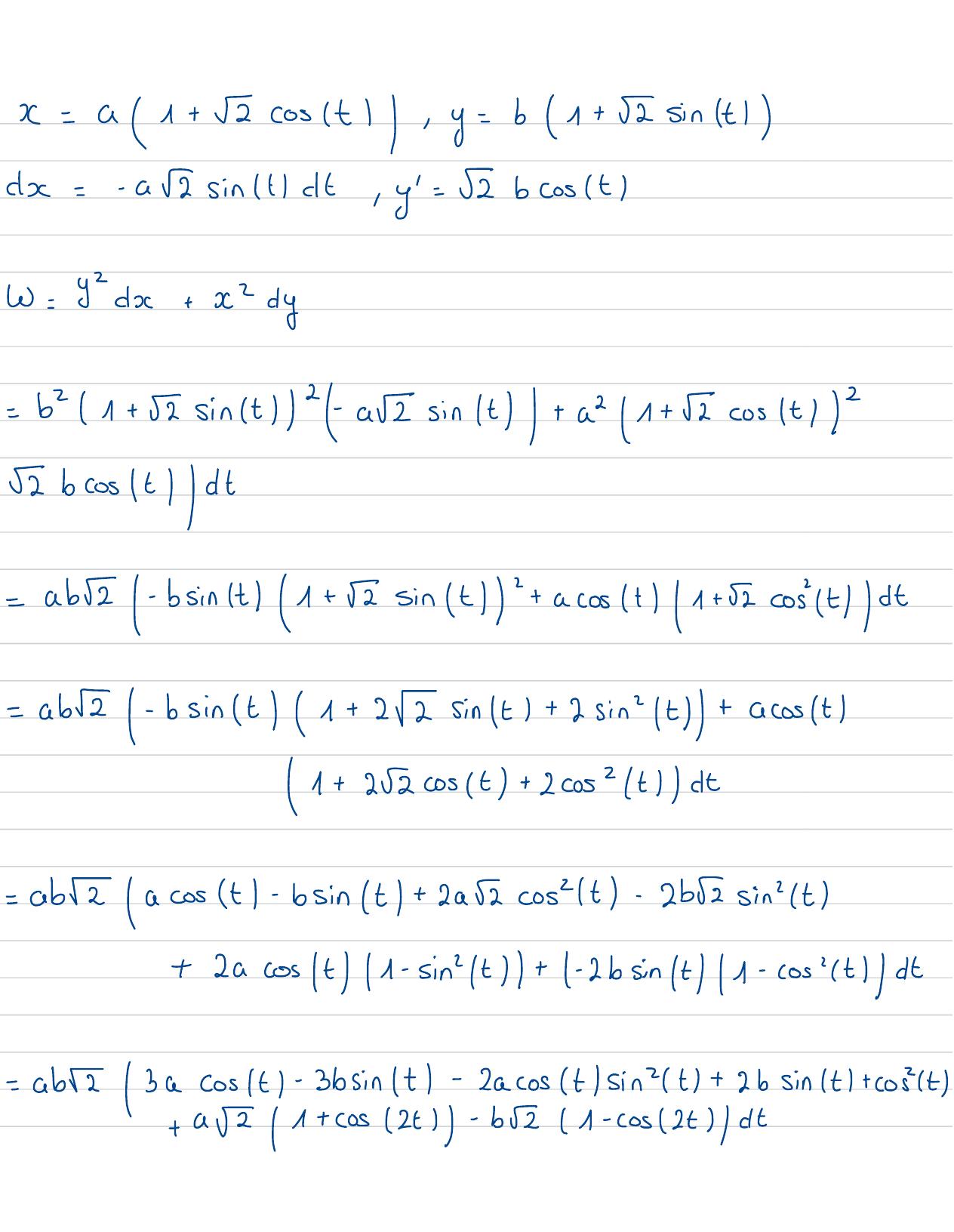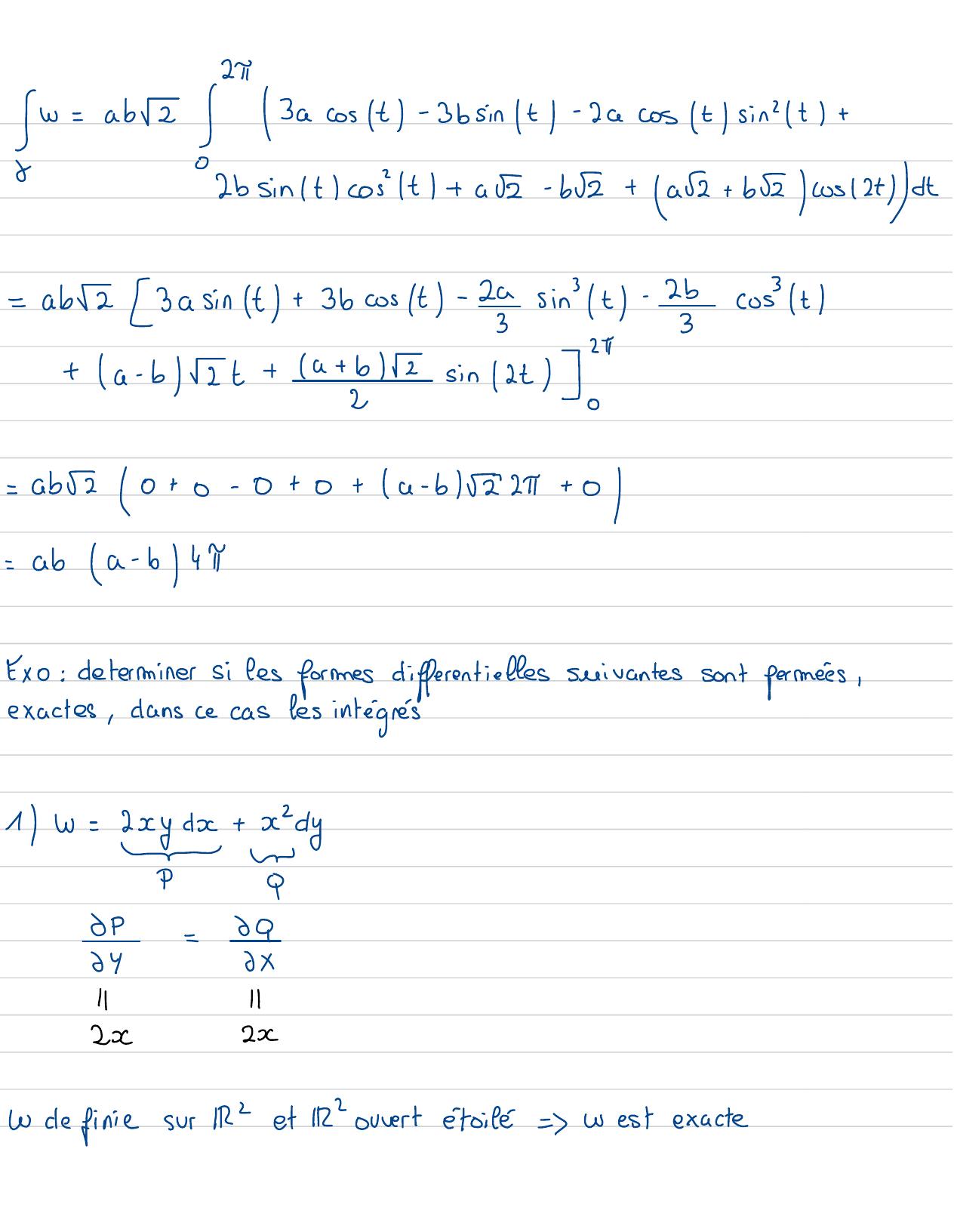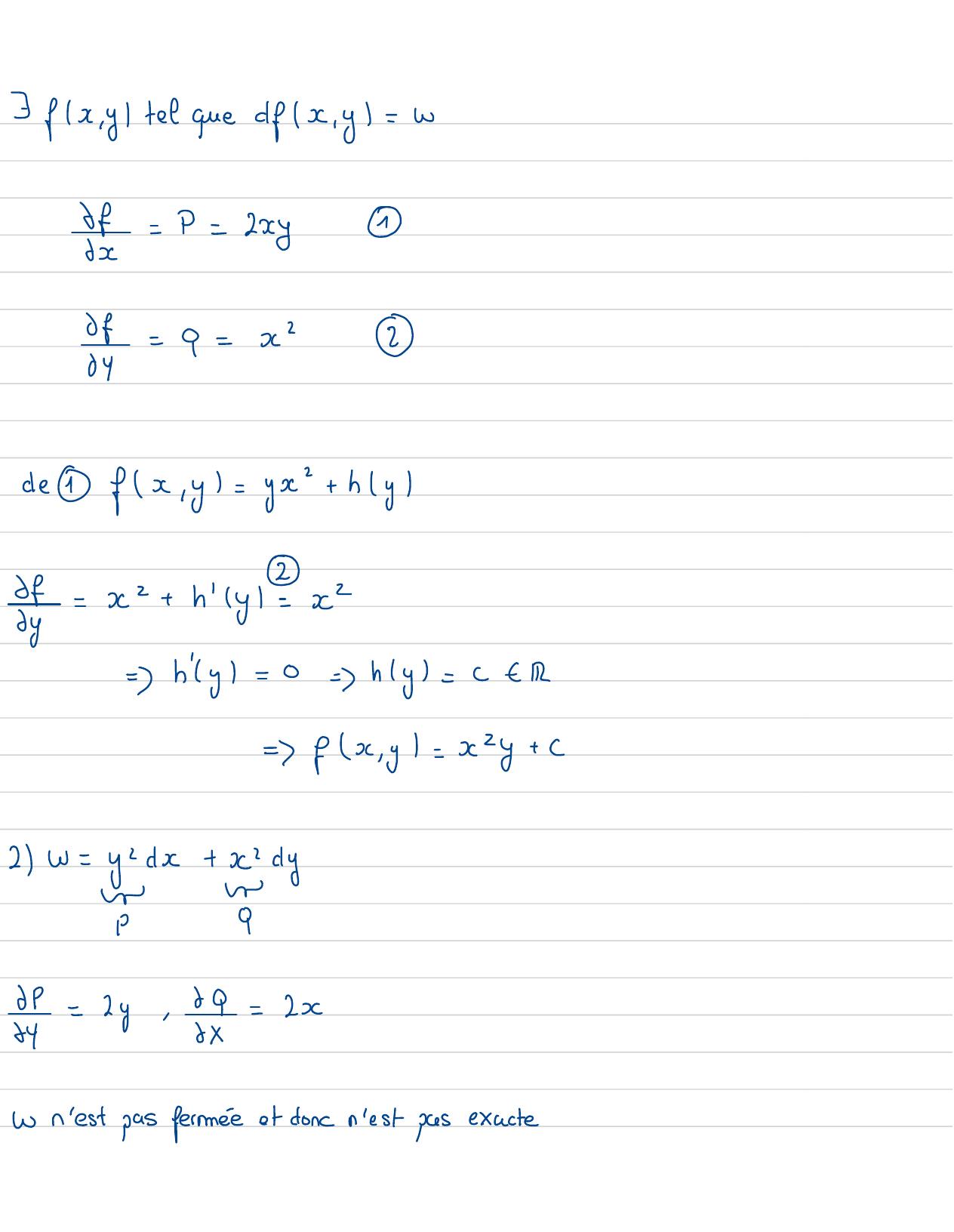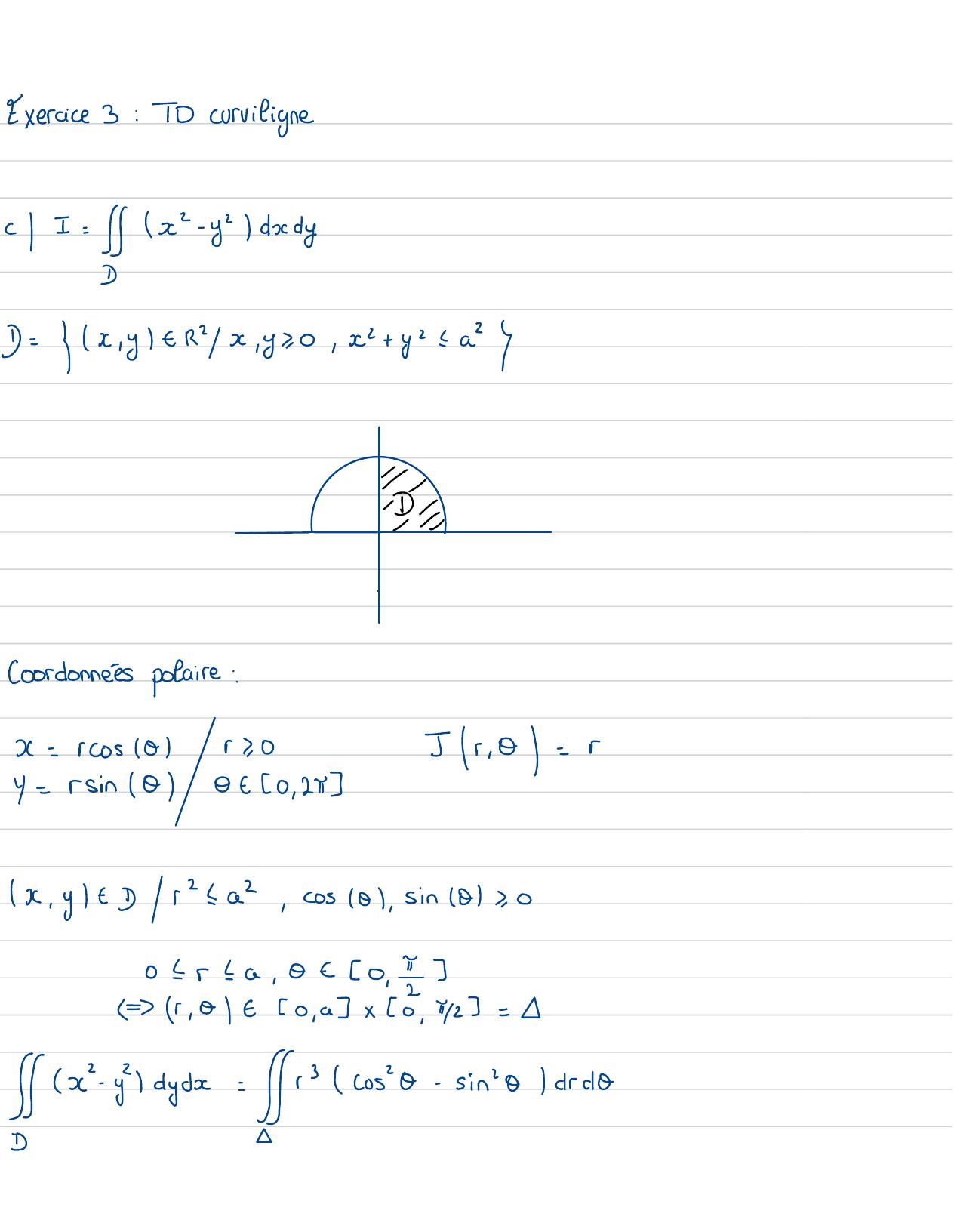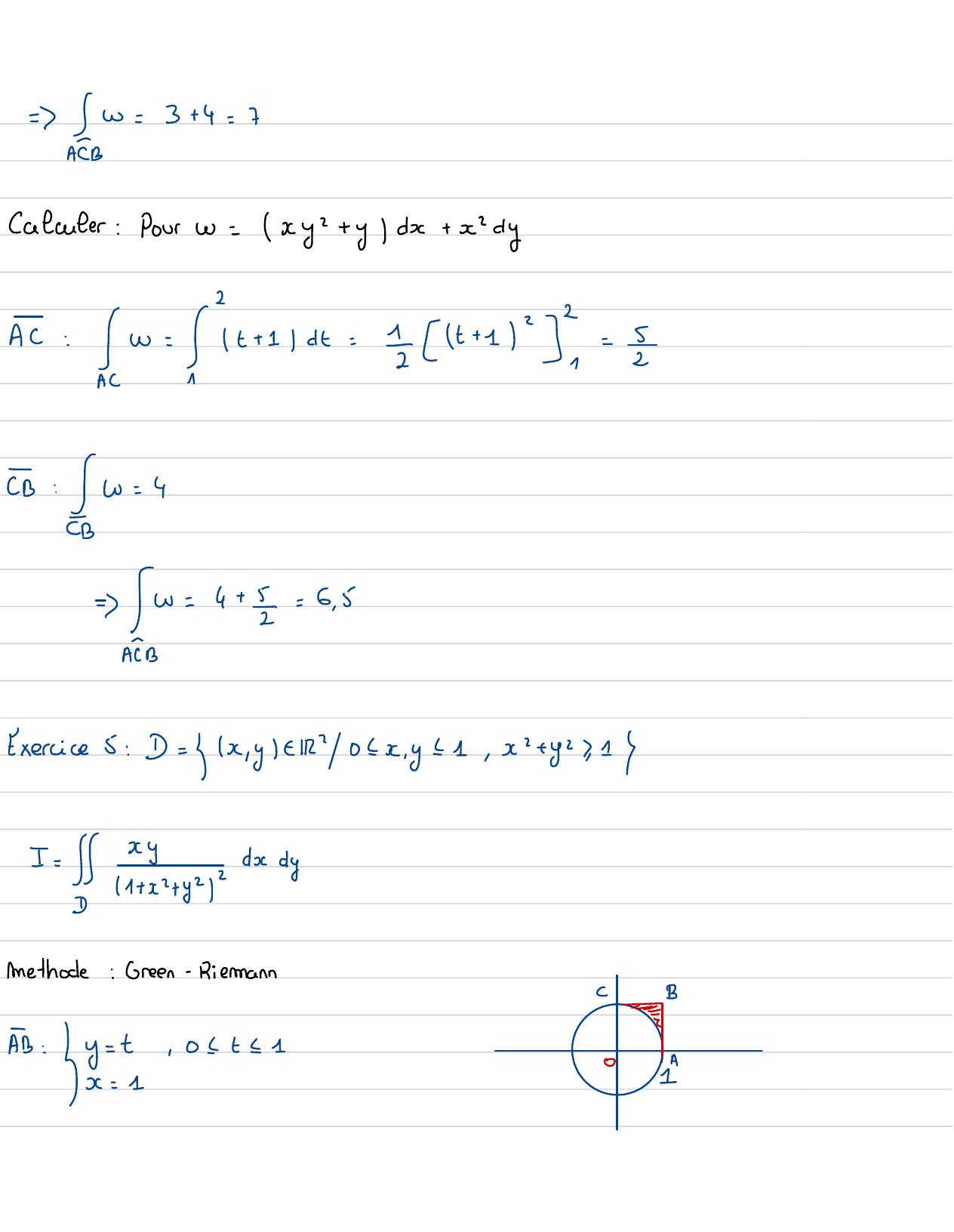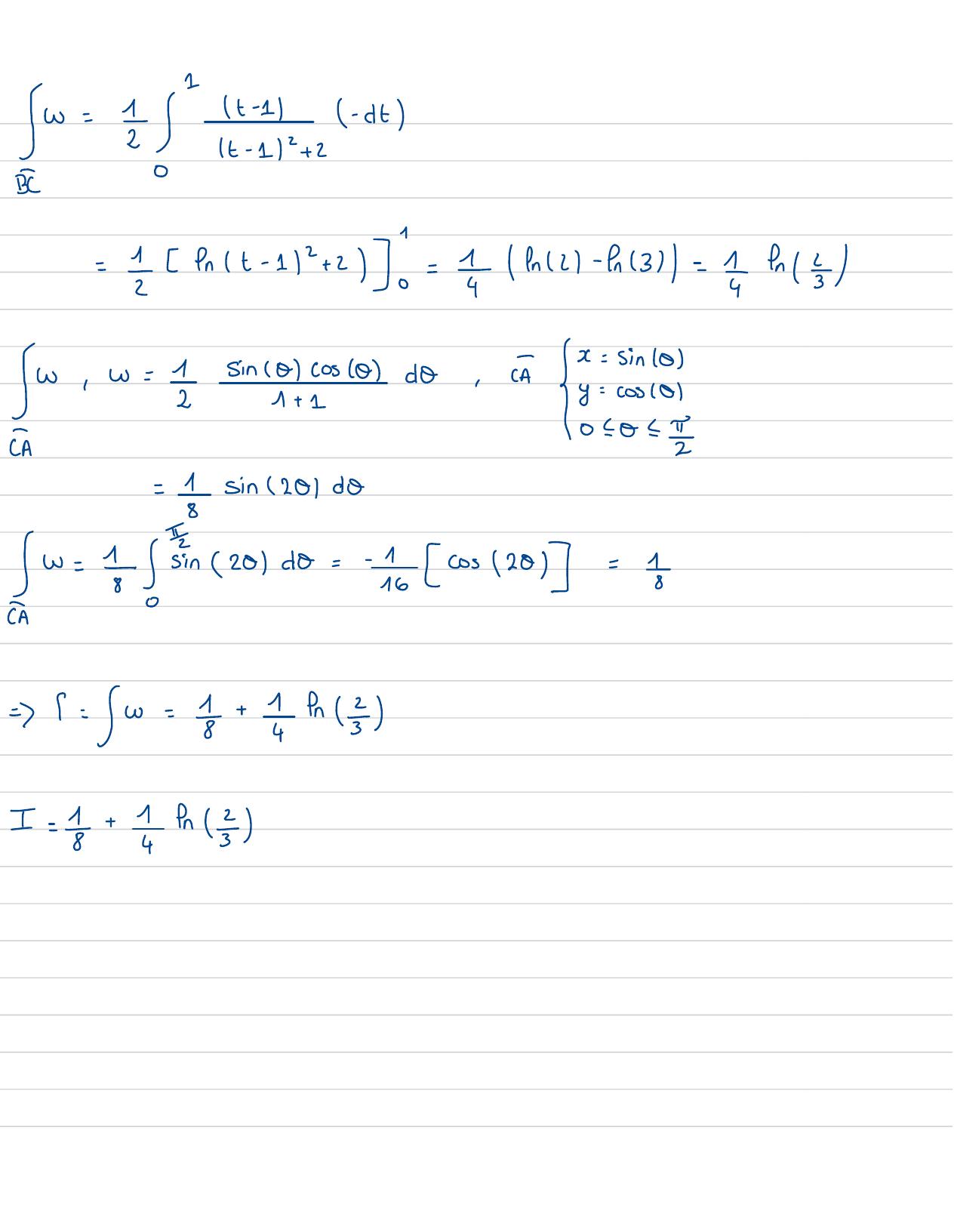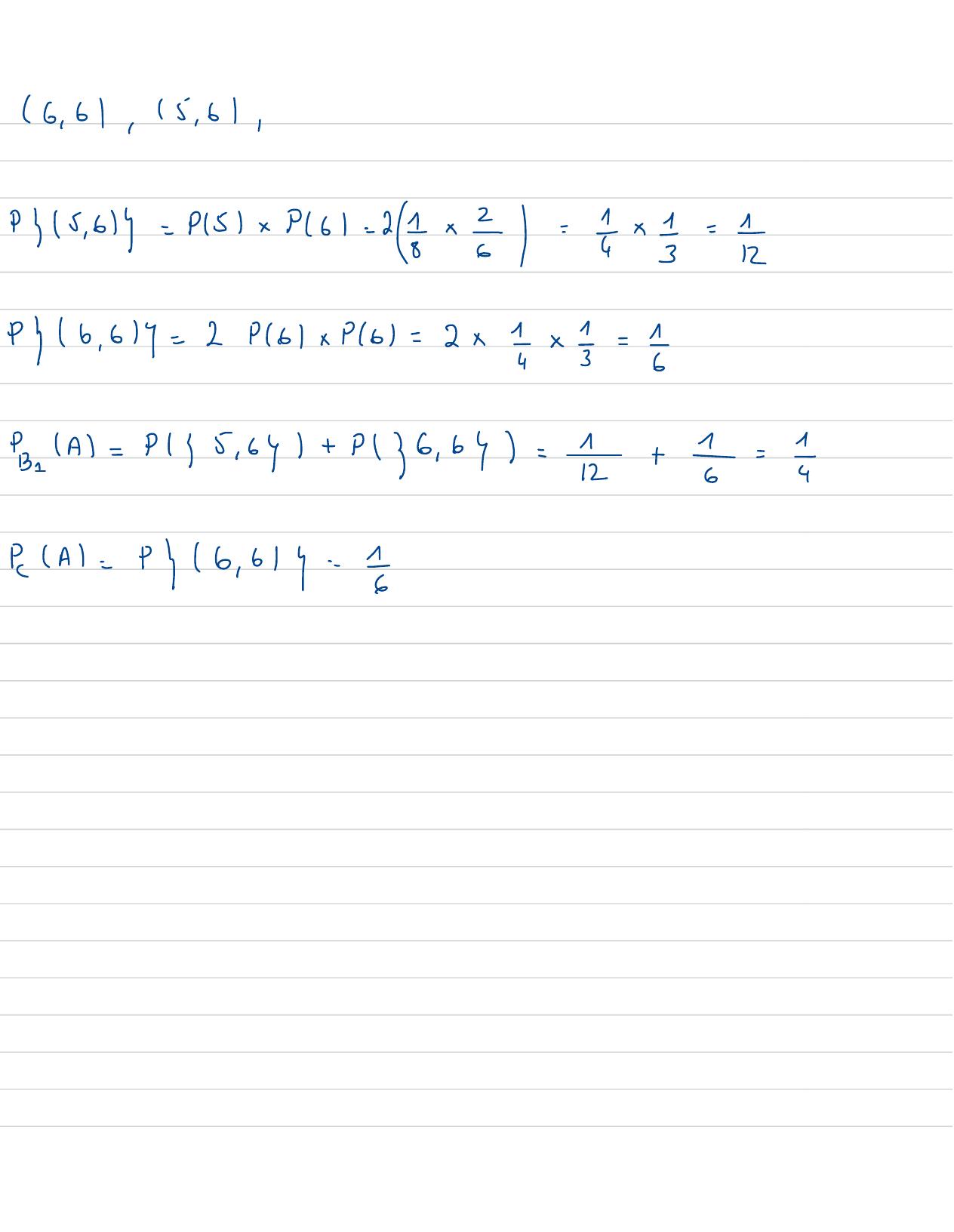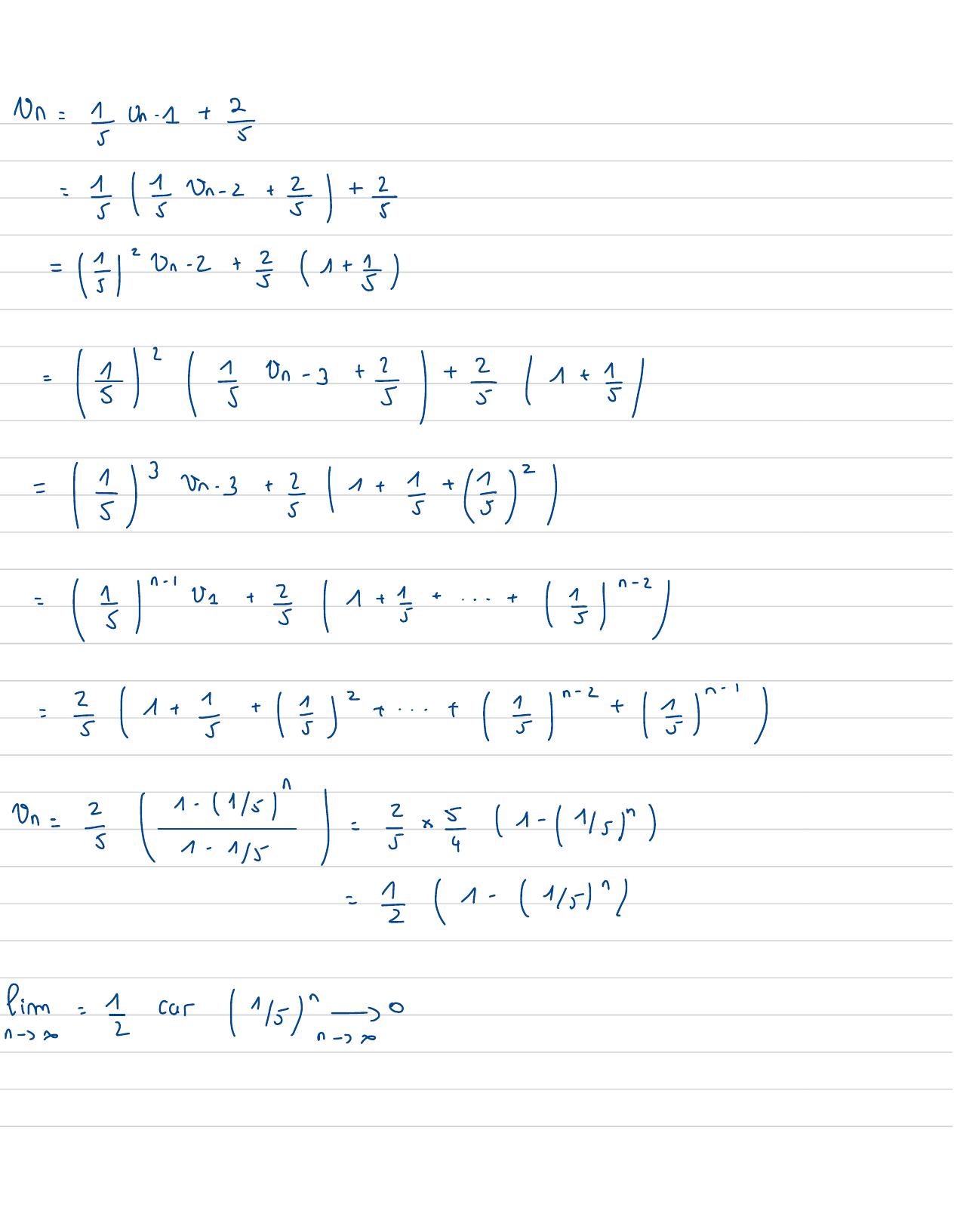TD Correction
Télécharger le TD Correction en pdf
Pages : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136
Page 1 : Intégration et ProbaTD 2022-2023
Page 2 : Rappels:Propriétés:Suit fet g deux fonctions definie parmorceauxsur I= a , b1 si f2ggltdt diverge =gltd divergeSi.gitconverge-gitc+ converge2 f= 0gDim!=- Sagitt diverge-gitd direre gitdt converge= fitd converge3859= Gagitat es ! gitaemg: 1de mere nature
Page 3 : 4Soit &continuesur Ja, bLbpour etudier la nature defltcOn choisitc- J a , bCet on étudieLbI1= fit1dt,Iz=!ftdtSi:Inet Izconvergent = IconvergeetonaI= 11+ 12Si: Inon Iz divergent= I diverge3Reglede Rienann ena EIR:f continue positifsur Ja, b0 5& 1LetqueIt-a gt , a=ftdtConverge 5 1letque It-algit ,at=fltdt diverge
Page 4 : 56ER , letque It-algit ,aEIR =ftdtconvergesightE divergesi, 16 Règle de Rierannento& continue, positivesura , +09 , aveca GIR 5& 1letqueth git0-3+ 0=ftdtConverge 5 27, 1letque th git ,+5=fltdt diverge 5GER , letqueth giteE112 t3+ 1=Itidt convergesixvdiverge si x ! 1
Page 5 : 71f continue positivesura , b, aveca etb EIRsig est prolongeable par continuitéen bfirm ft= 2 - 11 =gitatconverge⑧If continue positivesura,+x, avec at1si firmft= e- /1 =gitat diverget+ 0Exercice 1: I=- +1-ItSft=-1+1- tcontinue sur 30 , 17, negative sur 30, 17t-ft=1-1- tpositive sur 30 , 17tProbleme convergenceen Oeno:- tft=1-1- t0t0-ft=1-1- tvt01-1- t=1- 1- 2t- ft2+ 0t= It+ It+ 0t4
Page 6 : -ft= 1+ ft+ 0tfirm ft= 1 ERfest prolongeablepar continuité entprolongement= fitas: "Estatexistecarestcontinueen out 1511:GEccoEt e0 ; 16 "gitldtconvergeI= 1-1 +1-dtx= X- rdt=- 2xdxt01C10
Page 7 : I-excel-- nadx= 2-ex= 21- i +=ex= 2x- enx+1 1 ici -fr2fne= 1=fr2- 120deb5=/1+ x-1t= 1/x/ t+ 3tx -70txx+ 1x= 1/t=dx=-tt2x0+t+D
Page 8 : === +- aI-Site-1--izzetdt-- E5-/- -1172+ 1 dt25=61+ 1- 12 t2v= E- t=db= 1+ zdtt0+ 3- I+ 3E
Page 9 : 25=!2= Arctan w-=firmArctan2-Dim, Artan et5x+ y=I- 1-= π=25= π=5= 4Exercice 2 :111== 1 enfxest continue et negativesur J0 , 12pberoeten 1By gladi,78kdon vaetudier fa naturedesintegrateetl'uneen0et fautre en 1en o:imoten=0 EiR+=I prolongeablepar continuitéen 0
Page 10 : 1/2=fxdconvergeprolongeable-continue↓Ennesailpasen 1:pas prolongeable , if fant trouver ave autre proprieteOn posex= v+ 1=r=x- 1x 1, 0 -0fux= en1+ 5 - W=1en 1+01= 8x- 1- enI-1DYs=-0diverge diverge - aIIdiverge=a diverge cuto eMontronsavecRienann que ça divergesigl :=Dimexxx 1fux
Page 11 : X74= 1, fenx ==fadivergeJ =61fx=x+ x0,continuepour O1+Donchoisit c= 11fxdx -fxen 0: fx,BfxBsi=x+ x-BxB-xB-1-1+ xxBx- 1+ 1x- B+ 1x -0-01fxc1↓·Converge si 1
Page 12 : =glalcconverge si BId= B=yxB=12xB2fxv12xBdx6xConverge si= 1en to : fx,fxcd-dax+ xx1-BxBx- 4+ 1--1x- c+ 1x-+0Vo1fx ToSconvergesai ba= docconverge si La s
Page 13 : x2L= B=2x=fx toc+dxS2 aconverge siL 11+=fac converge si= d =6 jusia converges: Enjglacconvergesi is1B 1 x↓x dconvergesi1B
Page 14 : b-k= ,+/deR!fx= +x=1/20et continueSurSo ; +oLen to:fx= x+ x1 +1x2L==x1+1+1x2d-E1+11+ k2fx1+ 4+ 1x21En+ 2=1x -+ xfxFo /2x6 gxdexiste.desintegrate normaleintegrate généralisée icipbexisteau sensdeRienann
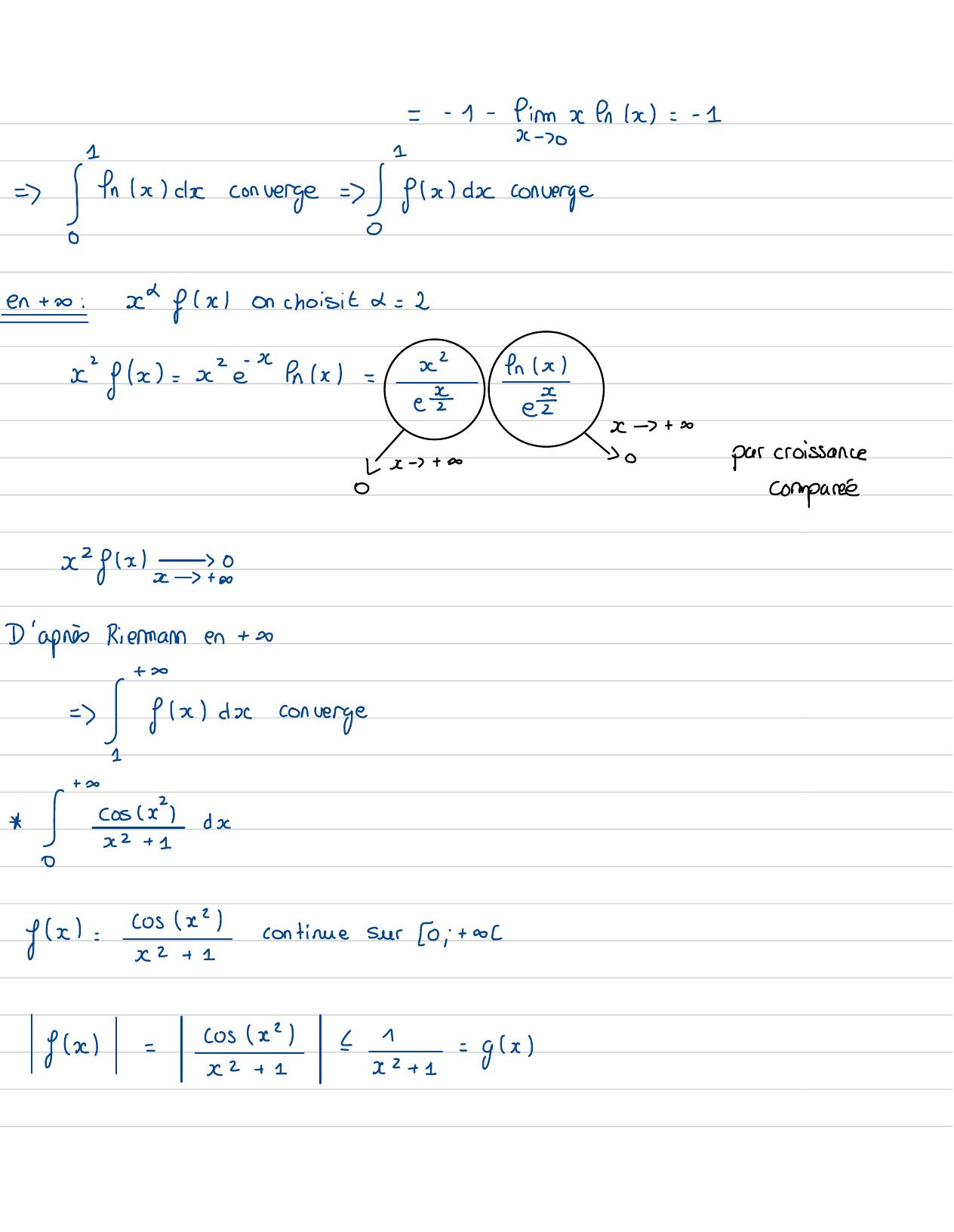
Page 15 : + 320sde: 1!=fx d convergess:1=lucconverge s:1Exerciceb :I= explenkaldafx= expfx2 0etcontinue sur30 , 13en0:firm fx=+ 0x0onva utiliserecd fx,onchoisit&= 1xfx= x expfx2= efxx elens=efx1+ fxx0+ 33+3↓1 1xtfxxx0d'aprèsRienmann ! gla ddiverge
Page 16 : 5 = +xdefx= efxcontinue Sur 30,+ 0 fx= 0Si xCJ0, 13 fx,0Sixt 1 :+ 3On vaetudiergra,x d-1eno: Ei= ea cofx= enx6 eakc =Ippm=fxdaxxdr=dxv=xnxc= xfk- dx= xfnx- x!nxck=xfx-x= 1xfr- 1- einfns- xx-0
Page 17 : =1- fimxnx=- =x -70=Inscconverge = gxdx converge!en to:c fxonchoisit= 2x"fx= x e " fx=xInxxxeex-+ 0Lx-+ 00par croissance0comparée0x2fxxx+ 0D'aprèsRiermannen+ 0+= fxdxconverge1+2I iefx:coscecontinuesur 0;t-cosseefx=x2+ 1= fx
Page 18 : I1= Arctann!-firm Arctans- Arctan 01x-3+ 0=I-0== a,convergeS C= ixdiconverge absolument= "Jadconverge+ 3x2:La vateur absofreen K= normeI2dxH=x2+ 1:x1fx=e-2-x2+ 1x+ 1x2+ 1= !converge= I convergeRappel:2=a+ ib=z=a+ b2
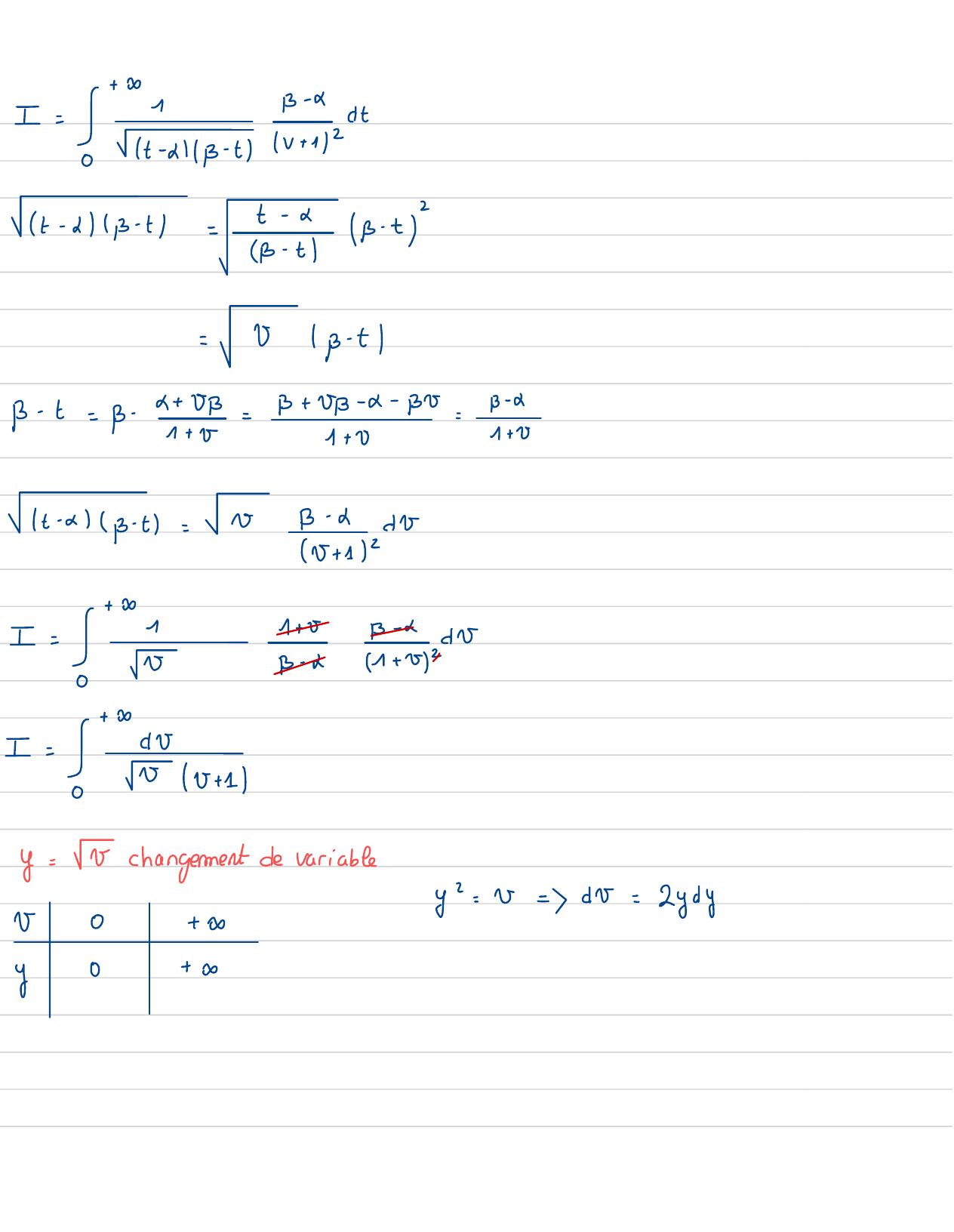
Page 19 : Exercice 4 :I= Pdtarea&, BtR, d BaIt-2 p- tf continueser 32 , BLact Poct- 2,p- t0ft, 0, dtBU=t- Gchangement de variableB- trésoudreenfunctionde "t"vB- t=t- x=Up- Ut+ x= t=tv+ 1=Up+ d=t=Bu+ xv+ 1dt= F12dbt2Bv0lim =- firmt- d=- Bj2=+3--tt- Bt↳B--t↳t
Page 20 : I= +1B -Cdt0It -alB-tIV +1/2t- B- t=t-cB- tB- t2-0p- t1B- t= B-c + 5p=B+ U- c- B=B- G1+ 01+ V1+ VIt-dB- t=NB- ddO5 + 12I=11+ 0B-d dVSvB- x1+ 020+I= SdVvv +10y=v changement de variabley2= v=dv= 2ydyv0+ Ay0+
Page 21 : I =2ydy=2+1=2 CArctanly=yy2+ 12 firm Arctanly -Arctan0=2x +=πy-+ xExercice 5:+ 0t=1- exp-1d2 1= é+ 1bxen= 101- e- 1xfx= x1- exp- 10continuesur J0 , +09if fant étudier fxdx, 9xdx ,Voisinage deO:f= 1- exp -1xx0=fxx= fxdconverge si -41=d- 1
Page 22 : Voisinage de + 0 :u=1Xx+ 31- exp-1= 1- ex=1- 11+ u+ 0a=- u+ 0ac- 42afx+yxx=x1=xxfx+=1x42- d+= fxdconverge55i 1 -11=&-12= Packconverge si -1-125-sic-inscontinueser e112
Page 23 : Voisinage deO:1x23xfx=11- x43x- 07= Ifxdconvergecar ? 1RiemannVoisinage de 1:x- 1x fx=11x2/3x -1CV Rienann1-x43= xcconvergecar1CVfx=1-12Donc1=fxcconverge6y= 1 -j=-y3= 2- 15 = ! -Tee-sy= Yx=1- xy3= xy3- y3x= x=1+ y3/x= y3=x=ys
Page 24 : by=dx= Mes, 3=x+ y3/247x01y0+5=yx=4 33=3y3+ 1= y+ 1y2-y+ 11y3+ 1= yi 1+by+ cyz- y+ 1y+ 1=xyz- y+ 1=a+by+ cy+ xyz- y+ 1ba= 1-ayy=-y+ 1y+ z+by+ cyy2- y+ 1y+ 0=0=a+ bb=-a=-=
Page 25 : y=0=-1=a+ c=7=1- 1= 21:++ 5121- y+ 2t 2y2- y+ 14 y=12y- 4- 1+10y+1- 2y2- y+ 1dy+13=Sy122-"y+ 1-2yx- y+14y0+3c+=1- 28y+ 1ly !- Iy- y+14y0+++2y- 13= y14y- 2yz- 8+ 1dy +- 2yr- y+=4 y0een+ 8=0+= y148:Set-enct alone 14:fy+11!0+S·yI14y= 9ny+ 1
Page 26 : ++- I4Iy+ 148= 24y+ 1 4y=-enlyz- y+11!!- !· = +148= /eny+1- Inlyr-y+1138=tr,2 +=y2yxyyy= 1+ 12I-firm= fr1=0y y+3- 3- 32 yy+=4=-3 xy+= 2. y+ 1= 2y-1= /y- 1 doncSant: Iarctanici =+l-SEssarctan arctant
Page 27 : firm- Tt1 055fi5=0+= EJ-x+ 02t=2y- 1Gin5= fin eny+ 1- 1 y- y+1+ Barctans-Barcton8=- 55= s6+ByT↑+ 4-I-3x2 -x3335535
Page 28 : I= 35+ 14y=3x3+ y:! +3Si= - g,=- 2y2y+ 14- 3/y+=Iny- y+ 1+ 2/yy+ 1y y + 1-y- 1+ 2= - + 1Syst: " page= " grenI= ny+ 1- 1nyx-y+ 1 +ArtanIcy= en y+ 5 Arctan 5= 3= Gmy- I0
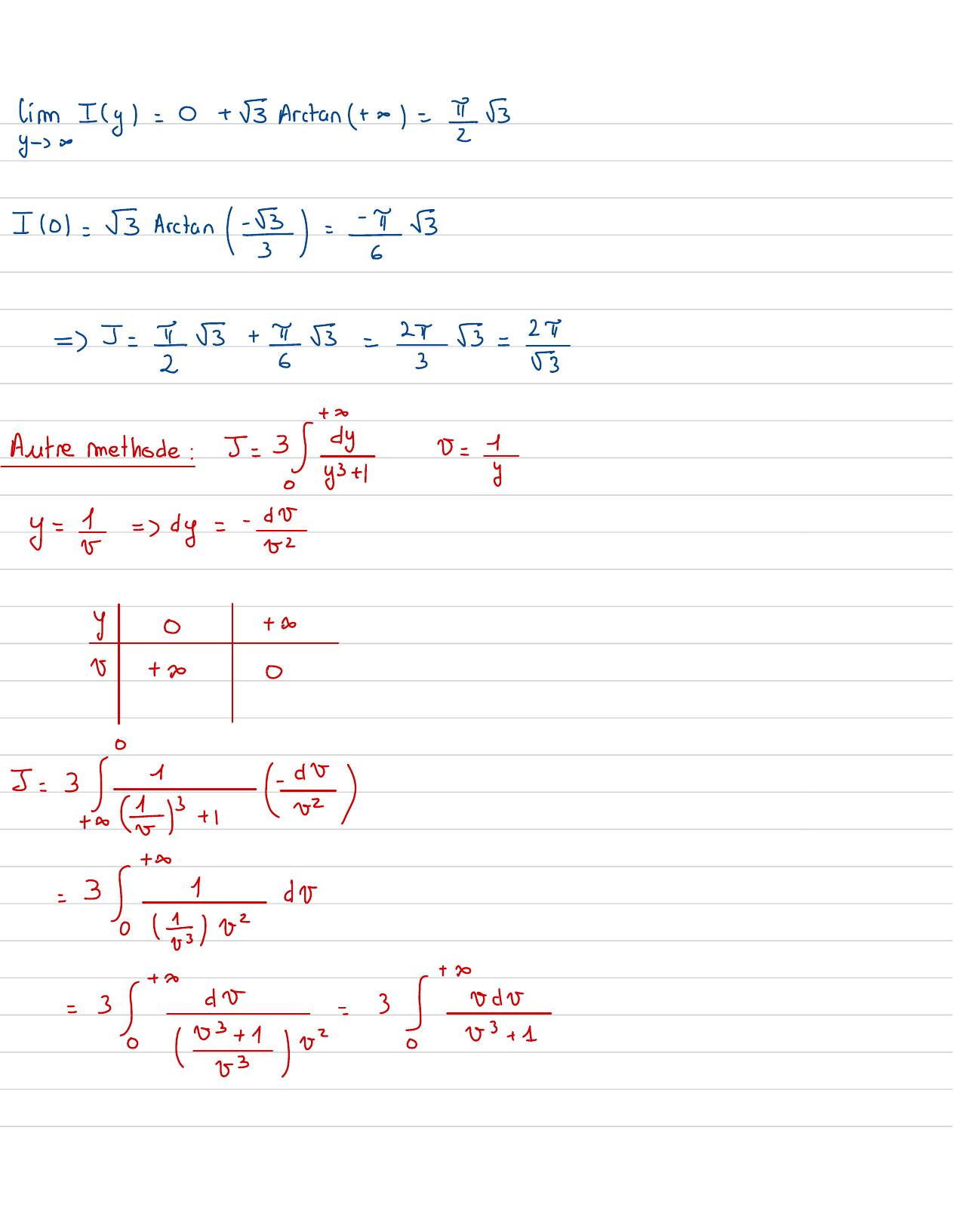
Page 29 : lim Iy=0+ 55 Arctan+01 =I 101= 55 Arctan= :5=5= 155+ 155= 25= 2Autremethode:PSEe53I0+ Av+ yD5=- 2 -3.un-3/a=3. A
Page 30 : +C25=5+ 5= 32 1+ jae00= 3z+ 11d12 + 122 - 2+ 122 - 2+ 1=3xArctan2-Arctan- -25= 2532+ 4= 455=J = 23Exercice 6 :I= oetft= frit0continueser 51: etAn voisinage de +o:1+to thflt Is frent=fait0Et
Page 31 : = !intconverge etstdtmême nature fnt"dti=!tft=ft0et continuesur 30 : 13tft 0et continuesur1 ; +0Sgitat.stat1/4Auvoisinage de 0: 1, tft= t fnt= c= ftdt convergeAn voisinage de +0 :ft-1019nt1/3tt3+ 1+ItI- Lenstia!sticonvergesi1IG= 1,B 1d'après Bertrand gitat diverge= ↳stat diverge
Page 32 : Exercice 7:I= +inklda, nEIRE1bABELftgtdt,Ca , b,aICbETR ftpositive ,decroissanteet ft0t-b 5k0, C,-a , bftgtdtconvergeCeI+Bindeno6fx= Six0sit 30, 17On doit etudierlack .laAn voisinage de 0:Sin x=fx=n- 1
Page 33 : I Flickconvergess:n-1 1= n21An voisinage de +0:U=xn·fx=Sin 1comme 0onaUliIdecroissanteet UIKI,10, Ulik0 Sar21 :+ 0F2, 1PsinscId=cosl=E=cosB1+1 cosd1= 2D'apres Abel fx diconverge= !+fxdconverge ,0 12+ D SdeLE Icosfx=Cosx0continue sur J0, 3x+ 36 qS fxck1xIAn voisinage de 0:Cos x = 1fx=
Page 34 : =fxcconverge si 1Auvoisinage de+ b : Mx=fx= cosxux0 ,,+ 3, sid0= Ui decroissanteet UIx0xx+ xDSBosco Circ=sinpl-sinen!guidxconvergesi21 I1 =osk dy= x=x=y, dx=4y2I1= 1+Pussy by of ty=I1converge
Page 35 : I=sin d2y= x=x=y, dx=4y2+ XIz= 1 6sinyby0L 12120 finieventaire convergentCV=Izconverge= +e Is6sinkchIddey= x=x=44, dx= 1yk-dyysi d 0x0+ Dy0+ 0+ DIs=!deconvergesi01- 172 1-1-1Ld1Si t LOx0+ 0yt 00
Page 36 : I=- 4inbyconvergesi 021-11-12 7- 1=d- 1= sing"dicconvergesi -1ach 1Exercice 8 :I =Ices: Befaience
Page 37 : TD 2:Exercice 1 :I= édtftldt= tet0continuesur 0 , +0Auvoisinage de +o: ft= titit =t -0Id'AprèsRiermannconvergeI PPI= t etl=t2li= 2t-- t0v= étv=eIlt=- te t+ 2 tedton a applique IPP2 foisle= tli=1- t- tv=ev=- eIlt=- tet+ 2- tét+etdt=- tet- ztet- etS ét et=lim Ilt-I 101t-3
Page 38 : -i-tit -=0+ 2=2I= t et dtbr=2tle = 2a=+2x- - ③étapes-X=signeIpp double- t- - t"= étv =- e-N=C10②I =- tét -2tét+2et=- tit- 2tet- cet215=efx=fxcontinuesur30 , 1M1, +0x2- 1fx30. 1u1,+ 02, fx01fxdx, fxcx. fxdx, gx1cx⑧1212An voisinage de0:frx1-j-1frx"- 1x- 30
Page 39 : fx=- fx6 42nxdx=xfx- x1/2=2-x= In2- I!"JuldConvergeAutre methode :1/2InxOx"- 1x-0d'après Rienann. sdconvergeAuvoisinage de 1:x- 1fxfx= firInx-finn1/x- 1x -1x2- 1x - 12x2= f prolongeablepar continuitéen 1= grake. fx deconvergent
Page 40 : Auvoisinage de +o :fx11d23/23/2xfrxxfx=Tofr0x2- 1x -+ x= Ti desconvergeExercice 2 :RE IRa- I= Tok- =cost dtftcontinuesur 1 , +021ft=+4- 1cost+==+ntconverge si-R11=k0=ftdtconvergesi Kodonc itatabsolument convergentepour ko
Page 41 : b-J=+ 3 tsin/tdtdéfiniepour KoSEif faut etudier convergencean bien definieu= +kv=k+ k- 1v=Sin tv=- cOSt+ A5= S- tcos1tl?+/ trfcosst dtSiko,Ek-1 costlatconvergeSikL0, im tcost=imcost=-t-+ 3-R=J convergek= S sint" dtx=t2=t=⑮c=dt=2xk= S Esindx2x=Scien singa / dad'aprèsaona kconvergente
Page 42 : Exercice 3: IcI= SfnsinldxMontrer quel cigenteau chi etSuit fx=Insins0continuesur30, Auvoisinage de0:Sin xI =xcomposition d'équivalence que=ensinxfnxavece"etfnxAvec DL: ensinx= fnx-+ 0 1=frx+ n1- -+ 0xfrsinx1=1+fr 1- =+ 0xYfnxfrxn1- 2+ 0xfrxx - 00In sinxnxenxck= xfx- x=-- imxenx- x
Page 43 : =n -= fxdconverge1I =+cos daI= 1 en2 sin2xdeI=ensinschlay= L- xx0+2x= - yyYz0E dx=-byI= ensin-fll-sin =- y= cosy =encoscyldy
Page 44 : 1Sin 2x = 2 sin x cosxfnsin 2x=fnsinx+fncosxSens sinIId -sinc+encossl d6= I+ I= 2I=I= 1 a = sinx/da+ D= I=/ +sinx/dx0on sait que: I=/In 1sin 2x/dx20-Sfr2+ fnsin2xdx2I=0= t+ 1 ensin d2x=vdx= = br
Page 45 : x0280I21=- Ien2+ 1ensinede=-en 2+ 1ensinedu -nssincaldeIIT=-fr2+ 1 I+ 1 ensincaldeIl=π - v21=F-+2+ 1 ensin-rl= = =-2+ 1 sintIla= I- In2=I=-n2
Page 46 : on remplacedans l'equation initiale2I= =en2+/ nsin2xIc=21= I+ sin2x de= I = ensinzaExercice 4:I=S+ 3e xtde i2pbenO eten+ yDftcontinuesur 30 ;+ 3Si0, pas defen oSfstic . itctAuvoisinage de +y:, t"ft=++ 2ett4.a-R= it dtconvergeati-tAn voisinage de0:ft-&t- 0+th1ft==C1dt6 -convergesa :-21
Page 47 : = Sftldtconvergentesias -1+ 3= Sftldtconvergentesias -1I= ! E-1 etdtfonction gama , Fadefiniesi L-17-1done&40 RIR +- Gammab fx+ 1, /xIf faut trouver me relationfx+ 1 existe six + 1 0/xexistesixc0On doittrouverune relationentre /x etfx+ 1quand 0x + 1=rettU= EW = etU= xtU=-et+20x+ 1=- it +xt-= edtfirm t=O parcroissance comparéeFactIt -+ Dte
Page 48 : fir Een=0car x0seut lesortir de l'integratecar elle est enfunction detor1+fx+ 1=0+ x f- 1 et dtfx+ 1= xfx six70Ant N , fx+ nfx + n= fx+ n- 1+ 1=x+n- 1fx+n- 1=x+ n- 1x+ n- 2fx+ n-2!=x + n- 1x+ n- 2x+ n- 3... xfx3Calculer/ 11 , /n+ 19111:.etdt=- ét=e-lin et=1t - 12f2= f1+ 1=1xf1=1=1!f31:f2+ 1=2xf1=2=2!f4=973+ 1=3xf3=3x 2+ 1=3 !
Page 49 : fn+ 1= nfn=nn- 1n- 1= nn- 1n- 2n- 3...x 2f2=n !4 gx= fnfxa- yx+ 1= gx+ fnxgx+ 1= enfx+ 1=fnxx=frx+ fnfx= yx+ enxb-Fn, 2gx+ n- gx= gx+ fx+fx+ k- fnryx+ n= nfx+ nde2b=frx+ n- 1x+ n- 2--- xfx-"enx+ k+ enfxR= 0= gx+x+ xyx+ n- gx= enx +enx+ k1
Page 50 : gn=en fn= fnn-1! =encm·= gn-enm21+ 2gx+ n- gx= gn+ enx+en+- frrSx= 2jEx-1-0,t= 0fx= j+x-1+dt, t=02dt=2udotD+ 2U0+x= 1 92p=02udo=2x 2+ 1jd=2 je- 1d
Page 51 : blx=4↓2Calculer / 2 = 2redo=2=id+ cn+ 1= n- zv- z... !2n+ 1= 02+ nn +n= x- n+ 1x+ n- 2... xfnSn +t= +n- 17+ n- 27+ n- 3.../2=n- zn- =r-...A=n- En-...π-2n-12n-32n-51 ....222↑2n-172n-2n-31 In-4 2n-512n-6...2x1=22n-c2n-42n-61... x
Page 52 : ⑮In-11!I20- 12n-12n-2...x 2x1T2n-1 !-2n-22n-1!Exercice:Soita , beIRB: RR , b1 Bia , b=="- t dt!1Pour quelles valeurs de a, b, Bla , b existe ?ft= ta-1- tb- 1 0continue 30. 121/2↳fltdt ,/fltAAuvoisinage de 0: fitdtconverge si-a+ 11=as0- b+ 1Auvoisinage de 1:1 -tft=+4- 711t1= Sfltdtconvergesi-b+ 1 =112=b0
Page 53 : =B G, b existeSia, b - /R +B: R 2 IRfonction Beta21 Fa, b0 , a , b= Bb , aBla, b= a=1- tb-1 dtV=1- t=t=1- v, dt=- bvt01v10Ba , b= 191- 0- 1Ob- 1- dv-b- 1c- 1SO1- 0dV= Bb , a3CalculerBla+ 1, ben fonction dea , ba , b 0
Page 54 : Ba+ 1, b=+ 1- tb- 1dtIPP=b=tav=1- tb- 1 aa+ 1, b=- =t1-t+ 2a+1- t+ !tcommea, b0, t" 1-t1=0=Ba+ 1, b= 2+ -t 1- tdt7-=5=+1- +P dt- 2+1- tb- 1 d= 8Ba, b- = Ba+ 1, b1+ 3Ba+ 1, b= a, bBa+ 1 i b= y aBa, b4Calculer pa , b+ 1 et trouverLa relation entrea , b+ 1, Ba+1 , b ,Ba , bBa, b+ 1+ Ba+ 1, b= atBa, b= pa , b
Page 55 : Exercice: Etudier fa nature de l'intégrate suivante:1= =2 +ft= = = +0continue 1 :+ xAn voisinage de to : 11en1t+ 2+ 1+ 3+2-12I10tt+ y3/21+ x= tftx0=ftdconvergetx+ 3+21 I= /tentdt0 t+ 112ft=tent0et continue 30 , 1ft0et continue sur 1 :+ 32t + 112Sizet t
Page 56 : Auvoisinage de 0:imft=fimtent=8t- 0t2+ 12f est prolongeable parcontinuitéen 0↓stdtconvergeAn voisinage de +y : tft= Eentt2+ 132Six= 2 1, tft= Est-fattt3+ I+S fltdtconverge+= !fitdtconvergeCalculer I= S= enctatchangement de variablet= 172+ 120dt=-do22t0+ 0O+ I⑧
Page 57 : I= 0409n1/wto/3401+ 112 - I- f+frv2 d-03/02S+fr88br=- I--002+ 1/2= I=- I=721=0=7 I=0
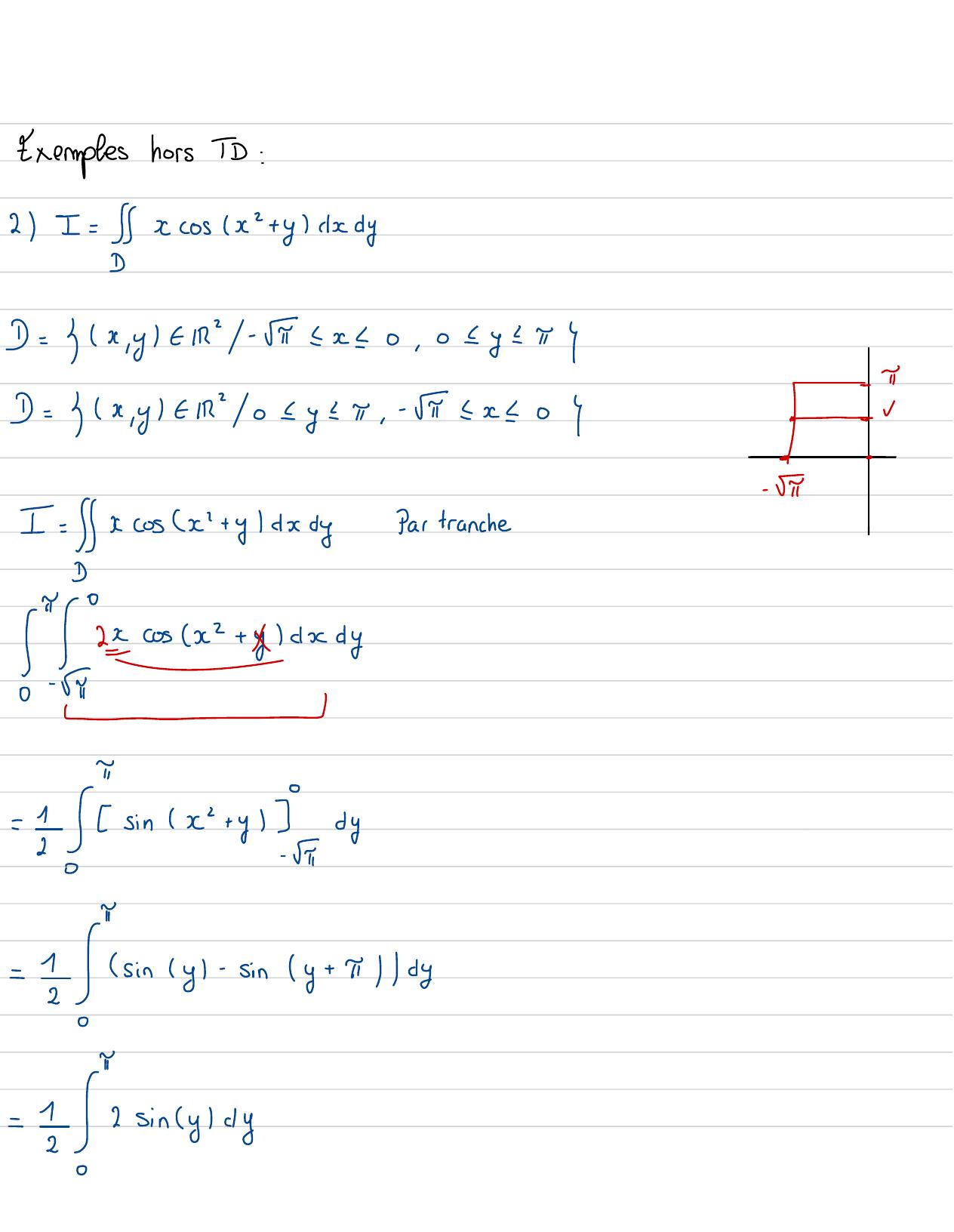
Page 58 : Exempleshors TD:2 I =xcosx+yckdyD= Gx ,yf2- 5 =x-0, 02y2π D= Gx ,yf02y2π,- =x-07I-.Ixcosc' +yldxdyPartranchecusx2+ ydxyT--siny=sincyl-siny+ 51dy=sincyldy!
Page 59 : =-cosyl"= 10sy=1+ 1=23 Ifx+ ydxyD= x ,ytR02y=1- x, 02x11y=1- 42, x=0, y= 1y=0= 7= 4=7x= 12Integration par bille jeI=gldy!"Cy+ 1yrs-sion remplace y parOtout s'annule1=x1-+1 - dx-x- c+ 1- 1x+ x"
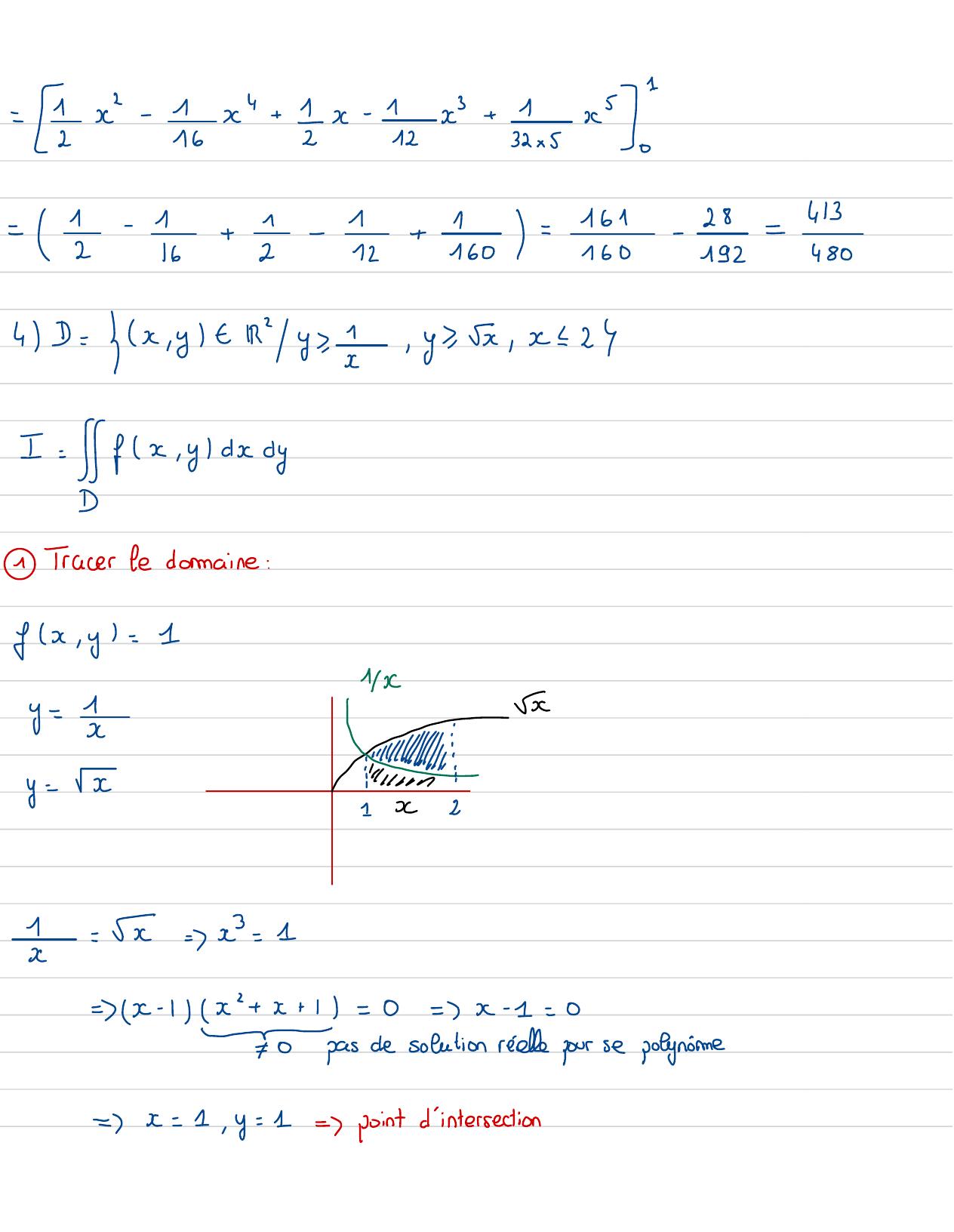
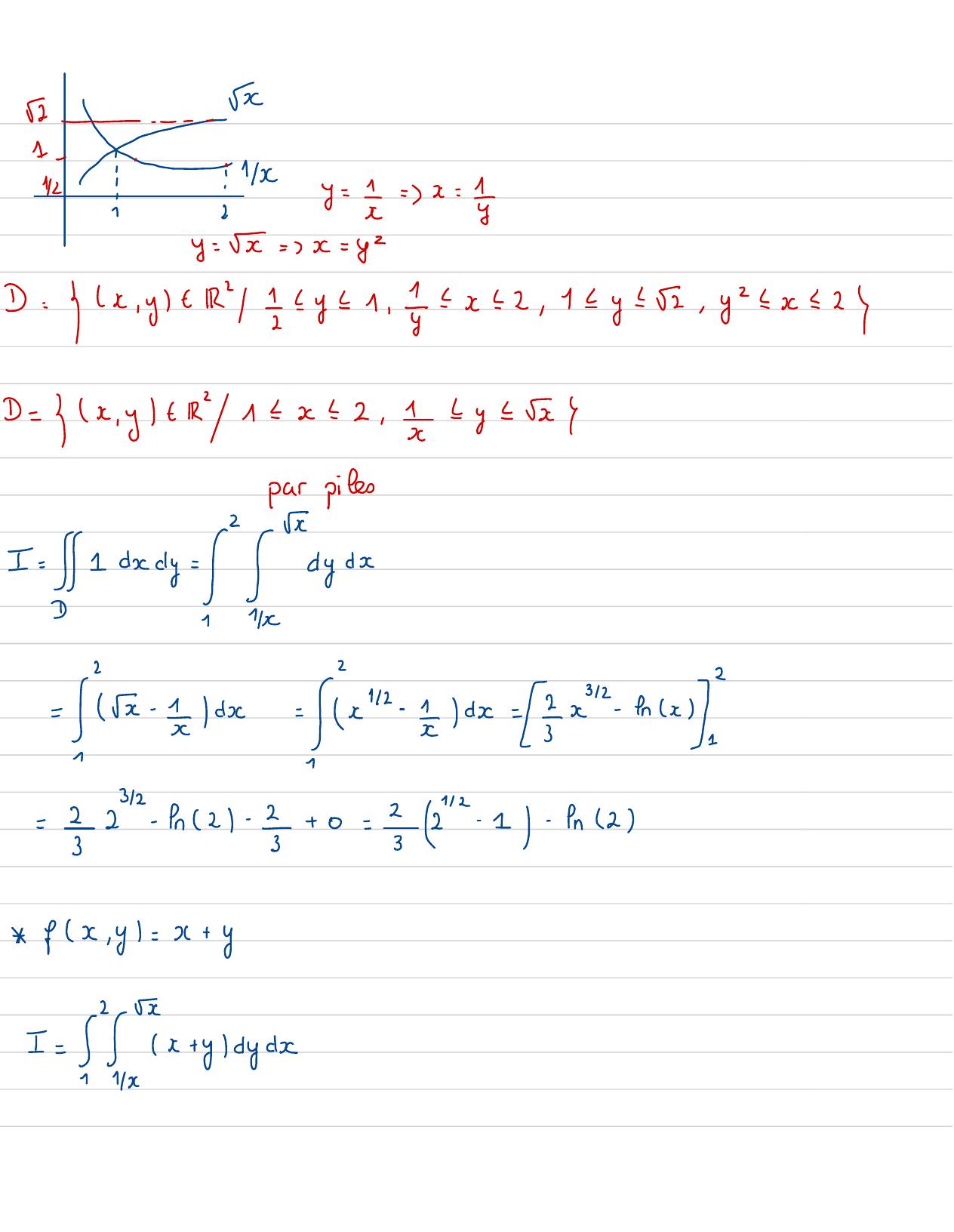
Page 60 : 1=x- 1x"+ 22x- 12+ 32x522jI0=2- i+ 21+ iso= 128-413--121924804C= x,yt Ry,,, y, x , x ! 2I= fx, ydxdyTracer Le domaine:fx, y= 1y= 3 :!IliIllurny=x1x2i= x=xx= 1= x- 1x+x+ 1=0= x- 1=0-=pas de solution riette pour se polynime=x= 1, y= 1= point d'intersection
Page 61 : Eny= 5=x= Gy= 5= xx= yzD= yx, ytRYzy=1, z2x22, 11y20, y2 2x 2D= 3x, yt1=x= 2, ty= 5II== ccdy = Cette-is-la/Ta ed=/Ex-en x=22- 2- 2+0= 2"- 1- n2 fx, y= x+yI=x+ y1dyd
Page 62 : =2y+ =y y=xx+ 2x- 1+ 2dx=Y+ Ex- 24- =dx22-I--12x=22x+ 1+ 4-2- + 4+ z- 7=I2+- 1- ERevision :+ bEx2: I=tcosCtdtBEIR!1 Iabsolument convergentesi koft= -- costcontinue 1,+ 02ft=+Pcost= +==1+1- R
Page 63 : SVs:1- Rh1-- R0=Pft/dtconvergesi KO= Adtabsolument convergentesi ko215= Ensinctldtest définiepour botsinCt! ImAbsCV=CVAbsCU&CU↳CV si R-1, donCrce -1- -mais ce 0-1on suit pasDoncIPP: /e= tke=k+k- 1v=sinCtV=-cost+5= tYcost10+ rt k- +cost at=cos11-imtcostIt costatS
Page 64 : SIRcostdtcuSi201firm t cost:SI -R 0t- -3pa e ek=00RCO=J= cus1+ r-1 costldtcr siRO!2H =sin dtt= x0=t= xet1+dt=cxx1+25H= 1 Éry" sincl Il=--2 sind d=1sinsh dR=- 140=HcV
Page 65 : Exercice 5:5=!"fx=1-x /1370et continuesur30 : 121Ane voisinagede0:x431-x136 =-2x-43fx=131- x113x- 01= fx=, 23mais EsCVcar-2/361↓Sageshacu21Am voisinagede 1:2= x- afx-0x - G621 , 2 1dV21,x- 11x - a&F 0,3L+ - DV↓=- 1ona prisx-1car il fart que sa soit positifet 1-c pas positif
Page 66 : d=-11-x-113fx= 213x -=1=franccu='gislacvI= ent'+dtft= fr+10continueSar51.+ An voisinage+ : 1+ 44nt+ 1 1, 000t2x2- 3 +nt+ 1t2- d2- 20- x- 1=72- 21=076- 2- 1=27213/2G=&tfrt+ 1=ent+ 102E+-+ 3
Page 67 : - gitictcu
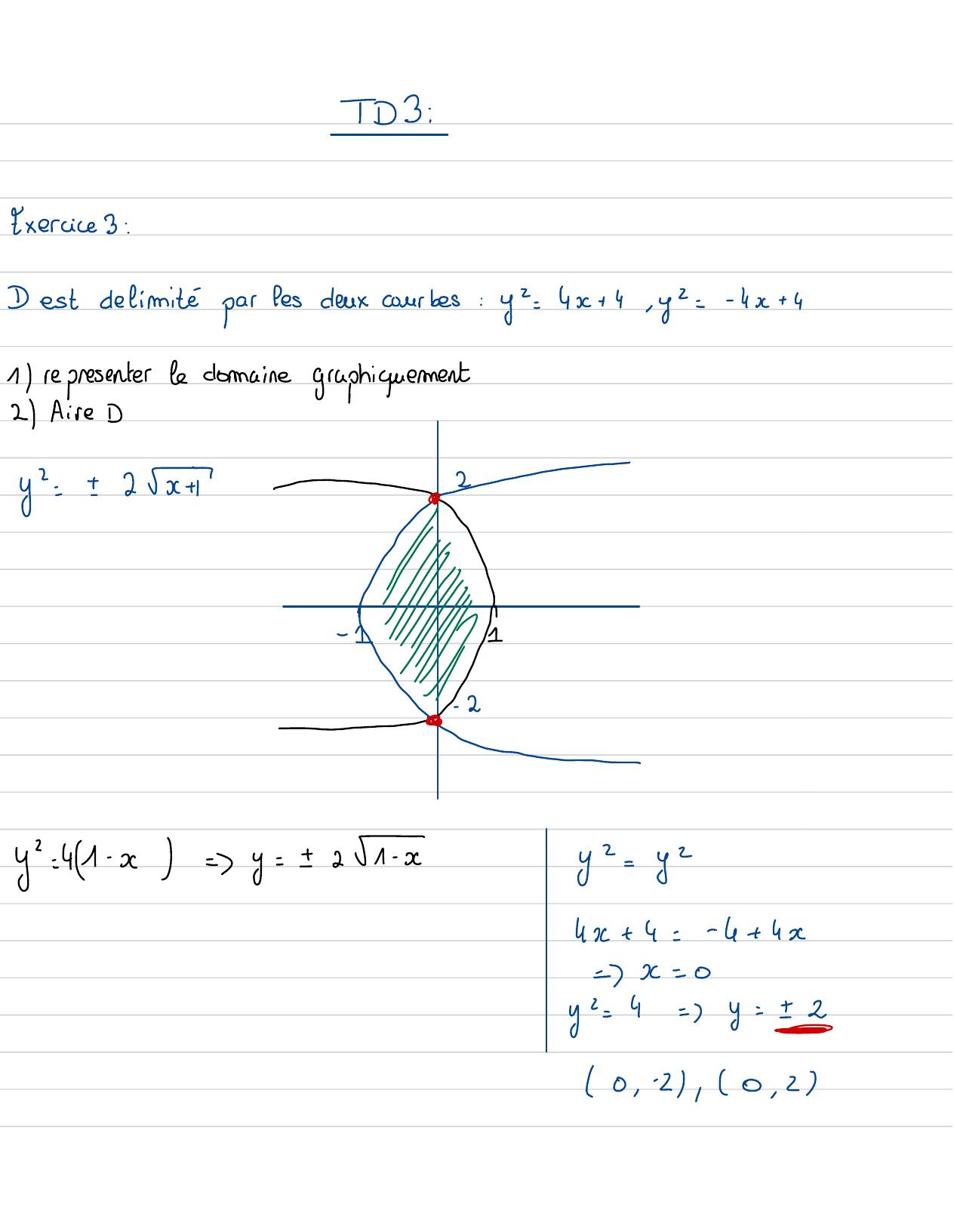
Page 68 : TDY :Exercice 3 :Destdelimitéparlesdeux courbes: y2=4x+4, y2=- 4x+ 41 representerle domaine graphiquement2 Aire Dy==2-⑧⑰⑧y= 471- x=y== auxy2= yz4x+ 4=- 4+ 4x=x=0yc=4= -y -0 , -2 , 0 , 2
Page 69 : AireD= S 1dxdyDpar tranchesD= Gx, ytR2- 22y22,2x2Grifi etD= yx, yfRY- 2xyz2, 342x= 4-Ar Frao et=I14- ydy= 154y- zy32
Page 70 : = -42+ 2- j23+ 23=3316- 516= 2 I= xydxdyScycody=04--5= 3
Page 71 : Rattraper Armers.Exercice 5 :b Calculerto volurede l'effiP22xty2+2=1 a, b, x0abCx=rasint cos 0r 0y=rb sint sin 101Stt 0, 42=rC cost0 - 20 , 243D= x, y, x + 3a+ 18+ == 1x, y, 2 -D t- 0 , T, 0 -20, 242rasintcos 02rbsintsin 0+recost"1GItbC= rsint 20510+ r2 sin 0 +r cost= 1= rsin"t cos 01 +sin 0+ rcost= 1 r1, te 0 , 4, 0 t0 , 25
Page 72 : r , +, 0t0 , 1 x0, 4 x 0, 24=x=rasint cos 0y=rb sint sin 1012=rC costasin t cos 01arcoslt/cosa- arsint sin 0J r , t, 0=bsinCtIsincalbrcostlsincalbr sin t cos /01II c cost-resint0facteur commun=ccostwab sint cos/t cos" Ol+ rab cost sin /t Sin /01+ resint /abr sint cos 0- abr sint sin 101-barcostist+ aborsint Sit=abor sintLe jacobien-aber sintvib1= 1dxdyd=1 aber sint dr alt da
Page 73 : 2π-aberdrxsinstat /de!=abc = r3- x -costl"25=abc 24 x2=abc4π3Volume sphere= 4 asia= b =question supplementaire:Calculerle volumede la sphère définie+y+z= aa0x+y+ z= aa70dx dy d2-221 2+ 15+2+1D rtzabe rsinst dt dr dO= abe r+ 1Sinst dt dr da
Page 74 : =abe?ux sinstidt o!!=abe -dr x-coslt!xCa=44 abc r-Arctan rJ=44 abc 1-Arctan 11parabolee4 Calcuter cycedyoest la partie délimitée par y= c, x= y2y=x21---y=x⑧y b-01=x,ye0yy2xSecyclady=/Yeyclocky=2 dady= !y-ydy
Page 75 : =2y2- y5dy= 15y3-- =ys3!=215- 5= 72Exercices: I= 11+ x+ y+ z 13n= x, y, z/f1R3x , y, z, 0,x+ y+ z11↑12x+y+ z= 1-1---0x, y=z=0=7x= 10MICKCj3y1 , 0, 01-M0y ,2= x=0= 7y= 10, 1 , 0x02=y= x=72= 10, 0. 1l'intersection dex + y+2=1,0x42= 0=x+ y= 1ryC= x,yt10 x 1, 02y= 1- xDy= 1- xx+y= 1n =x, y, z/f-Rx , ytD , 0221- x- y 4=x, y, z/f1R30x1, 02y21- x, 021- x-y
Page 76 : I = je estytysd2 dy c eI= Je inxty+ ayd=-E-sybyd=- !+ ixx+ydx= 2 + 1 x+ =- I+x4x= I !- 1x- 4+xdx=-8- fx-- 1+x2= =8- 8- 12=- - 42
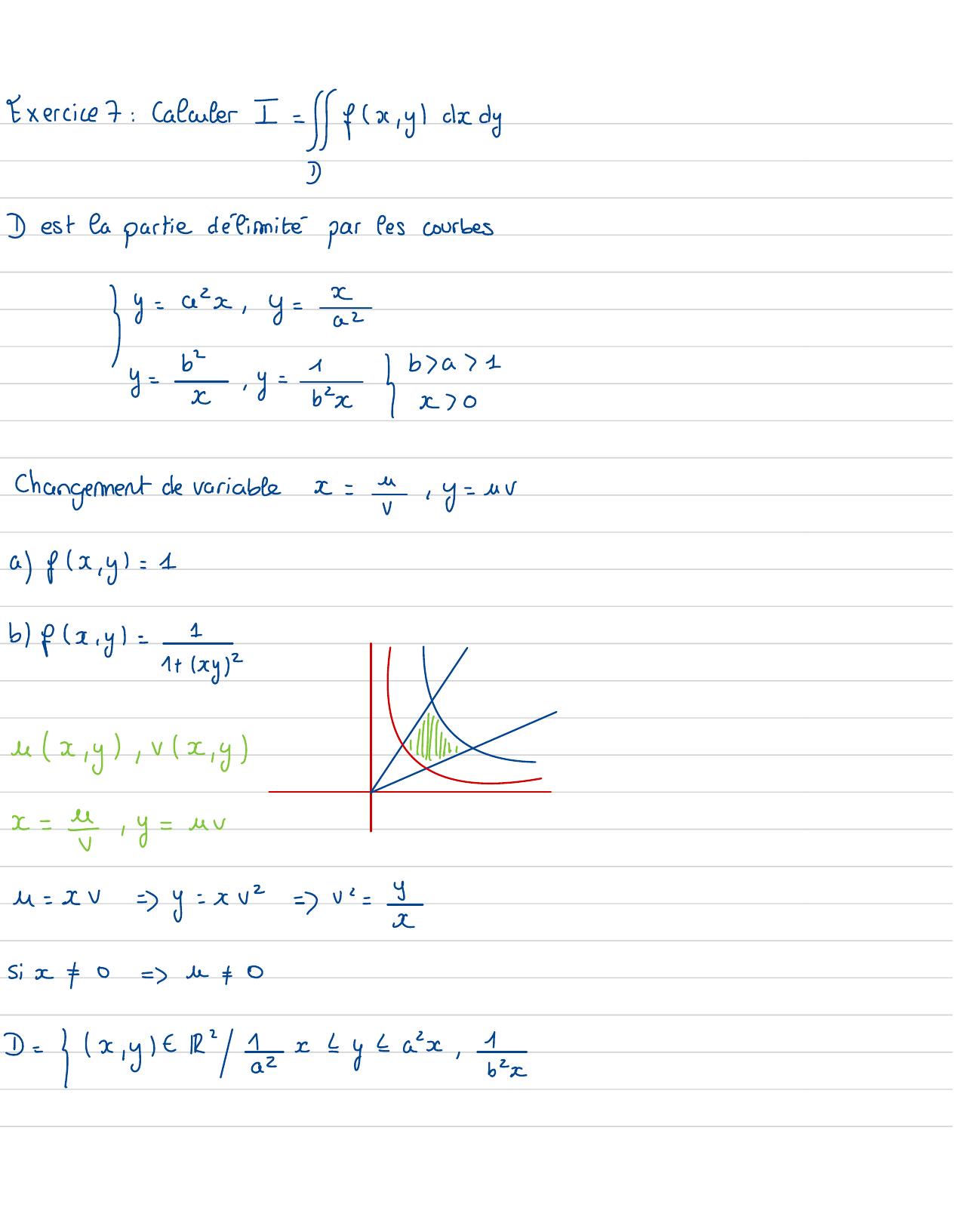
Page 77 : Exercicet:Calculer I=fx, yadyClest la partie délimitéparlescourbesIy= ax,y=2y=b2ba 1x: y= bxxh3270changementde variablex=Y, y= avafx , y= 1b fx, y=1 + Pyux,y, vx , yIIIIIIIx= M, y=avu= xv=y= xv2=v=Y32Six+0=b+0D= x,yt -22xyza, x
Page 78 : Exercice: I=x -ycdyD= x,yex+yx, 1, 15+1-yx-1x+y= 1,1x+1- y= 1y=1-xy= 1- x=1- 25+ x=y =1- y= 1-1x=1- y= - 1x2=1+ 1- x- 25-1- 32=2-x- 251-xy=-1+ x+ 2x=Pointd'intersection:11=yz=1- 25+ x=- 1+ x+ 2Tx=2- 25= 251 - x1- 5= r1- xx=0, x= 1y =- 720K 11- 2x+ x- - 1+x+ 2xx=1- 25+ x+ 1- x- 25-1-x=2-255- 20x
Page 79 : Fet 0 ; 12-25- 2x0f=0=x= 12x=Yx0 L f3201/21x If0ft↓-Tf2- 252vXx - 0, 1 on a y =YzD= x,ye0xk,y = =y zIx-y, decdy:"Pix-y"dyde-x-yp=-5//x- y.- x-3d=-=x+ 1- x- 21/0- x- 1+ 2x- xP/dx
Page 80 : =-!1- 21 x+1- 25dx1- 21- x=1- 3x41- x+ 3x21- x42- 81- x32=1- 121- x+ 6/1- x112- 81-x3121- 25=1- 3 x4x+ 3x2x- 8x3I=-+ 2z1x2- 261-x3+ 8,x21x5+ x -+ 6 x2x3- 8x2x512 I=- 31- 6- 4+ 1+ 1- 6+ 4- 2=-1- 2- 1= + 2=2x2= 1Exercise: I= catyzy=e--------b-me-x= Gx,yf2a2x + y= b/a111, !
Page 81 : 5r, 0= rx,yD ar2 = bE 0 = 0 , 2π ar -b,0 - 0, 2π- r, 0 - a , bx 0, 25=Ifydy= Yzrarde=24do= co=2enrl?= 259
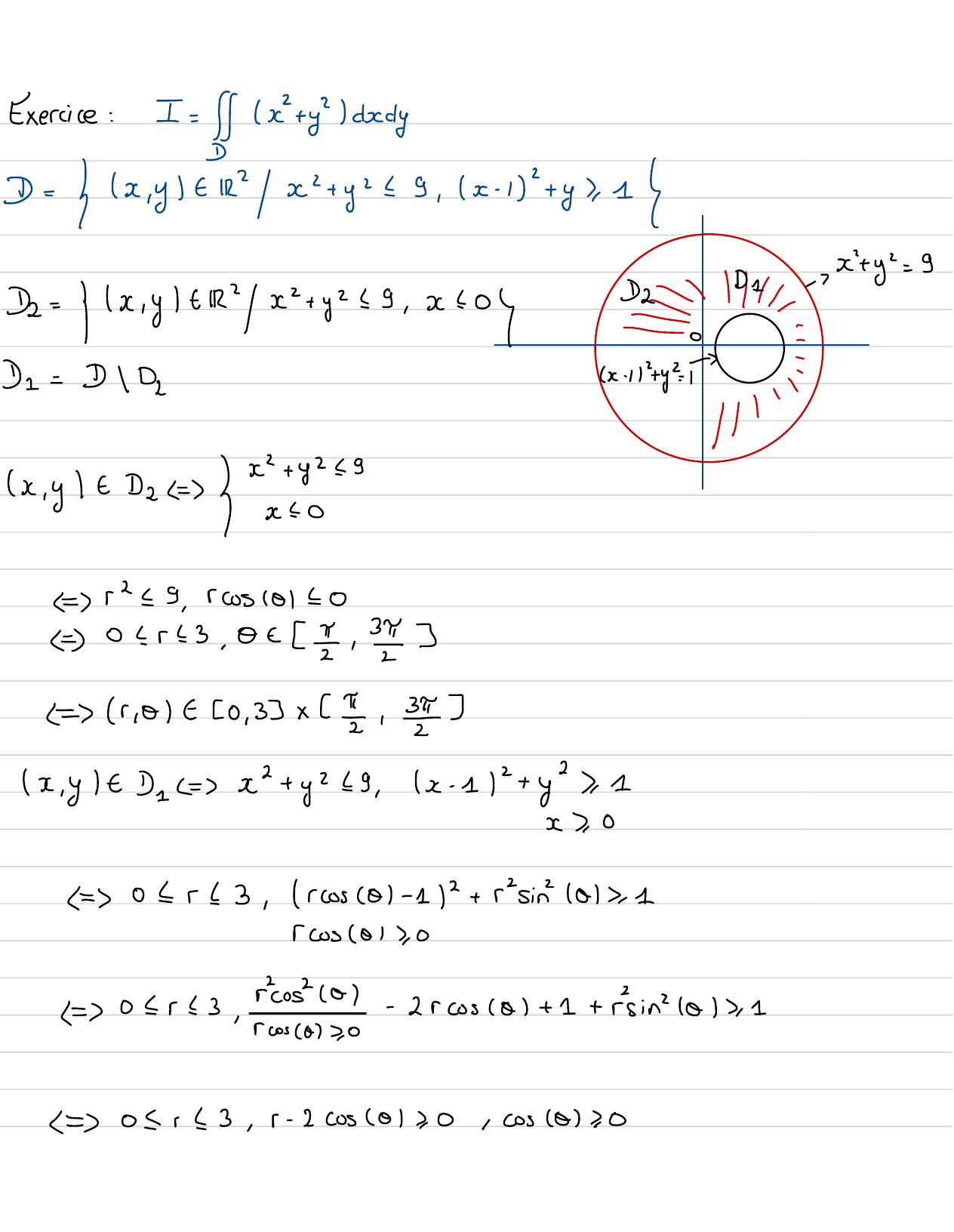
Page 82 : Exercice:I=2x +y"ddyx= Gx,yf2x+ y- -9, x- 1+ y, 1D1- x+y= 92= x,yt/x+ yz29, x0D22 11 1-/-0-D1= DID2x-1 y?IIIx,yt 2=3E= r9,rcus 10 100 r 23, 0 - =, 3 r ,0t20 , 33 x , x ,yt = x+ y229 ,x- 112+ y2, 1x,0= 01 r13,rcoscol-1+ r sin 101, 1rcos 01, 0=0 r1 3,rost 0- 2rcus0 + 1+ rsin" /OK, 1rcos 0, 0= 0r 13,r-2cosOK, 0,cos 00
Page 83 : 04r13, r-2cosOK, 0, 0 t- 2 2cos012 r-3, 0t- , r , 01 - 2cos0 , 33 x2-2, 13=1D= D1UD2D1RD2=0x+ y
Page 84 : Exercice: I= x2+y2 dxdyBD= yx,yf-x2+ yz- 2x= 0x2- 2x+ 1- 1+ y=0- 112+ yz= 110x- 1=rcos 10/y= rsin 0x+ y= r cos0+ r2sin 0=2fx , y= p=rx, yED= rcos" /Ol +r sin 181 -2rcos 020C 0== r-20cos 0 0, rcos 1017, 0E 0r2cos 10, cos 101, 0r ,01 - 20 , 20s10 x-+3=
Page 85 : I= rardo=do2= s-io dalinearisécos" 101cos 301--3cosa+ 4 cos 0Acomaîtresin 301=cos 0=cos 30+ 3 cos1011I= cos130+ 3 coscoll do= 2sin 30 + 3 sinI.=5- 1- 1+ 31+ 1
Page 86 : = 31- 3+ 6=32Icos3x=4 cos x- 3cosxSin 3x=3 sin x -4 sinxI cos x=1+ cos2xSins=1-cos2x22Polaire:J r , 0cylindrique:J r, 0 , 2= rsphérique:5 r , 0, 4= rsin 0ellipoidique:J r , 0 , 4= abersin 0aveca , b, c 70DS année passé:①== x, ye=x2 + y- =3, x+ y, 0y=xIn= 3π- π= 2π= 411II111//1IIIIs/x- a +y-b 2 = r- =
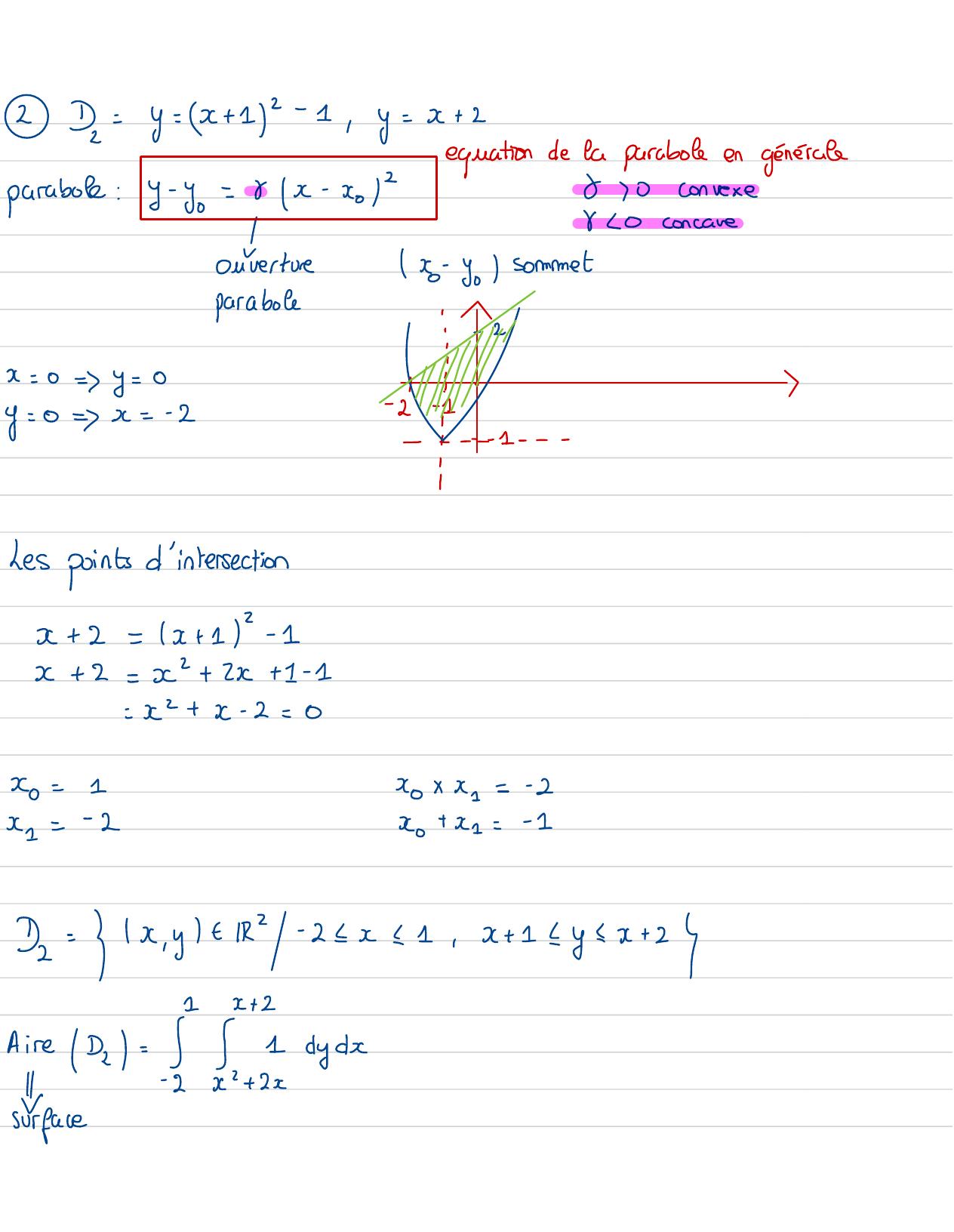
Page 87 : 2=y= + 12- 1,y=x+ 2parabole:y-y= 0x- xo/2eqnationde La paraboleen générale&0convexeULOconcaveoutertreIC- Jol Sommetparabolex=0=7y=0-y= 0=yx=-2- i-------Les points d'intersectionx+ 2= x+1- 1x+ 2= x+ 2x+ 1- 1= x+x- 2=020=10Xk 1=- 2x==- 2x+ x 1=- 12= x, yt 12- 22x 1 1,x +2yxx+21x+ 2AirePa=a Site4surface
Page 88 : - jx+ 2- x- 2x dx-2=Ta+ x-2= 5x+ Ex- xx2=8- 1+4- 1- z- 2=2Ex02: D= x,y - Rx+ yz- 2x101montrer que Dun disquetecentreet b rayon2 I= x+ydxdycos x=Ycos3x+ -cosxx+yz- 2x= 0x- 2x+ 1- 1+ y20x- 1+ y21B1 , 0/ 1x- 112+ yz- 1=0
Page 89 : Exercices: I= entdeIntégratesicar definieen0et en 1rple119n1+ x= 6 y4yS= en 1+xy= en 1+ x1Seilly/de etdxdy=partranchefaut mieux integre par pilesI! dyd=parpilE!c +!ydydx= +1+ xI=-entdx= E
Page 90 : inet edx bydx dydxdyI= -4y+xyx2== 0y-1+xy+x+ 11+xydxdy2x+1y+ 1x2+ 1y+ y2+ 1x=x+ y+ cy+ y2xy2+1x2+ 11+ xyy2+1x+ 11+xyx+ y+ xyx+ y= x+ y1+ xyx+ 1y+ y2+ 1x=x +y1+ xy=x+ yy2+ 1x2+ 11+xyx2+1y2+ 11xxyxi+ 1y2+ 1endeduire que I =In 22 ==1intyy dy
Page 91 : - insiergesdy +interessenges de-Sainte densets" By inter 41y"+ 112=e2.+in= en 21=In 2 ArctanyJ=In 2 Arctan 1- In221= 492I= I2Exercice: I=artyzCycD= x, y , zf13x , y, 0, x+ y225, 02216x =rcos 0r, 0x+ y225ry= rsin 0Of C0, 25xy2=I5r , 0 , 21=r
Page 92 : x, y, 2 EDrcos0 ,Sin /OK, 0Ir22501 2= 6 Ot0, I, 02r= 5,0 226=r , 0 . 2 +20, 5x 0-7x 20 , 63=I= IIS Iwardock=Sir x 40x/a= 1521 In= xyz dxdydzD= x, y , 2 -13x , y, 2, 0. 2+ 3+ 2= =x=arsin 0 cos4& = 0 , 53 , 57, 0y= br sin 01sin 44 t 20 , 252= crcos 0
Page 93 : 12Jr , 0 , 2=abcsin 0les3x , y , z- D = 2x0 r'1 , 05 0,3, 4e0 , 13r , 0 , yt20 , 13 x0 ,23x0 , 13=
Page 94 : Rappel:Wonw=Px,ycx+ px , ydyavecU parametreparx= xt, y= ytbw=PxH+, ytxtdt+ 0xt , ytytdtSS2ab=Px1+, ytxtdt+ 9/xt , yt 1ytdtaExercice 1: I=yI1: x + y 2-ay=0a02C2=0x+ y2- 29y+222x+ y- 2=C23+3- 42=19/2t- 0 , 24xy-42asz=cost9/2- sin t
Page 95 : x=aacostt-0 , 24y=ca+ asintxt =- 2sintyt= acostw=y= dx+ x2dy=221+ sint -sinH dt+a coslt'qcosidt=2- 1+ sintsint +costdt=2sintl-2sint -sin t +costdtsin"t=1-cus 2t1cos"t+ sint= 12=2 sintl-1-cos27 -sint1-cost +cost1-sinthI=2P- sin 1t+cost +cos2t- 1+ sinCtlcost-cost sintdt/
Page 96 : dtcost sintwilas, voe=a0+0+0- 25- 1x0- 2x0=- anI219=32+ 32=1as0,b0x= acost,y= bsintte 0 , 25w= y2dx+x2dy=b sint- asint+ acost1-sint dt=ab- bsint+ bsinlt/cost+ acosIt-acos/t sin'tlldtSw=abYY-bsinCt+bsinIt/cost +acos/t -acosIsint dt!=abbcos/t+asintl-b cost -sin t?= 0
Page 97 : force orthogonale30:/ 2 + B2- 2- 23=0,a , 60- 2+ 1- 1ty2- 2b2P-14- 112- 1+ z- 112- 1=0x=/2- 1+ yjb2- 1=0x=/2+ yjb2= 122l+ B= 1x- a= cost , b= sint+EC0 , 25a
Page 98 : x= a1+ r2cost, y= b1+ =sintcx=- asintdt, y=bcostW=Ydx+ x-dy=b21+ 5 sinstl2 a sint+ a21+costEbcost/dt-ab-bsint 1+5 sint"+ acost /1 +E cost/dt-ab- bsint 1+22 sint +2 sint+ acost1+ 252cost+ 2 cos2t dt-ab2 /acost-bsint +2a cost -2bE sint+ 2acost1-sint+-2bsint1-cos'stl dt-ab 2bacos/t-3bsint-Zacostsint +2b sin t +cost+ av/1+ cos2t1- b5 1-cos2t/dt
Page 99 : w= aba3acost-3bsinlt-2acost sin't2b sinItcost1 +a -bi +avz+ b5cos12tdt=ab2 3asint+ 3bcost-2 sin t -2cost+a- b2t+a + b2 sinkt=abz0+0- 0+0+ a- b2π+ 0/=aba- b4πExo: determiner si les formes differentielles suivantessont fermées,exactes,dansce casles intégrés1W= xydx+ xP9-P-60646XIlIl2x2x2W definiesur IRet IR2 ouvertétoilé=Westexacte
Page 100 : 5 fx ,y tel que dfx, y=w4f= P= xy⑪6=P=x②defx, y= yx+ hy02Sy= x+ hiy= x=hily=0=hy=c -R=fx ,y= x2y+ C2W=y cdx+3en dywaP96P=cy,4,4=2x54w n'est pas ferméeet donc n'estpasexacte
Page 101 : w= wo, y= Podx +00dy0P=6910646X21w= 2+ xdx=-2cbyenonP①8P=43, !=-ex64y3-P64 =ta=W ferme-w est definie surU= RXR --étoilé donc---eexacte.
Page 102 : Exercice 3: TD curviligneF= x- ydxdy= x,yeRx, yx0, x+ ya-D--I-Coordonnées polaire :x=rcos 0r 0J r , 0=ry=rsin 0OEC0, 25x, ytra2,cos0 , sin 101S, 001 r =a, 0 - 0, 2= r, 01 0 , ax0, i=- y dydes= / r3 /cos'0-sin'o/drd
Page 103 : -Jarsino da!=xa"x !sin 120l=Ow= Px,yc+ 0x , ydy 188 -dy=ex- ycbdy6= x , =qx ,y= 2x,Px , y=5y3w =BJD=UABUB2S0aAxo : yoa
Page 104 : AB: x= acoscal0= 0, 4/2y=a sin 05: Etto=a, to4 =01t 1aw= w+w+/wJDOAOBSurOA := t, oct ! ay=0w=ydx+ xdy=I0dt+3x 0= 0w=oOA
Page 105 : SurOB:x= t, oct ! ay=0w=ydx+ xdy=I0dt+3x 0= 0w=oOBAB:c= acos01y=bsin /01w =y3dx+w= = /Sin3 101/-asin 01d0+ cos 0 acos0 do="cos" /01-sin" 101/ do=acos" cal +sin 01 cos" 01 -sin101dO="cos /201 daGw :cosicalam :" sin12a=
Page 106 : Onchoisit68=050= x - y2=qx, y= 1x- yx530= Ia " /7cos" 01 -cos' 01sin' 101/ dOcos" 0=1+ cos202Sin01 :1-cos2012cos" 0=41+cos12,=+ 20sa+ s402cos"0 Sin10= 1 1-cos"01=i1-1+0520/=I1- xs140/w= a"F 2+ 20s0+ =cos40- -11 -cos1481=a" Il ?- 2 sin 0 + sin 1401- f-sin10s
Page 107 : I= xy2+ xdx+ xidysi fermé on prend la primitiveIen fb-fu1 = AcA= 1, 1, c= 2 , 1B= 2,2Icice n'est pas ferme2 cotea calculerAletCB2-B-CA9= Atu cI2I11t = 2Ec== Ei= 4 =211 t = 2w =wire=Sw,w= xy+ xdx+ x-dy=2t dtr= 2=d= t 3 =A2B= /idt=4
Page 108 : =w=3+ 4=7Calculer:Pourw=xy"+ ydx+ xdyAc: w= it+ 11d= zt+1 3= 2B:w=4= w=4+I=6, 5AExercice5: D= x,yt02x, y= 1, x+yx, 1=rtyz ,a dymethode: Green-RienmannC -BAB: !=4 10= =01A
Page 109 : BC:t02711I:? et or:, On00 2w=xyr +,s= w, Sw,So. WABBEGreen. RiemannSy, dedy =ww,w=o =w=0, AYiSE022 1ABW,w=1- t-dt : ItS2+ 1- t2E022 1BC
Page 110 : Sw=!!-+B=fnst- 11+28= 91- 13= 1fnw,w= 1sincolcos0do ,!S1+ 1ECA020 ==sin 201 doz= =sin 201 do=- is COS 1201= 8=I= w= G+ !I= G+ !n
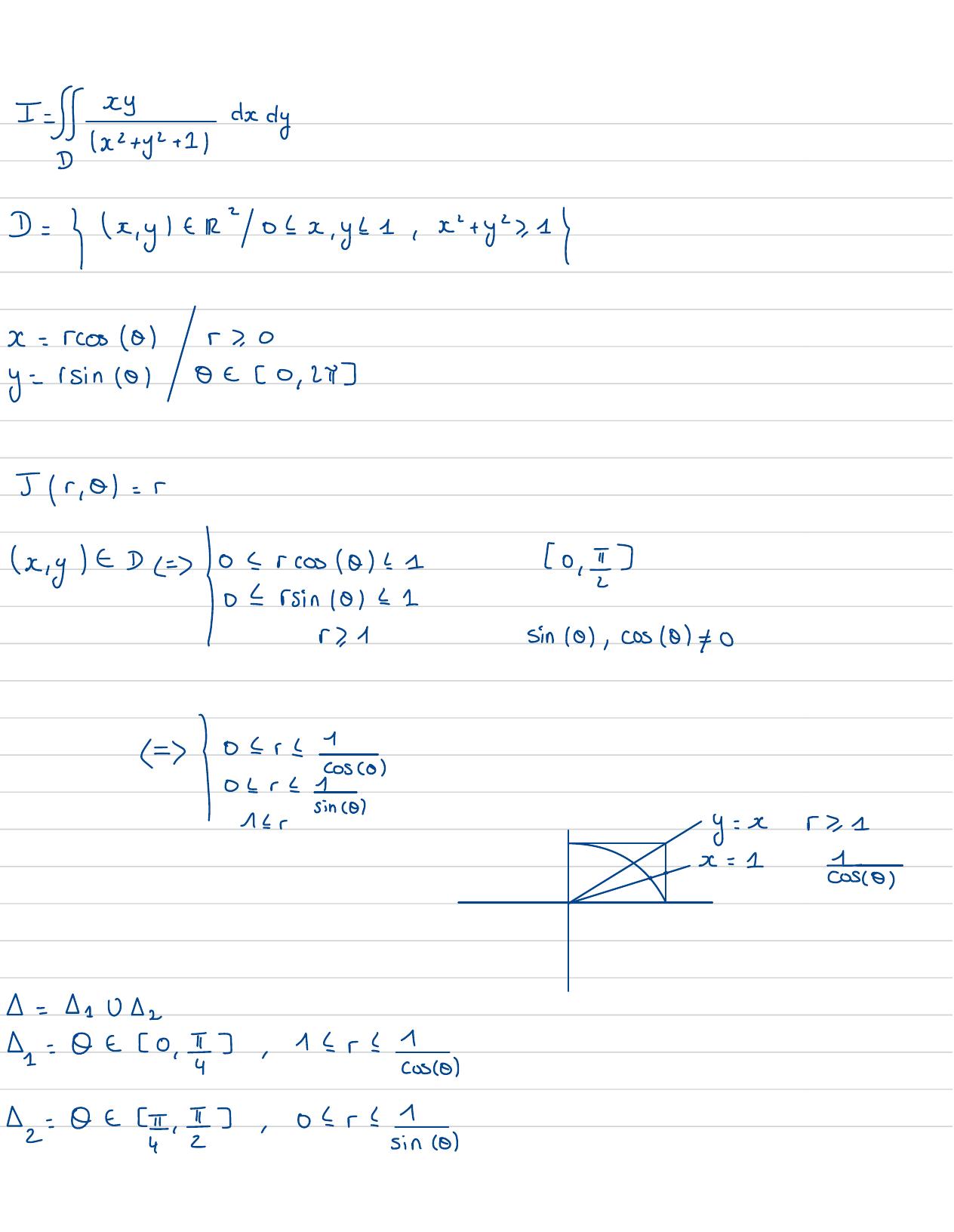
Page 111 : ya +1,dy= yx,ytR02x, y 1, x+ yx, kx=rcos 0rs,0y=rsin 0Oe So , 25Jr , 0=rx ,ytD=0= rcos0 ! =So,I0rsin 10= 1r 1sin 0 ,cos 0 = OE0 r21cos0I0incol1ry=xr 1·.x= 11COSIO,cos02= 0t1 , 13,0 r!14sin 0
Page 112 : S8decdy= 8+18eIintyyddy=-sin20 drda+-12-1sin 20 drda2↑cos012 ! nizon+ 1dau= r + 1C:cercle,:carrée"IlDIfdecdy= fdxcdy
Page 113 : Exercice 4:2= 41... , 97tirer 2 boules⑦:on tireen mme temps2 boulesRemarque:Soit nun ensembleP-1 un ensembledes parties de r, P1/ espace probabilisablep: P1 R+ fonction1 Pr= 121 FA, Be P-2avecARB= &PAUB=PA+ PB1, P1, Pespace probabilisepG=0,PA=1 -PA, PALB= PA- PBProbabilitéconditionnelle:A et B =P1On sait que l'evenement Aa été réaliséPA +0, PABIProbabilité deSachantA.
Page 114 : PpB=PAniPAPA4=0, PB'=1- PABPAB=PAc- PABA et Bsont indépendant siPARB= PA. PBSiPB= PaB+O-finie , At PrPA=Card AProbabilité uniformecardof 1 I1, P2/espace équiprobableXy , x 2P3xy= P333Exercice 4:on tire2 boulesen meme tempstoutestespossibilitésdetirer 2 boulesenmare temps 2A=A 1UAzAr="Avoir2 boules paires"
Page 115 : Az: "Avoir2 boules impaires"CardA=carcA1+cardAz-card A1MAz-=0=card Al+card Azcard A=1= 2 I=cardA= 2+ 2card Ar= 2=6+ 10= 16IR = n2= n! m-RI !0↳ nPA=card Al-16card136Ontireuneboule,onhe l'a remet pas ,on tire la deuxièmeboute-1er bout y'en a 9, le boul gen a 8card 21:9 x8=72toutes les possibilités
Page 116 : card A=card A1+ card AzCard A1=4 x 3= 12card A2: 5x4=20=PA=cardA= Ecard-3On tireuneboule,on la remet avant de tirerta deuxieme boutecardr=92cardA11=42IcardA= 41card A2=524 1-PA=casie ,aExercice 5:⑭4on tirefoisuneburte de cetteboiteen la remettant après avoirnoté sa combeur.An="obtenirlesboulesde2 corfeursau cours de n tirage"
Page 117 : Br" obtenirau plusuneboutenoire"PAn, PlBn, card An, card BnAnc=l'evenement, "les tirages donnent debuntes deneme couleurs"Rr= "leKieme tiragedonneuneboute rouge"Nx="leKieme tiragedonneuneboute noire"Rx, Nxsont indépendant
Page 118 : Exercice 6:10 paires de chaussure toutes differentesOn tire4 chaussure1 la probabilitédeux paires completes?r= 1 ...., 20carb-2= 2iA= l'evenement de tirer deux paires complètescard Al=- 2PA=cardA= 2 =carb-1273232 As="avoirau moinsunepaires"Ar= "Les4chaussures sont differentes"card Ar= I X = on choisit4paires completes paromistes 10 paires it ya Pcas
Page 119 : pour chaquecason choisit 4 chaussuresdeces4paires it ya2 "cascard ALY:2 " ? PA=2 " 414PA1=1- PAr=1-1640= EsEZeie methode :A1=AUBBuoirune serle paine complete"PA1=PA+ PBonchoisitune paire complete it yal ? cas,pour chaque cas ,on choisit2 pairesdifferentes it ya 3 etpour chaquecas, onchoisitchaussures2de deuxpaires differentes , il y a2cascard B= = ? 2=cardA1=card A+ 40 2
Page 120 : =2+ 4012=PA==2+ 40253une paireetmineserle?As"avoirune paireetune seule"As= BPB=cardB= 40296-card n14323Autres je:
Page 121 : 1Demonstration decours:entiers natureln et k tels que1k In,on a :i+ ==8li= ins :=n= 1 !+n- 1!=n= 1 !-n- 1!n-R : 1-1 !n--- kik !n-R : 1-1 !n--- k : kR-1 !i: in: = !anm : -min-n : -i2 En déduire que Fentiers naturelnettel que2 kn-1,ona :m22+ 2= + 2= a2- 2= =
Page 122 : -2+ n =2 = 2+ 222+ 2= i=+ E= 53 .- boubeanche....Al'evenementau moinsune boule rougesPAC, PAA "l'evenement "it y a quedesboateblanches quiantate tires:"tirerKbouksparmisa boules"card AY= 42, cardr= 8PAY= l=PA=1-PAS=i- - Ek
Page 123 : Exercice :A et B2 evenementPA=1/5et PAUB= ZPAUB=PA +PB- PAMBARB= 0=PARB1=0=PLAUB1=PA+PB=PB=PAUB-PA= I- 5 =2 PAnB=PAPB=1PBPAUB1= PA+ PB- =PBIPB=PLAUB- PA=3-10-2=PB =-- -31d'aprèsla condition--⑰-E- -B --- -AcB
Page 124 : PAnB= PA= IPAUB= I+ PB- I=PB= PAUB= IExercice:ScientA,Bet Cdes evenement·On pose 1= Ann IetEz= ANBUC①Montrer que E etz sont incompatible.- intersection des 2= 0.②Determiner l'ensemble E1VEzk=BUCkBincEr= KA, E2=ARKE = nez= Ankn Ank=Anknx= And= 0=Es, tzsont incompatibles
Page 125 : 2== Utz= AnkU Ankl=AnkUK=An= Aou iest l'univers.E1UEz=A, E1nEz= 02= PA3 PA=0, 6,PB=0, 4,PC=0 . 3PBRC1=0 , 1,PLANC=0 , 1PARB=0, 2, PABRC1=0, 05E2=An BUCIPAUBUC1=PA+ PBUC1- PANBUC =PA+ PBUC- PfzPAUBUC=PA+PB+ PC- PAMB- PLANC -PBRC+PARBRCPAUBUC1=0, 6+ 0, 470 , 3- 0, 1x2- 0 , 2+ 0 , 05=0, 95
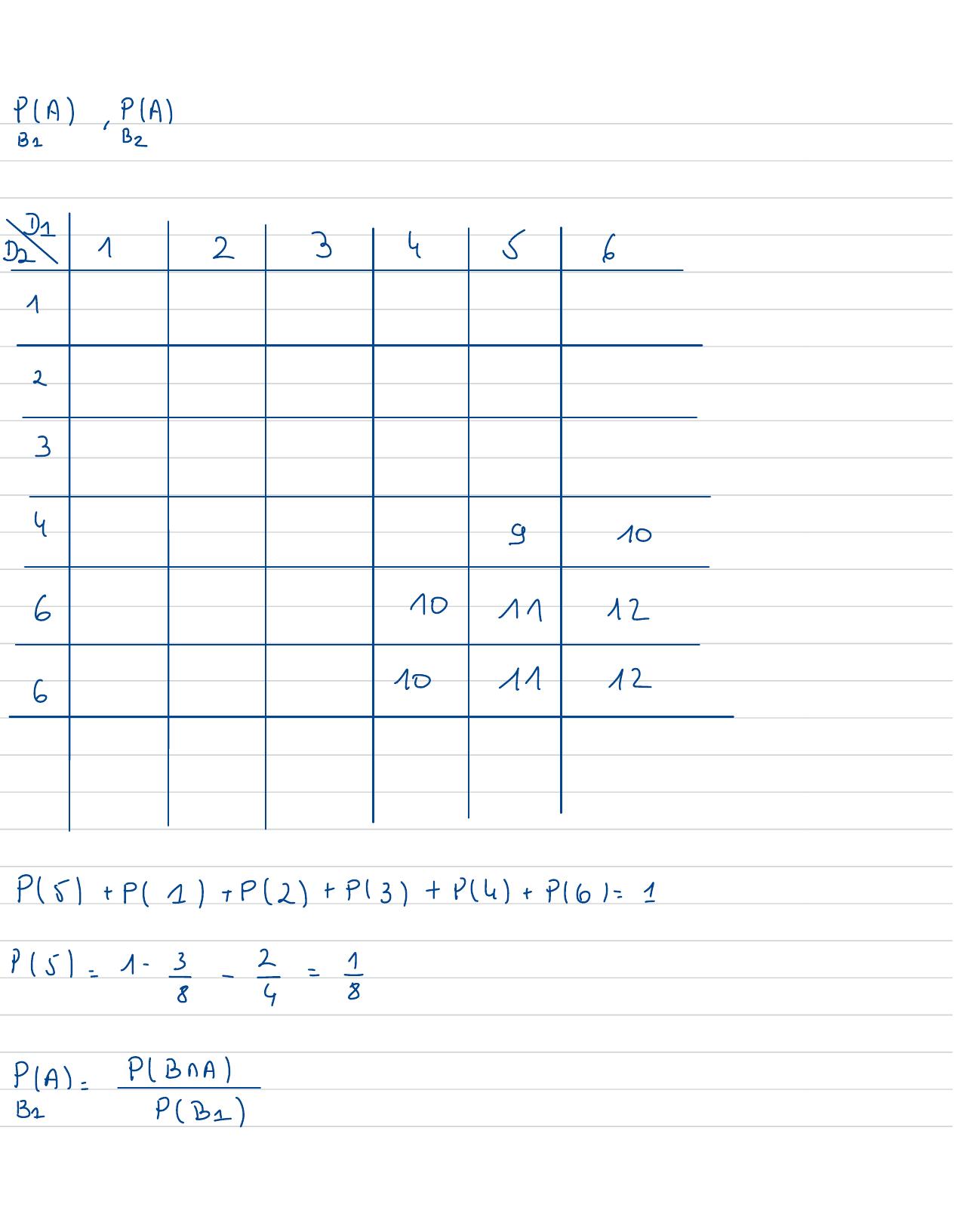
Page 126 : PBUC=PB+ PC- PBNC=0, 4+0, 3 -0, 1=0 , 6PEz=PA+ PBuc- PAUBUC=0, 6+ 0, 6-0 , 95=0, 25P2+ Pt ==PAPE=PA- P62=0, 6 -0 . 25= 0, 35Exercice 4:On Lance2 dèspipesD1etD2P1=P3=P4= 18D1= I P2=P6=1/4Da=un dé pipé tel queona deux facede 6A : "l'evenement: la summedes deuxfaces 10"B1 :"l'evenement:un des résultatest 6 "By :"l'evenement: le premier résultatest 6 "
Page 127 : PA, BeD1D21234j61234I1061011126101112P5+ P1+ P2+ P3+ P4+ 9161=1P5=1- 8- 2= 5PA=PlBNAB1PB =
Page 128 : 6, 61,15, 61,P5 , 61y=p151+ P61- 27+ 5= 4 5= EP6, 617=2P6 xP6=2x 1x == 5PA= 415 , 64+ P136, 64= i+5= 4P, A= 46 , 31y=5
Page 129 : ·. Argent= 56C1C2C3onovreauhasardun des6 tirroirs,on trouveune pieces d'argent.Aestf'evenement"avoirmepiecesd'argenten ouvrantun tiroir parmiles6tirroirsC2:l'evenement"avoir cette piècede coffreC2"PA2=PAncelPAPA=P 1 na+ P2 nA+ P3nA=P11. PxA+ PxPzA+ PCsPcyA-0x+ 5x5= z= EPAR2= 5=PaCe= 1,=23
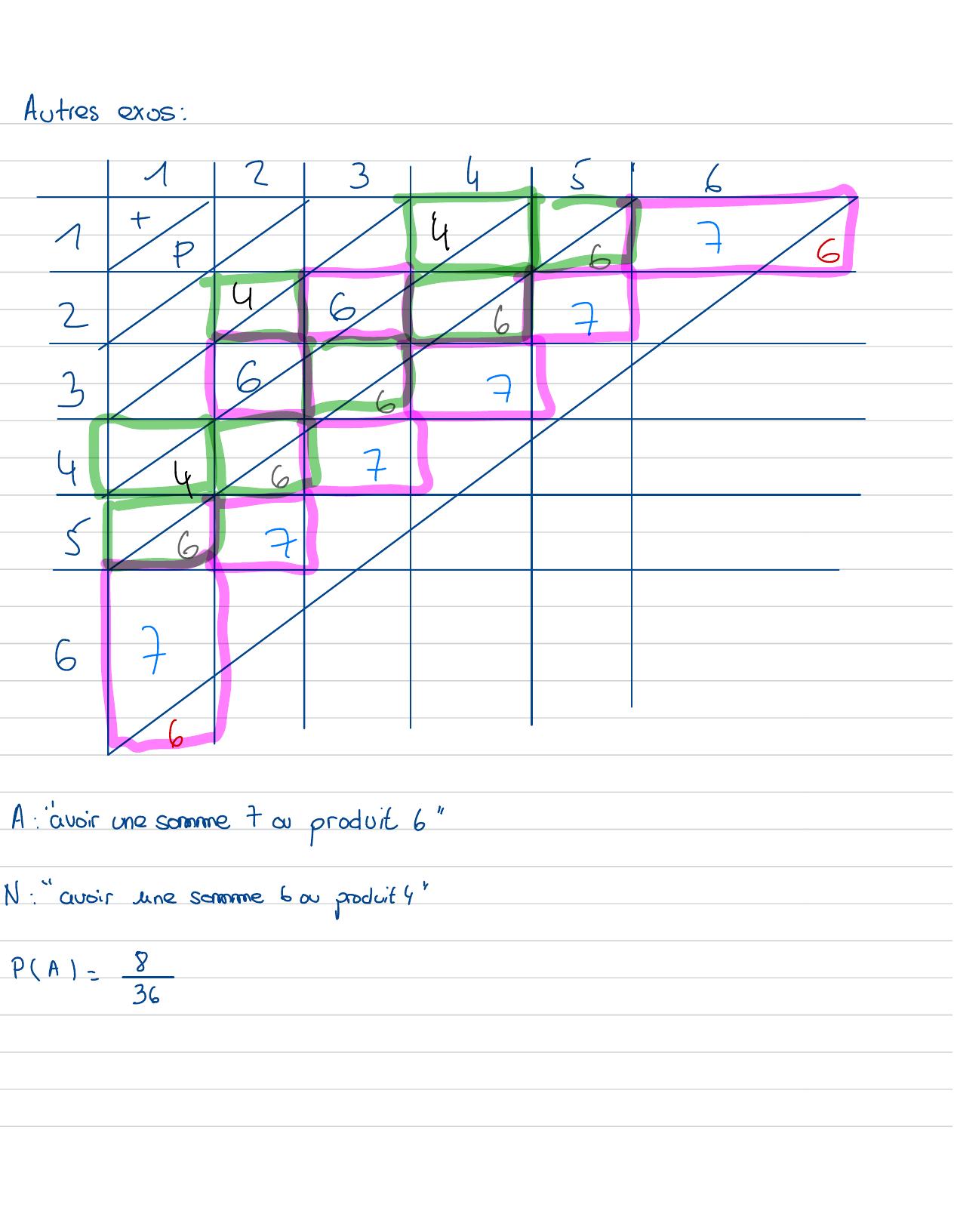
Page 130 : Autresexos :12345↑61IP467624667367·447-S62676A:" avoirune somime 7 or product 6 "N: "avoirunesomeonebou produit4"PA=836
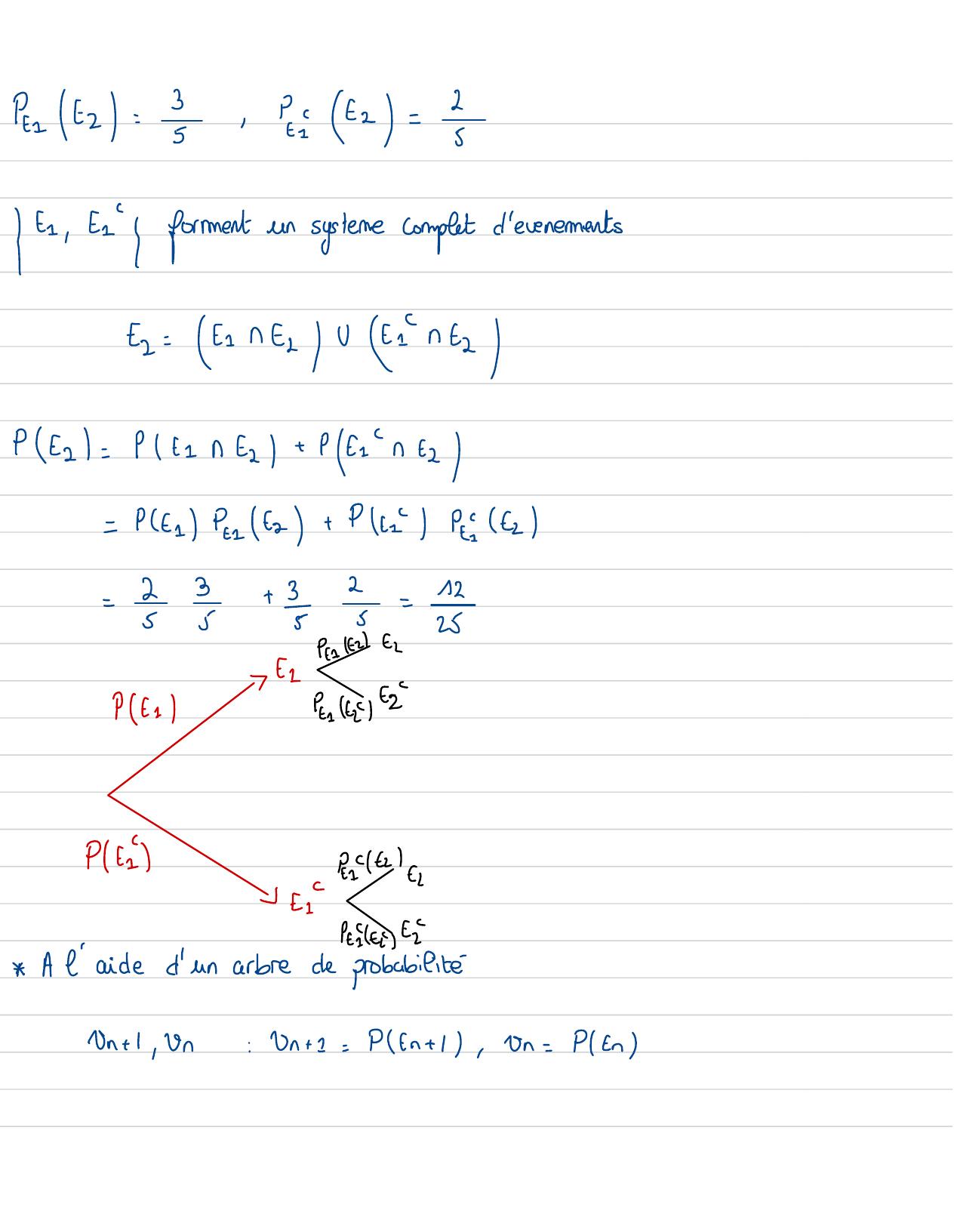
Page 131 : Ex01: TD 2 probaPA= 5PB= 1 PC=112A, B, C, Dformentun systeme complet d'evenementPA+PB+ Pc+ PD=1PD=1- PA+PB+ P= =2 R "arriveren retardExo 3 :00008 000E----StS2En: "La billetiréedanssnest verte"Ptn= En1 PE=3Pt=1- = =
Page 132 : Pe62=== = 2==It, Elformentun systeme completd'evenementsf= 2= nE/0= ntzPE2=Pt = n2+ Pfin+2= PE1Pertz+ P2Pe?f=29+3,2=12525Pt 12EzE17Pt=Ptt24622PEEte21Petitl'aided'un arbrede probabilitéUnt1, Un:Un+1= PLEntI,On=PlEn
Page 133 : en, En1un systeme complet d'evenementEn + 1=en+ 1nenUen+2 nenUn+1=PenPenEn+1+PenPen /n+1En+1= Onen +1+ - Pen Pa en + 1=On P+1+/1-8n+ 1-00000608Sn+1SPlen+1=len+1= IUn+1=En+ 11-8nIEUn +1==Un+ Ive= In
Page 134 : Un= 1Un- 1 +=F=n- 2+ E+ I=5- 8- 2+1+ E=5=8- 3+ E+1+ 5=F-s+1+ I+ "=5r+ =1+ 1+...+ I =E1+ =+ 5+...+ F+ 5 a=! === 11-145=1- 15G: Icar l'k se
Page 135 : Exo 4:Xvariablealéatoire, elleprend les valeurs1 . 2.. .., 6aveclesprobabilitéPX= 1=0, 1,PX= 2=0 , 2,pX= 3= 0 , 1PX= 4=0, 3 ,PX= 5=0 , 2,PX= 6=0 , 2CalcuferEIx1 , VXI,X = K123456PX= k0, 10, 20 ,10 , 30, 10 , 2esperance6EX== : PX= xi=1 x 0,1+2 x0, 2+ 3x0,1+ 4x0, 3+ 5 x 0,+ 6x0 , 2= 3 , 7vix1=E x-E1x1:Ex2- fx"
Page 136 :
Pages : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136